Drug Catalog - Product Detail
PROBENECID W/COLCHICINE TB 500/.5MG 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00591-5325-01 | ACTAVIS PHARMA | 100 | 0.5-500MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
PROBENECID AND COLCHICINE
Substance Name
COLCHICINE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA084279
Description
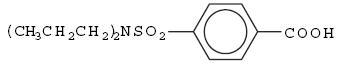
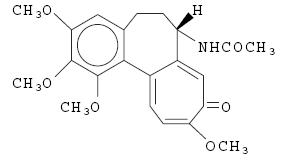
DESCRIPTION Probenecid and colchicine contains probenecid, which is a uricosuric agent, and colchicine, which has antigout activity, the mechanism of which is unknown. Probenecid is the generic name for 4-[(dipropylamino)sulfonyl] benzoic acid. The structural formula is represented below: C 13 H 19 NO 4 S M.W. 285.36 Probenecid is a white or nearly white, fine, crystalline powder. It is soluble in dilute alkali, in alcohol, in chloroform, and in acetone; it is practically insoluble in water and in dilute acids. Colchicine is an alkaloid obtained from various species of Colchicum. The chemical name for colchicine is ( S )- N -(5,6,7,9- tetrahydro-1,2,3,10-tetramethoxy-9-oxobenzo[ α ]heptalen-7-yl) acetamide. The structural formula is represented below: C 22 H 25 NO 6 M.W. 399.44 Colchicine consists of pale yellow scales or powder; it darkens on exposure to light. Colchicine is soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol and in chloroform, and slightly soluble in ether. Each tablet for oral administration contains 500 mg of probenecid and 0.5 mg of colchicine. Each tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate and sodium starch glycolate. Probenecid structural formula Colchicine structural formula
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Probenecid and Colchicine Tablets USP 500 mg-0.5 mg are bisected, white, capsule-shaped tablets imprinted DAN DAN and 5325 supplied in bottles of 100. Dispense in a well closed, light-resistant container with child-resistant closure. Store at 20 - 25°C (68 - 77°F). [See USP controlled room temperature.] Protect from light. Manufactured by: Watson Pharma Private Ltd. Verna, Salcette Goa 403 722 INDIA Distributed by: Actavis Pharma, Inc. Parsippany, NJ 07054 USA Revised: December 2016
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE For the treatment of chronic gouty arthritis when complicated by frequent, recurrent acute attacks of gout.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Therapy with probenecid and colchicine should not be started until an acute gouty attack has subsided. However, if an acute attack is precipitated during therapy, probenecid and colchicine may be continued without changing the dosage, and additional colchicine or other appropriate therapy should be given to control the acute attack. The recommended adult dosage is 1 tablet of probenecid and colchicine daily for one week, followed by 1 tablet twice a day thereafter. Some degree of renal impairment may be present in patients with gout. A daily dosage of 2 tablets may be adequate. However, if necessary, the daily dosage may be increased by 1 tablet every four weeks within tolerance (and usually not above 4 tablets per day) if symptoms of gouty arthritis are not controlled or the 24 hour uric acid excretion is not above 700 mg. As noted, probenecid may not be effective in chronic renal insufficiency particularly when the glomerular filtration rate is 30 mL/minute or less. Gastric intolerance may be indicative of overdosage, and may be corrected by decreasing the dosage. As uric acid tends to crystallize out of an acid urine, a liberal fluid intake is recommended, as well as sufficient sodium bicarbonate (3 to 7.5 g daily) or potassium citrate (7.5 g daily) to maintain an alkaline urine (see PRECAUTIONS ). Alkalization of the urine is recommended until the serum urate level returns to normal limits and tophaceous deposits disappear, i.e., during the period when urinary excretion of uric acid is at a high level. Thereafter, alkalization of the urine and the usual restriction of purine-producing foods may be somewhat relaxed. Probenecid and colchicine (or probenecid) should be continued at the dosage that will maintain normal serum urate levels. When acute attacks have been absent for six months or more and serum urate levels remain within normal limits, the daily dosage of probenecid and colchicine may be decreased by 1 tablet every six months. The maintenance dosage should not be reduced to the point where serum urate levels tend to rise.
