Drug Catalog - Product Detail
TETRABENAZINE TB 12.5MG 112
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68682-0421-12 | OCEANSIDE PHARMACEUTICALS | 112 | 12.5MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
TETRABENAZINE
Substance Name
TETRABENAZINE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
NDA021894
Description
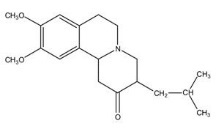
11 DESCRIPTION Tetrabenazine tablets are a monoamine depletor for oral administration. The molecular weight of tetrabenazine is 317.43; the pKa is 6.51. Tetrabenazine is a hexahydro-dimethoxy-benzoquinolizine derivative and has the following chemical name: cis rac –1,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-9,10-dimethoxy-3-(2-methylpropyl)-2H-benzo[a]quinolizin-2-one. The empirical formula C 19 H 27 NO 3 is represented by the following structural formula: Tetrabenazine is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol. Each tetrabenazine tablet contains either 12.5 or 25 mg of tetrabenazine as the active ingredient. Tetrabenazine tablets contain tetrabenazine as the active ingredient and the following inactive ingredients: lactose, magnesium stearate, maize starch, and talc. The 25 mg strength tablet also contains yellow iron oxide as an inactive ingredient. Tetrabenazine tablets are supplied as a yellowish-buff, scored tablet containing 25 mg of tetrabenazine or as a white, non-scored tablet containing 12.5 mg of tetrabenazine. Chemical Structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 16.1 How Supplied Tetrabenazine tablets are available in the following strengths and packages: The 12.5 mg tetrabenazine tablets are white, cylindrical, biplanar tablets with beveled edges, non-scored, embossed on one side with “CL” and “12.5”. NDC 68682-421-12 12.5 mg 112-count bottle The 25 mg tetrabenazine tablets are yellowish-buff, cylindrical, biplanar tablets with beveled edges, scored, embossed on one side with “CL” and “25”. NDC 68682-422-25 25 mg 112-count bottle 16.2 Storage Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Tetrabenazine tablets are indicated for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease. Tetrabenazine tablets are a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease. ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Individualization of dose with careful weekly titration is required. The 1 st week's starting dose is 12.5 mg daily; 2 nd week, 25 mg (12.5 mg twice daily); then slowly titrate at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg to a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. ( 2.1 , 2.2 ) • Doses of 37.5 mg and up to 50 mg/day should be administered in three divided doses per day with a maximum recommended single dose not to exceed 25 mg. ( 2.2 ) • Patients requiring doses above 50 mg/day should be genotyped for the drug metabolizing enzyme CYP2D6 to determine if the patient is a poor metabolizer (PM) or an extensive metabolizer (EM). ( 2.2 , 5.3 ) • Maximum daily dose in PMs: 50 mg with a maximum single dose of 25 mg ( 2.2 ) • Maximum daily dose in EMs and intermediate metabolizers (IMs): 100 mg with a maximum single dose of 37.5 mg ( 2.2 ) • If serious adverse reactions occur, titration should be stopped and the dose should be reduced. If the adverse reaction(s) do not resolve, consider withdrawal of tetrabenazine tablets. ( 2.2 ) 2.1 General Dosing Considerations The chronic daily dose of tetrabenazine tablets used to treat chorea associated with Huntington's disease (HD) is determined individually for each patient. When first prescribed, tetrabenazine tablets therapy should be titrated slowly over several weeks to identify a dose of tetrabenazine tablets that reduces chorea and is tolerated. Tetrabenazine tablets can be administered without regard to food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. 2.2 Individualization of Dose The dose of tetrabenazine tablets should be individualized. Dosing Recommendations Up to 50 mg/day The starting dose should be 12.5 mg/day given once in the morning. After 1 week, the dose should be increased to 25 mg/ day given as 12.5 mg twice a day. Tetrabenazine tablets should be titrated up slowly at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg daily, to allow the identification of a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. If a dose of 37.5 to 50 mg/day is needed, it should be given in a three times a day regimen. The maximum recommended single dose is 25 mg. If adverse reactions such as akathisia, restlessness, parkinsonism, depression, insomnia, anxiety or sedation occur, titration should be stopped and the dose should be reduced. If the adverse reaction does not resolve, consideration should be given to withdrawing tetrabenazine tablets treatment or initiating other specific treatment (e.g., antidepressants) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Dosing Recommendations Above 50 mg/day Patients who require doses of tetrabenazine tablets greater than 50 mg/day should be first tested and genotyped to determine if they are poor metabolizers (PMs) or extensive metabolizers (EMs) by their ability to express the drug metabolizing enzyme, CYP2D6. The dose of tetrabenazine tablets should then be individualized accordingly to their status as PMs or EMs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Extensive and Intermediate CYP2D6 Metabolizers Genotyped patients who are identified as extensive (EMs) or intermediate metabolizers (IMs) of CYP2D6, who need doses of tetrabenazine above 50 mg/day, should be titrated up slowly at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg daily, to allow the identification of a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. Doses above 50 mg/day should be given in a three times a day regimen. The maximum recommended daily dose is 100 mg and the maximum recommended single dose is 37.5 mg. If adverse reactions such as akathisia, parkinsonism, depression, insomnia, anxiety or sedation occur, titration should be stopped and the dose should be reduced. If the adverse reaction does not resolve, consideration should be given to withdrawing tetrabenazine tablets treatment or initiating other specific treatment (e.g., antidepressants) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Poor CYP2D6 Metabolizers In PMs, the initial dose and titration is similar to EMs except that the recommended maximum single dose is 25 mg, and the recommended daily dose should not exceed a maximum of 50 mg [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment with CYP2D6 Inhibitors Strong CYP2D6 Inhibitors Medications that are strong CYP2D6 inhibitors such as quinidine or antidepressants (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine) significantly increase the exposure to α-HTBZ and β-HTBZ; therefore, the total dose of tetrabenazine tablets should not exceed a maximum of 50 mg and the maximum single dose should not exceed 25 mg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) , Drug Interactions (7.1) , Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. 2.4 Discontinuation of Treatment Treatment with tetrabenazine tablets can be discontinued without tapering. Re-emergence of chorea may occur within 12 to 18 hours after the last dose of tetrabenazine tablets [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2) ]. 2.5 Resumption of Treatment Following treatment interruption of greater than 5 days, tetrabenazine tablets therapy should be re-titrated when resumed. For short-term treatment interruption of less than 5 days, treatment can be resumed at the previous maintenance dose without titration.
