Drug Catalog - Product Detail
ZONISAMIDE CAP 100 MG 100 CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69097-0861-07 | CIPLA USA | 100 | 100MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
ZONISAMIDE
Substance Name
ZONISAMIDE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA077869
Description
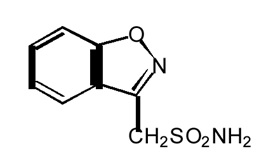
DESCRIPTION Zonisamide, USP is an antiseizure drug chemically classified as a sulfonamide and unrelated to other antiseizure agents. The active ingredient is zonisamide USP, 1,2-benzisoxazole-3-methanesulfonamide. The empirical formula is C 8 H 8 N 2 O 3 S with a molecular weight of 212.23. Zonisamide USP is a white powder, pKa = 10.2, and is moderately soluble in water (0.80 mg/mL) and 0.1 N HCl (0.50 mg/mL). The chemical structure is: Zonisamide is supplied for oral administration as capsules containing 100 mg zonisamide. Each 100 mg capsule contains the labeled amount of zonisamide plus the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, hydrogenated vegetable oil, gelatin and colorants. Components of gelatin capsules (For 100 mg: titanium dioxide, gelatin and FDA/E172 red iron oxide). Imprint ink dye (Black SW- 9008/SW-9009). image
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Zonisamide, USP is available as 100 mg two-piece hard gelatin capsules. The capsules imprinted with codes are printed in black ink. Zonisamide, USP is available in bottles with strengths and capsule description as follows: Dosage Strength Capsule Description NDC# 100 mg 100 Count Size "1" Brown Opaque Cap and White Opaque Body imprinted with 100 mg on the cap and IG228 on the body in black ink, filled with White to Off-white powder. 69097-861-07 100 mg 500 Count Size "1" Brown Opaque Cap and White Opaque Body imprinted with 100 mg on the cap and IG228 on the body in black ink, filled with White to Off-white powder. 69097-861-12 Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature], in a dry place and protected from light. Revised: 07/2020
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Zonisamide capsules are indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures in adults with epilepsy.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Zonisamide, USP is recommended as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial seizures in adults. Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 16 have not been established. Zonisamide should be administered once or twice daily, using 25 mg or 100 mg capsules. Zonisamide is given orally and can be taken with or without food. Capsules should be swallowed whole. Adults over Age 16: The prescriber should be aware that, because of the long half-life of zonisamide, up to two weeks may be required to achieve steady state levels upon reaching a stable dose or following dosage adjustment. Although the regimen described below is one that has been shown to be tolerated, the prescriber may wish to prolong the duration of treatment at the lower doses in order to fully assess the effects of zonisamide at steady state, noting that many of the side effects of zonisamide are more frequent at doses of 300 mg per day and above. Although there is some evidence of greater response at doses above 100 to 200 mg/day, the increase appears small and formal dose-response studies have not been conducted. The initial dose of zonisamide should be 100 mg daily. After two weeks, the dose may be increased to 200 mg/day for at least two weeks. It can be increased to 300 mg/day and 400 mg/day, with the dose stable for at least two weeks to achieve steady state at each level. Evidence from controlled trials suggests that zonisamide doses of 100 to 600 mg/day are effective, but there is no suggestion of increasing response above 400 mg/day (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY , Clinical Studies subsection). There is little experience with doses greater than 600 mg/day. Patients with Renal or Hepatic Disease: Because zonisamide is metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys, patients with renal or hepatic disease should be treated with caution, and might require slower titration and more frequent monitoring (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS ).
