Drug Catalog - Product Detail
TACROLIMUS CP 1MG 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00781-2103-01 | SANDOZ | 100 | 1MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
TACROLIMUS
Substance Name
TACROLIMUS
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA065461
Description
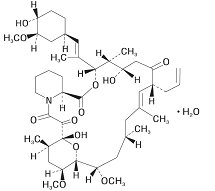
11 DESCRIPTION Tacrolimus, previously known as FK506, is the active ingredient in tacrolimus capsules. Tacrolimus is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant produced by Streptomyces tsukubaensis. Chemically, tacrolimus is designated as [3 S -[3 R *[ E (1 S*, 3 S*, 4 S* )],4 S*, 5 R*, 8 S*, 9 E, 12 R* ,14 R*, 15 S*, 16 R*, 18 S*, 19 S*, 26 aR* ]]-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propenyl)-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone, monohydrate. The chemical structure of tacrolimus is: Tacrolimus has a molecular formula of C 44 H 69 NO 12 •H 2 O and a formula weight of 822.03. Tacrolimus appears as white crystals or crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol, and very soluble in methanol and chloroform. Tacrolimus capsules, USP are available for oral administration containing the equivalent of 0.5 mg, 1 mg or 5 mg of anhydrous tacrolimus. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate. The tacrolimus capsule shell for 0.5 mg strength consists of gelatin, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide. The tacrolimus capsule shell for 1 mg strength consists of black iron oxide, gelatin, red iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide. The tacrolimus capsule shell for 5 mg strength consists of red iron oxide, gelatin, and titanium dioxide. Tacrolimus capsules, USP 0.5 mg, 1 mg and 5 mg are printed with edible black ink. The black ink is comprised of ammonia, black iron oxide, butyl alcohol, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and shellac. USP Dissolution test 2 and Organic Impurities procedure 2 used. chemical structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 16.1 Tacrolimus Capsules, USP Tacrolimus capsules, USP containing white to off-white powder equivalent to 0.5 mg of anhydrous tacrolimus, are hard gelatin capsules with white opaque body and ivory cap. The body is imprinted ‘643’ and cap is imprinted ‘ ’ in black ink. They are supplied as follows: NDC 0781-2102-01, bottle of 100 capsules with child-resistant closure Tacrolimus capsules, USP containing white to off-white powder equivalent to 1 mg of anhydrous tacrolimus, are hard gelatin capsules with white opaque body and brown cap. The body is imprinted ‘644’ and cap is imprinted ‘ ’ in black ink. They are supplied as follows: NDC 0781-2103-01, bottle of 100 capsules with child-resistant closure Tacrolimus capsules, USP containing white to off-white powder equivalent to 5 mg of anhydrous tacrolimus, are hard gelatin capsules with white opaque body and orange cap. The body is imprinted ‘645’ and cap is imprinted ‘ ’ in black ink. They are supplied as follows: NDC 0781-2104-01, bottle of 100 capsules with child-resistant closure Store and Dispense Tacrolimus capsules, USP should be stored at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. 'S' 'S' 'S' 16.4 Handling and Disposal Tacrolimus can cause fetal harm. Tacrolimus capsules should not be opened or crushed. Avoid inhalation or direct contact with skin or mucous membranes of the powder contained in tacrolimus capsules. If such contact occurs, wash the skin thoroughly with soap and water; if ocular contact occurs, rinse eyes with water. In case a spill occurs, wipe the surface with a wet paper towel. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures 1 .
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Tacrolimus capsules are a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant indicated for the prophylaxis of organ rejection in adult patients receiving allogeneic liver, kidney, or heart transplants, and pediatric patients receiving allogenic liver transplants in combination with other immunosuppressants. ( 1.1 ) 1.1 Prophylaxis of Organ Rejection in Kidney, Liver, or Heart Transplant Tacrolimus capsules are indicated for the prophylaxis of organ rejection, in adult patients receiving allogeneic kidney transplant [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1) ] , liver transplant [see Clinical Studies ( 14.2 )], and heart transplant [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3 )] , and pediatric patients receiving allogeneic liver transplants [see Clinical Studies ( 14.2 )] in combination with other immunosuppressants. Additional pediatric use information is approved for Astellas Pharma US, Inc.’s Prograf (tacrolimus) products. However, due to Astellas Pharma US, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Administer capsules consistently with or without food. ( 2.1 ) • Therapeutic drug monitoring is recommended. ( 2.1 , 2.6 ) • Avoid eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice. ( 2.1 ) • See dosage adjustments for African-American patients ( 2.2 ), hepatic and renal impaired. ( 2.4 , 2.5 ) • For complete dosing information, see Full Prescribing Information. ADULT Patient Population Initial Oral Dosage Whole Blood Trough Concentration Range Kidney Transplant With azathioprine 0.2 mg/kg/day capsules, divided in two doses, every 12 hours Month 1 to 3: 7 to 20 ng/mL Month 4 to 12: 5 to 15 ng/mL With MMF/IL-2 receptor antagonist 0.1 mg/kg/day capsules, divided in two doses, every 12 hours Month 1 to 12: 4 to 11 ng/mL Liver Transplant With corticosteroids only 0.1 to 0.15 mg/kg/day capsules, divided in two doses, every 12 hours Month 1 to 12: 5 to 20 ng/mL Heart Transplant With azathioprine or MMF 0.075 mg/kg/day capsules, divided in two doses, every 12 hours Month 1 to 3: 10 to 20 ng/mL Month ≥4: 5 to 15 ng/mL PEDIATRIC Patient Population Initial Oral Dosage Whole Blood Trough Concentration Range Liver Transplant 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg/day capsules, divided in two doses, every 12 hours Month 1 to 12: 5 to 20 ng/mL MMF=Mycophenolate mofetil 2.1 Important Administration Instructions Tacrolimus capsules should not be used without supervision by a physician with experience in immunosuppressive therapy. Tacrolimus capsules are not interchangeable or substitutable for other tacrolimus extended-release products. This is because rate of absorption following the administration of an extended-release tacrolimus product is not equivalent to that of an immediate-release tacrolimus drug product. Under- or overexposure to tacrolimus may result in graft rejection or other serious adverse reactions. Changes between tacrolimus immediate-release and extended-release dosage forms must occur under physician supervision [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3 )]. Intravenous Formulation – Administration Precautions due to Risk of Anaphylaxis Intravenous use is recommended for patients who cannot tolerate oral formulations, and conversion from intravenous to oral tacrolimus is recommended as soon as oral therapy can be tolerated to minimize the risk of anaphylactic reactions that occurred with injectables containing castor oil derivatives [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 )]. Oral Formulation (Capsules) If patients are able to initiate oral therapy, the recommended starting doses should be initiated. Tacrolimus capsules may be taken with or without food. However, since the presence of food affects the bioavailability of tacrolimus, if taken with food, it should be taken consistently the same way each time [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )]. General Administration Instructions Patients should not eat grapefruit or drink grapefruit juice in combination with tacrolimus capsules [see Drug Interactions ( 7.2 )] . Tacrolimus should not be used simultaneously with cyclosporine. Tacrolimus or cyclosporine should be discontinued at least 24 hours before initiating the other. In the presence of elevated tacrolimus or cyclosporine concentrations, dosing with the other drug usually should be further delayed. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is recommended for all patients receiving tacrolimus capsules [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.6 )]. 2.2 Dosage Recommendations for Adult Kidney, Liver, or Heart Transplant Patients – Capsules Capsules If patients are able to tolerate oral therapy, the recommended oral starting doses should be initiated. The initial dose of tacrolimus capsules should be administered no sooner than 6 hours after transplantation in the liver and heart transplant patients. In kidney transplant patients, the initial dose of tacrolimus capsules may be administered within 24 hours of transplantation, but should be delayed until renal function has recovered. The initial oral tacrolimus capsule dosage recommendations for adult patients with kidney, liver, or heart transplants and whole blood trough concentration range are shown in Table 1 . Perform therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) to ensure that patients are within the ranges listed in Table 1 . Table 1. Summary of Initial Oral Tacrolimus Capsules Dosage Recommendations and Whole Blood Trough Concentration Range in Adults Patient Population Tacrolimus Capsules Initial Oral Dosage African-American patients may require higher doses compared to Caucasians (see Table 2 ) Whole Blood Trough Concentration Range Kidney Transplant With Azathioprine 0.2 mg/kg/day, divided in two doses, administered every 12 hours Month 1 to 3: 7 to 20 ng/mL Month 4 to 12: 5 to 15 ng/mL With MMF/IL-2 receptor antagonist In a second smaller trial, the initial dose of tacrolimus was 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg/day and observed tacrolimus concentrations were 6 to 16 ng/mL during month 1 to 3 and 5 to 12 ng/mL during month 4 to 12 [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1 )]. 0.1 mg/kg/day, divided in two doses, administered every 12 hours Month 1 to 12: 4 to 11 ng/mL Liver Transplant With corticosteroids only 0.10 to 0.15 mg/kg/day, divided in two doses, administered every 12 hours Month 1 to 12: 5 to 20 ng/mL Heart Transplant With azathioprine or MMF 0.075 mg/kg/day, divided in two doses, administered every 12 hours Month 1 to 3: 10 to 20 ng/mL Month ≥4: 5 to 15 ng/mL Dosage should be titrated based on clinical assessments of rejection and tolerability. Tacrolimus capsules dosages lower than the recommended initial dosage may be sufficient as maintenance therapy. Adjunct therapy with adrenal corticosteroids is recommended early post-transplant. The data in kidney transplant patients indicate that the African-American patients required a higher dose to attain comparable trough concentrations compared to Caucasian patients ( Table 2 ) [ see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.8 ) and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] . Table 2. Comparative Dose and Trough Concentrations Based on Race Time After Transplant Caucasian N=114 African-American N=56 Dose (mg/kg) Trough Concentrations (ng/mL) Dose (mg/kg) Trough Concentrations (ng/mL) Day 7 0.18 12.0 0.23 10.9 Month 1 0.17 12.8 0.26 12.9 Month 6 0.14 11.8 0.24 11.5 Month 12 0.13 10.1 0.19 11.0 Intravenous Injection Anaphylactic reactions have occurred with injectables containing castor oil derivatives, such as tacrolimus injection. Therefore, monitoring for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9 )]. 2.3 Dosage Recommendations for Pediatric Liver Transplant Patients Oral formulation (capsules) Pediatric patients, in general, need higher tacrolimus doses compared to adults: the higher dose requirements may decrease as the child grows older. Recommendations for the initial oral dosage for pediatric transplant patients and whole blood trough concentration range are shown in Table 3 . Perform TDM to ensure that patients are within the ranges listed in Table 3 . Table 3. Summary of Initial Tacrolimus Capsule Dosage Recommendations and Whole Blood Trough Concentration Range in Children Patient Population Initial Tacrolimus Capsule Dosing Whole Blood Trough Concentration Range Pediatric liver transplant patients See Clinical Studies (14.2) , Liver Transplantation 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg/day capsules, divided in two doses, administered every 12 hours Month 1 to 12: 5 to 20 ng/mL For conversion of pediatric patients from tacrolimus granules to tacrolimus capsules or from tacrolimus capsules to tacrolimus granules, the total daily dose should remain the same. Following conversion from one formulation to another formulation of tacrolimus, therapeutic drug monitoring is recommended [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.6 )]. Additional pediatric use information is approved for Astellas Pharma US, Inc.’s Prograf (tacrolimus) products. However, due to Astellas Pharma US, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information. 2.4 Dosage Modification for Patients with Renal Impairment Due to its potential for nephrotoxicity, consider dosing tacrolimus capsules at the lower end of the therapeutic dosing range in patients who have received a liver, or heart transplant, and have pre-existing renal impairment. Further reductions in dose below the targeted range may be required. In kidney transplant patients with post-operative oliguria, the initial dose of tacrolimus capsules should be administered no sooner than 6 hours and within 24 hours of transplantation, but may be delayed until renal function shows evidence of recovery [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.2 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6 ), and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] . 2.5 Dosage Modification for Patients with Hepatic Impairment Due to the reduced clearance and prolonged half-life, patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh ≥10) may require lower doses of tacrolimus capsules. Close monitoring of blood concentrations is warranted. The use of tacrolimus capsules in liver transplant recipients experiencing post-transplant hepatic impairment may be associated with increased risk of developing renal insufficiency related to high whole blood concentrations of tacrolimus. These patients should be monitored closely, and dosage adjustments should be considered. Some evidence suggests that lower doses should be used in these patients [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.2 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.7 ), and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )]. 2.6 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Monitoring of tacrolimus blood concentrations in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical parameters is considered an essential aid to patient management for the evaluation of rejection, toxicity, dose adjustments, and compliance. Whole blood trough concentration range can be found in Table 1 . Factors influencing frequency of monitoring include but are not limited to hepatic or renal dysfunction, the addition or discontinuation of potentially interacting drugs and the post-transplant time. Blood concentration monitoring is not a replacement for renal and liver function monitoring and tissue biopsies. Data from clinical trials show that tacrolimus whole blood concentrations were most variable during the first week post-transplantation. The relative risks of toxicity and efficacy failure are related to tacrolimus whole blood trough concentrations. Therefore, monitoring of whole blood trough concentrations is recommended to assist in the clinical evaluation of toxicity and efficacy failure. Methods commonly used for the assay of tacrolimus include high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection (HPLC/MS/MS) and immunoassays. Immunoassays may react with metabolites as well as parent compound. Therefore, assay results obtained with immunoassays may have a positive bias relative to results of HPLC/MS. The bias may depend upon the specific assay and laboratory. Comparison of the concentrations in published literature to patient concentrations using the current assays must be made with detailed knowledge of the assay methods and biological matrices employed. Whole blood is the matrix of choice and specimens should be collected into tubes containing ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) anti-coagulant. Heparin anti-coagulation is not recommended because of the tendency to form clots on storage. Samples which are not analyzed immediately should be stored at room temperature or in a refrigerator and assayed within 7 days; see assay instructions for specifics. If samples are to be kept longer, they should be deep frozen at -20° C. One study showed drug recovery >90% for samples stored at -20° C for 6 months, with reduced recovery observed after 6 months.
