Drug Catalog - Product Detail
TOPIRAMATE TB 100MG 500
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69097-0124-12 | CIPLA USA | 500 | 100MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
Substance Name
Product Type
Route
Application Number
Description
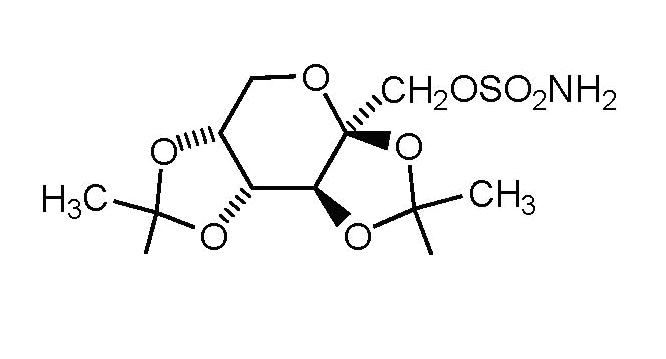
11 DESCRIPTION Topiramate is a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide. Topiramate tablets USP are available as 25mg, 50 mg and 100 mg circular tablets and 200 mg capsule shaped tablets for oral administration. Topiramate USP is a white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. Topiramate USP is most soluble in alkaline solutions containing sodium hydroxide or sodium phosphate and having a pH of 9 to 10. It is freely soluble in acetone, chloroform, dimethylsulfoxide, and ethanol. The solubility in water is 9.8 mg/mL. Its saturated solution has a pH of 6.3. Topiramate has the molecular formula C 12 H 21 NO 8 S and a molecular weight of 339.36. Topiramate is designated chemically as 2,3:4,5Di- O -isopropylidene-ß-D-fructopyranose sulfamate and has the following structural formula: Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg and 200 mg topiramate and has the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, pregelatinized starch, sodium starch glycolate and titanium dioxide. In addition, the 25 mg also contains FD&C Blue #2; the 50 mg and 100 mg also contain red iron oxide and yellow iron oxide; and the 200 mg also contains red iron oxide. topi
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 16.1 How Supplied Topiramate tablets USP Topiramate tablets USP are available in the following strengths and colors: 25 mg, White colored, circular, biconvex film-coated tablets, debossed with "122" on one side and "C" on the other side and are available in Bottles of 60's (NDC 69097-122-03) Bottles of 500's (NDC 69097-122-12) Bottles of 1000's (NDC 69097-122-15) 50 mg, Light orange colored, circular, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "123" on one side and "C" on the other side and are available in Bottles of 60's (NDC 69097-123-03) Bottles of 500's (NDC 69097-123-12) Bottles of 1000's (NDC 69097-123-15) 100 mg, Orange colored, circular, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "124" on one side and "Cipla" on the other side and are available in Bottles of 60's (NDC 69097-124-03) Bottles of 500's (NDC 69097-124-12) Bottles of 1000's (NDC 69097-124-15) 200 mg, Pink colored, capsule shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "125" on one side and "Cipla" on other side and are available in Bottles of 60's (NDC 69097-125-03) Bottles of 500's (NDC 69097-125-12) Bottles of 1000's(NDC 69097-125-15) PHARMACIST: Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP. Use child-resistant closure (as required). 16.2 Storage and Handling Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [See USP controlled room temperature]. Protect from moisture.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Topiramate tablets USP is indicated for: Monotherapy epilepsy: Initial monotherapy in patients ≥ 2 years of age with partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures ( 1.1 ) Adjunctive therapy epilepsy: Adjunctive therapy for adults and pediatric patients (2 to 16 years of age) with partial onset seizures or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and in patients ≥2 years of age with seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) ( 1.2 ) Prophylaxis of migraine in patients 12 years of age and older ( 1.3 ) 1.1 Monotherapy Epilepsy Topiramate tablets USP are indicated as initial monotherapy in patients 2 years of age and older with partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. 1.2 Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy Topiramate tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy for adults and pediatric patients 2 to 16 years of age with partial onset seizures or primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and in patients 2 years of age and older with seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. 1.3 Migraine Topiramate tablets are indicated for patients 12 years of age and older for the prophylaxis of migraine headache.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Topiramate tablets initial dose, titration, and recommended maintenance dose varies by indication and age group. See Full Prescribing Information for recommended dosage, and dosing considerations in patients with renal impairment, geriatric patients, and patients undergoing hemodialysis ( 2.1 , 2.2 , 2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 2.6 ) 2.1 Dosing in Monotherapy Epilepsy Adults and Pediatric Patients 10 Years and Older The recommended dose for topiramate monotherapy in adults and pediatric patients 10 years of age and older is 400 mg/day in two divided doses. The dose should be achieved by titration according to the following schedule (Table 1): Table 1: Monotherapy Titration Schedule for Adults and Pediatric Patients 10 years and older Morning Dose Evening Dose Week 1 25 mg 25 mg Week 2 50 mg 50 mg Week 3 75 mg 75 mg Week 4 100 mg 100 mg Week 5 150 mg 150 mg Week 6 200 mg 200 mg Children Ages 2 to 9 Years Dosing in patients 2 to 9 years of age is based on weight. During the titration period, the initial dose of topiramate should be 25 mg/day administered nightly for the first week. Based upon tolerability, the dosage can be increased to 50 mg/day (25 mg twice daily) in the second week. Dosage can be increased by 25–50 mg/day each subsequent week as tolerated. Titration to the minimum maintenance dose should be attempted over 5–7 weeks of the total titration period. Based upon tolerability and seizure control, additional titration to a higher dose (up to the maximum maintenance dose) can be attempted at 25–50 mg/day weekly increments. The total daily dose should not exceed the maximum maintenance dose for each range of body weight (Table 2). Table 2: Monotherapy Target Total Daily Maintenance Dosing for Patients 2 to 9 Years of Age *Administered in two equally divided doses Weight(kg) Total Daily Dose(mg/day)* Minimum Maintenance Dose Total Daily Dose(mg/day)* Maximum Maintenance Dose Upto 11 150 250 12–22 200 300 23–31 200 350 32–38 250 350 Greater than38 250 400 2.2 Dosing in Adjunctive Therapy Epilepsy Adults (17 Years of Age and Over) The recommended total daily dose of topiramate tablets as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial onset seizures or Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome is 200 to 400 mg/day in two divided doses, and 400 mg/day in two divided doses as adjunctive treatment in adults with primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Topiramate tablets should be initiated at 25 to 50 mg/day followed by titration to an effective dose in increments of 25 to 50 mg/day every week. Titrating in increments of 25 mg/day every week may delay the time to reach an effective dose. Doses above 400 mg/day have not been shown to improve responses in dose-response studies in adults with partial onset seizures. Pediatric Patients Ages 2 – 16 Years The recommended total daily dose of topiramate tablets as adjunctive therapy for pediatric patients 2 to 16 years of age with partial onset seizures, primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures, or seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome is approximately 5 to 9 mg/kg/day in two divided doses. Titration should begin at 25 mg/day (or less, based on a range of 1 to 3 mg/kg/day) nightly for the first week. The dosage should then be increased at 1- or 2-week intervals by increments of 1 to 3 mg/kg/day (administered in two divided doses), to achieve optimal clinical response. Dose titration should be guided by clinical outcome. 2.3 Dosing in Migraine Prophylaxis The recommended total daily dose of topiramate tablets as treatment for patients 12 years of age and older for prophylaxis of migraine headache is 100 mg/day administered in two divided doses (Table 3). The recommended titration rate for topiramate tablets for migraine prophylaxis is as follows: Table 3: Migraine Prophylaxis Titration Schedule for Patients 12 Years of Age and Older Morning Dose Evening Dose Week 1 None 25 mg Week 2 25 mg 25 mg Week 3 25 mg 50 mg Week 4 50 mg 50 mg 2.4 Administration Information Topiramate tablets can be taken without regard to meals. Topiramate tablets Because of the bitter taste, tablets should not be broken 2.5 Dosing in Patients with Renal Impairment In renally impaired subjects (creatinine clearance less than 70 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), one-half of the usual adult dose is recommended. [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5 , 8.6 ), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] . 2.6 Dosing in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis To avoid rapid drops in topiramate plasma concentration during hemodialysis, a supplemental dose of topiramate may be required. The actual adjustment should take into account 1) the duration of dialysis period, 2) the clearance rate of the dialysis system being used, and 3) the effective renal clearance of topiramate in the patient being dialyzed [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.7 ), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] .
