Drug Catalog - Product Detail
TELMISARTAN 40MG TB 30
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00378-2921-93 | MYLAN | 30 | 40MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
TELMISARTAN
Substance Name
TELMISARTAN
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA202397
Description
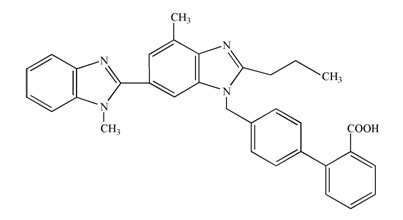
11 DESCRIPTION Telmisartan tablets, USP are a non-peptide angiotensin II receptor (type AT 1 ) antagonist. Telmisartan is chemically described as 4′-[[4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-1 H -benzimidazol-2yl)-2-propyl-1 H -benzimidazol-1yl] methyl] biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid. Its molecular formula is C 33 H 30 N 4 O 2 , its molecular weight is 514.60, and its structural formula is: Telmisartan, USP is a white or slightly yellowish crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water and in the pH range of 3 to 9, sparingly soluble in strong acid (except insoluble in hydrochloric acid), and soluble in strong base. Telmisartan is available as tablets for oral administration, containing 20 mg, 40 mg or 80 mg of telmisartan. The tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, mannitol, meglumine, povidone and sodium hydroxide. Telmisartan Structural Formula
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Telmisartan Tablets, USP are available containing 20 mg, 40 mg or 80 mg of telmisartan, USP. The 20 mg tablets are white, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and TN over 20 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-2920-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-2920-77 bottles of 90 tablets The 40 mg tablets are white, oblong, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and TN40 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-2921-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-2921-77 bottles of 90 tablets The 80 mg tablets are white, oblong, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and TN80 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-2922-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-2922-77 bottles of 90 tablets Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Telmisartan tablets are an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) indicated for: • Treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. ( 1.1 ) • Cardiovascular (CV) risk reduction in patients unable to take ACE inhibitors ( 1.2 ) 1.1 Hypertension Telmisartan tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including the class to which this drug principally belongs. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. Telmisartan tablets may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . 1.2 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Telmisartan tablets are indicated for reduction of the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes in patients 55 years of age or older at high risk of developing major cardiovascular events who are unable to take ACE inhibitors. High risk for cardiovascular events can be evidenced by a history of coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease, stroke, transient ischemic attack, or high-risk diabetes (insulin-dependent or non-insulin dependent) with evidence of end-organ damage [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Telmisartan tablets can be used in addition to other needed treatment (such as antihypertensive, antiplatelet or lipid-lowering therapy) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Studies of telmisartan in this setting do not exclude the possibility that telmisartan may not preserve a meaningful fraction of the effect of the ACE inhibitor to which it was compared. Consider using the ACE inhibitor first, and, if it is stopped for cough only, consider re-trying the ACE inhibitor after the cough resolves. Use of telmisartan with an ACE inhibitor is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] .
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • May be administered with or without food ( 2.1 ) • When used for cardiovascular risk reduction, monitoring of blood pressure is recommended, and if appropriate, adjustment of medications that lower blood pressure may be necessary ( 2.2 ) Indication Starting Dose Dose Range Hypertension ( 2.1 ) 40 mg once daily 40 to 80 mg once daily Cardiovascular Risk Reduction ( 2.2 ) 80 mg once daily 80 mg once daily 2.1 Hypertension Dosage must be individualized. The usual starting dose of telmisartan tablets is 40 mg orally once a day. Blood pressure response is dose-related over the range of 20 to 80 mg [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Most of the antihypertensive effect is apparent within 2 weeks and maximal reduction is generally attained after 4 weeks. No initial dosage adjustment is necessary for elderly patients or patients with renal impairment, including those on hemodialysis. Patients on dialysis may develop orthostatic hypotension; their blood pressure should be closely monitored. Telmisartan tablets may be administered with other antihypertensive agents. Telmisartan tablets may be administered with or without food. 2.2 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction The recommended dose of telmisartan tablets is 80 mg once a day and can be administered with or without food. It is not known whether doses lower than 80 mg of telmisartan are effective in reducing the risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. When initiating telmisartan therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction, monitoring of blood pressure is recommended, and if appropriate, adjustment of medications that lower blood pressure may be necessary.
