Drug Catalog - Product Detail
PRASUGREL HCL TAB 10 MG (BASE EQUIV) 30 CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67877-0605-30 | ASCEND LABORATORIES | 30 | 10MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
Substance Name
Product Type
Route
Application Number
Description
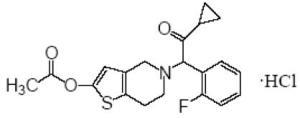
11 DESCRIPTION Prasugrel tablets contains prasugrel, a thienopyridine class inhibitor of platelet activation and aggregation mediated by the P2Y12 ADP receptor. Prasugrel tablets is formulated as the hydrochloride salt, a racemate, which is chemically designated as 5[(1RS)-2-cyclopropyl-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridin-2-yl acetate hydrochloride. Prasugrel hydrochloride has the empirical formula C 20 H 20 FNO 3 S•HCl representing a molecular weight of 409.90. The chemical structure of prasugrel hydrochloride is: Prasugrel hydrochloride is a white to practically white solid. It is soluble at pH 2, slightly soluble at pH 3 to 4, and practically insoluble at pH 6 to 7.5. It also dissolves freely in methanol and is slightly soluble in 1-and 2-propanol and acetone. It is practically insoluble in diethyl ether and ethyl acetate. Prasugrel tablet is available for oral administration as 5-mg or 10-mg oval, biconvex, film-coated, non-scored tablets, debossed on one side and plain on other side. Each yellow 5-mg tablet is manufactured with 5.49 mg prasugrel hydrochloride, equivalent to 5-mg prasugrel and each yellow 10-mg tablet with 10.98 mg prasugrel hydrochloride, equivalent to 10-mg of prasugrel. Other ingredients include mannitol, hypromellose, stearic acid, microcrystalline cellulose, Glyceryl behenate and low substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose. The color coatings contain lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, triacetin and iron (Ferric) oxide yellow. Prasugrel Structure
How Supplied
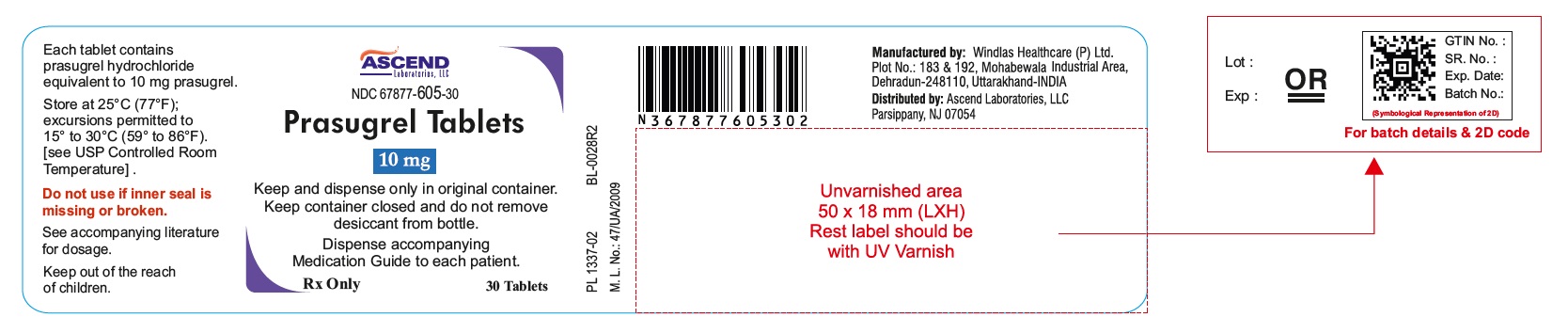
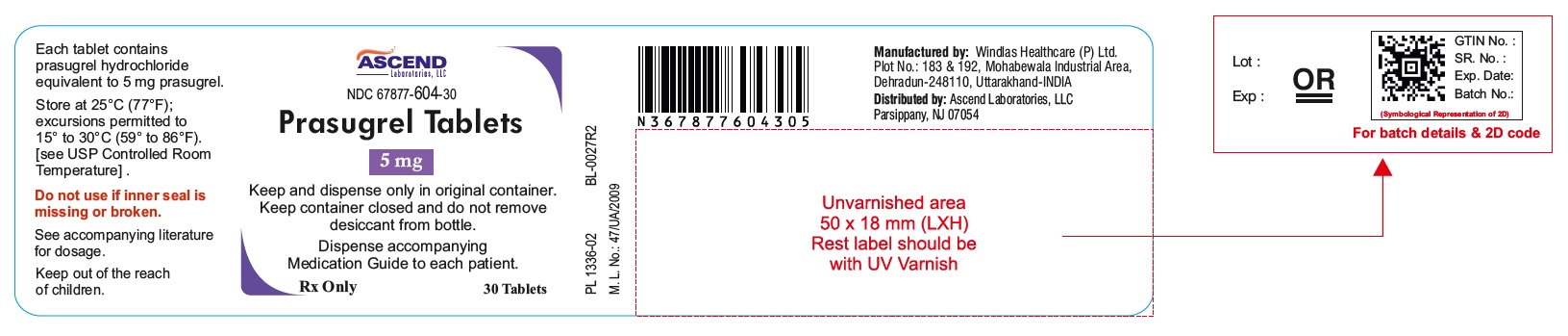
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 16.1 How Supplied Prasugrel tablets is available as oval, biconvex, film coated tablets, in the following strengths, colors, deboss, and presentations: Feature Strengths 5 mg 10 mg Tablet color Yellow Yellow Tablet debossed P5 P1 Presentation and NDC Codes Bottles of 30 67877-604-30 67877-605-30 16.2 Storage and Handling Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep and Dispense only in original container. Keep container closed and do not remove desiccant from bottle. Do not break the tablet.
Indications & Usage
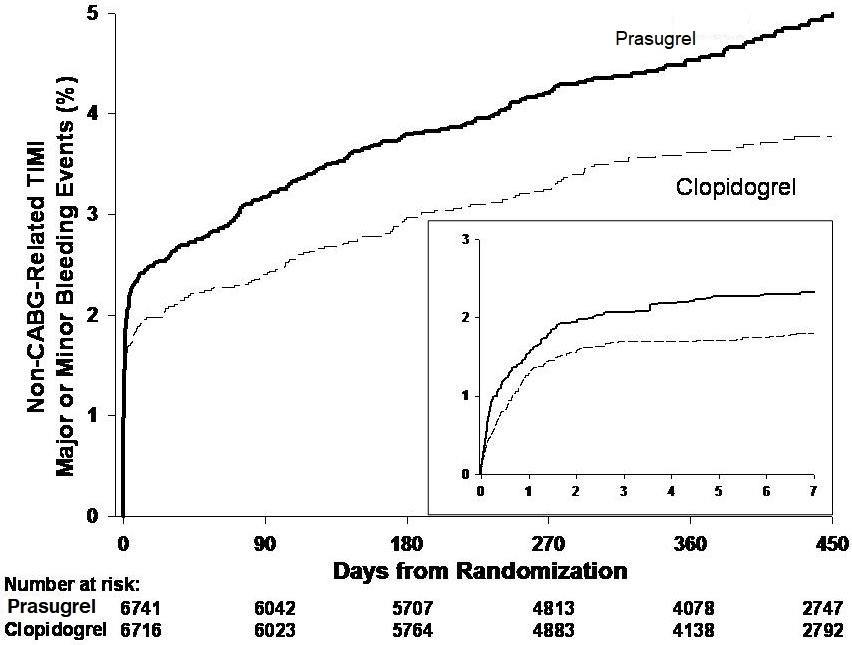
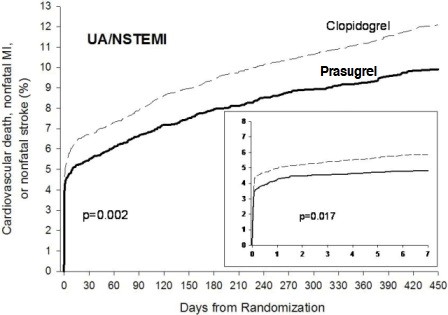
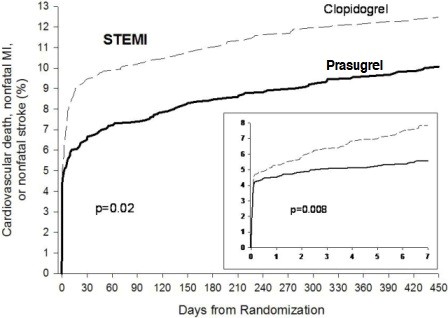
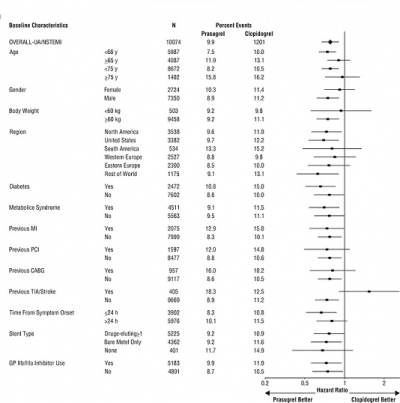
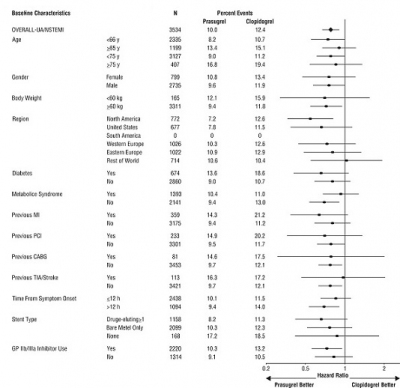
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Prasugrel tablets is a P2Y 12 platelet inhibitor indicated for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events (including stent thrombosis) in patients with acute coronary syndrome who are to be managed with PCI as follows: Patients with unstable angina or non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) ( 1.1 ). Patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) when managed with either primary or delayed PCI ( 1.1 ). 1.1 Acute Coronary Syndrome Prasugrel tablets is indicated to reduce the rate of thrombotic cardiovascular (CV) events (including stent thrombosis) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who are to be managed with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) as follows: Patients with unstable angina (UA) or non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). Patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) when managed with primary or delayed PCI. Prasugrel tablets has been shown to reduce the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), or nonfatal stroke compared to clopidogrel. The difference between treatments was driven predominantly by MI, with no difference on strokes and little difference on CV death [see Clinical Studies ( 14 )].
Dosage and Administration
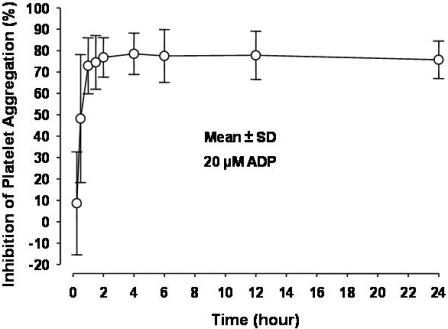
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Initiate Prasugrel tablets treatment as a single 60-mg oral loading dose and then continue at 10-mg orally once daily. Patients taking Prasugrel tablets should also take aspirin (75-mg to 325-mg) daily [see Drug Interactions ( 7.4 ) and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )]. Prasugrel tablets may be administered with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 ) and Clinical Studies ( 14 )]. • Initiate treatment with a single 60-mg oral loading dose ( 2 ). • Continue at 10-mg once daily with or without food. Consider 5-mg once daily for patients <60 kg ( 2 ). • Patients should also take aspirin (75-mg to 325-mg) daily. Timing of Loading Dose In the clinical trial that established the efficacy and safety of Prasugrel tablets, the loading dose of Prasugrel tablets was not administered until coronary anatomy was established in UA/NSTEMI patients and in STEMI patients presenting more than 12 hours after symptom onset. In STEMI patients presenting within 12 hours of symptom onset, the loading dose of Prasugrel tablets was administered at the time of diagnosis, although most received Prasugrel tablets at the time of PCI [see Clinical Studies ( 14 )] . For the small fraction of patients that required urgent CABG after treatment with Prasugrel tablets, the risk of significant bleeding was substantial. Although it is generally recommended that antiplatelet therapy be administered promptly in the management of ACS because many cardiovascular events occur within hours of initial presentation, in a trial of 4033 NSTEMI patients, no clear benefit was observed when Prasugrel tablets loading dose was administered prior to diagnostic coronary angiography compared to at the time of PCI; however, risk of bleeding was increased with early administration in patients undergoing PCI or early CABG. Dosing in Low Weight Patients Compared to patients weighing ≥60 kg, patients weighing <60 kg have an increased exposure to the active metabolite of prasugrel and an increased risk of bleeding on a 10-mg once daily maintenance dose. Consider lowering the maintenance dose to 5-mg in patients <60 kg. The effectiveness and safety of the 5-mg dose have not been prospectively studied [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 ), Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 ), and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
