Drug Catalog - Product Detail
OXCARBAZEPINE TABS 150MG 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68462-0137-01 | GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS | 100 | 150MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES




Generic Name
OXCARBAZEPINE
Substance Name
OXCARBAZEPINE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA077802
Description
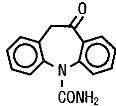
11 DESCRIPTION Oxcarbazepine Tablets USP are an antiepileptic drug available as 150 mg, 300 mg, and 600 mg film-coated tablets for oral administration. Oxcarbazepine, USP is 10,11-Dihydro-10-oxo- 5H -dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide, and its structural formula is: Oxcarbazepine, USP is a light orange to creamish white or off-white powder. It is soluble in acetic acid, sparingly soluble in chloroform, practically insoluble in water. Its molecular weight is 252.27 g/mol. Oxcarbazepine film-coated tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, ferric oxide (yellow), hypromellose, magnesium stearate, meglumine, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide. structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 150 mg Film-Coated Tablets: yellow, film-coated oval, biconvex tablets with a deep break line on both sides and "G" engraved on one side of the deep break line on one side of the tablet and "13" and "7" engraved on either side of the deep break line on the other side of the tablet. Bottle of 100.........NDC 68462-137-01 Bottle of 500.........NDC 68462-137-05 300 mg Film-Coated Tablets: yellow, film-coated oval, biconvex tablets with a deep break line on both sides and "G" and "4" engraved on either side of the deep break line on one side of the tablet. Bottle of 100.........NDC 68462-138-01 Bottle of 500.........NDC 68462-138-05 600 mg Film-Coated Tablets: yellow, film-coated oval, biconvex tablets with a deep break line on both sides and "G" engraved on one side of the deep break line on one side of the tablet and "13" and "9" engraved on either side of the deep break line on the other side of the tablet. Bottle of 100.........NDC 68462-139-01 Bottle of 500.........NDC 68462-139-05 Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in tight container (USP).
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Oxcarbazepine tablets are indicated for use as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures in adults and as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures in pediatric patients aged 4 years and above and as adjunctive therapy in pediatric patients aged 2 years and above with partial-onset seizures. Oxcarbazepine tablets are indicated for: • Adults: Monotherapy or adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures • Pediatrics: o Monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures in children 4 to 16 years o Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures in children 2 to 16 years ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Adults: initiate with a dose of 600 mg/day, given twice-a-day • Adjunctive Therapy: Maximum increment of 600 mg/day at approximately weekly intervals. The recommended daily dose is 1200 mg/day ( 2.1 ) • Conversion to Monotherapy: withdrawal concomitant over 3 to 6 weeks; reach maximum dose of oxcarbazepine tablets in 2 to 4 weeks with increments of 600 mg/day at weekly intervals to a recommended daily dose of 2400 mg/day ( 2.2 ) • Initiation of Monotherapy: Increments of 300 mg/day every third day to a dose of 1200 mg/day ( 2.3 ) • Initiate at one-half the usual starting dose and increase slowly in patients with a creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, ( 2.7 ) Pediatrics: initiation with 8 to 10 mg/kg/day, given twice-a-day. For patients aged 2 to <4 years and under 20 kg, a starting dose of 16 to 20 mg/kg/day may be considered. Recommended daily dose is dependent upon patient weight. • Adjunctive Patients (Aged 2 to 16 Years): For patients aged 4 to 16 years, target maintenance dose should be achieved over 2 weeks ( 2.4 ). For patients aged 2 to <4 years, maximum maintenance dose should be achieved over 2 to 4 weeks and should not to exceed 60 mg/kg/day ( 2.4 ) • Conversion to Monotherapy for Patients (Aged 4 to 16 Years) • Maximum increment of 10 mg/kg/day at weekly intervals, concomitant antiepileptic drugs can be completely withdrawn over 3 to 6 weeks ( 2.5 ) • Initiation of Monotherapy for Patients (Aged 4 to 16 Years) • Increments of 5 mg/kg/day every third day ( 2.6 ) 2.1 Adjunctive Therapy for Adults Initiate oxcarbazepine tablets with a dose of 600 mg/day, given twice-a-day. If clinically indicated, the dose may be increased by a maximum of 600 mg/day at approximately weekly intervals; the maximum recommended daily dose is 1200 mg/day. Daily doses above 1200 mg/day show somewhat greater effectiveness in controlled trials, but most patients were not able to tolerate the 2400 mg/day dose, primarily because of CNS effects. Dosage adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducers or UGT inducers, which include certain antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1 , 7.2 )]. 2.2 Conversion to Monotherapy for Adults Patients receiving concomitant AEDs may be converted to monotherapy by initiating treatment with oxcarbazepine tablets at 600 mg/day (given in a twice-a-day regimen) while simultaneously initiating the reduction of the dose of the concomitant AEDs. The concomitant AEDs should be completely withdrawn over 3 to 6 weeks, while the maximum dose of oxcarbazepine tablets should be reached in about 2 to 4 weeks. Oxcarbazepine tablets may be increased as clinically indicated by a maximum increment of 600 mg/day at approximately weekly intervals to achieve the maximum recommended daily dose of 2400 mg/day. A daily dose of 1200 mg/day has been shown in one study to be effective in patients in whom monotherapy has been initiated with oxcarbazepine tablets. Patients should be observed closely during this transition phase. 2.3 Initiation of Monotherapy for Adults Patients not currently being treated with AEDs may have monotherapy initiated with oxcarbazepine tablets. In these patients, initiate oxcarbazepine tablets at a dose of 600 mg/day (given a twice-a-day); the dose should be increased by 300 mg/day every third day to a dose of 1200 mg/day. Controlled trials in these patients examined the effectiveness of a 1200 mg/day dose; a dose of 2400 mg/day has been shown to be effective in patients converted from other AEDs to oxcarbazepine tablets monotherapy (see above). 2.4 Adjunctive Therapy for Pediatric Patients (Aged 2 to 16 Years) In pediatric patients aged 4 to 16 years, initiate oxcarbazepine tablets at a daily dose of 8 to 10 mg/kg generally not to exceed 600 mg/day, given twice-a-day. The target maintenance dose of oxcarbazepine tablets should be achieved over 2 weeks, and is dependent upon patient weight, according to the following chart: 20 to 29 kg – 900 mg/day 29.1 to 39 kg – 1200 mg/day >39 kg – 1800 mg/day In the clinical trial, in which the intention was to reach these target doses, the median daily dose was 31 mg/kg with a range of 6 to 51 mg/kg. In pediatric patients aged 2 to <4 years, initiate oxcarbazepine tablets at a daily dose of 8 to 10 mg/kg generally not to exceed 600 mg/day, given twice-a-day. For patients less than 20 kg, a starting dose of 16 to 20 mg/kg may be considered [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. The maximum maintenance dose of oxcarbazepine tablets should be achieved over 2 to 4 weeks and should not exceed 60 mg/kg/day in a twice-a-day regimen. In the clinical trial in pediatric patients (2 to 4 years of age) in which the intention was to reach the target dose of 60 mg/kg/day, 50% of patients reached a final dose of at least 55 mg/kg/day. Under adjunctive therapy (with and without enzyme-inducing AEDs), when normalized by body weight, apparent clearance (L/hr/kg) decreased when age increased such that children 2 to <4 years of age may require up to twice the oxcarbazepine dose per body weight compared to adults; and children 4 to ≤12 years of age may require a 50% higher oxcarbazepine dose per body weight compared to adults. Dosage adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducers or UGT inducers, which include certain antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)]. 2.5 Conversion to Monotherapy for Pediatric Patients (Aged 4 to 16 Years) Patients receiving concomitant antiepileptic drugs may be converted to monotherapy by initiating treatment with oxcarbazepine tablets at approximately 8 to 10 mg/kg/day given twice-a-day, while simultaneously initiating the reduction of the dose of the concomitant antiepileptic drugs. The concomitant antiepileptic drugs can be completely withdrawn over 3 to 6 weeks while oxcarbazepine tablets may be increased as clinically indicated by a maximum increment of 10 mg/kg/day at approximately weekly intervals to achieve the recommended daily dose. Patients should be observed closely during this transition phase. The recommended total daily dose of oxcarbazepine tablets is shown in Table 1. 2.6 Initiation of Monotherapy for Pediatric Patients (Aged 4 to 16 Years) Patients not currently being treated with antiepileptic drugs may have monotherapy initiated with oxcarbazepine tablets. In these patients, initiate oxcarbazepine tablets at a dose of 8 to 10 mg/kg/day given twice-a-day. The dose should be increased by 5 mg/kg/day every third day to the recommended daily dose shown in the table below. Table 1: Range of Maintenance Doses of Oxcarbazepine Tablets for Pediatrics by Weight During Monotherapy From To Weight in kg Dose (mg/day) Dose (mg/day) 20 600 900 25 900 1200 30 900 1200 35 900 1500 40 900 1500 45 1200 1500 50 1200 1800 55 1200 1800 60 1200 2100 65 1200 2100 70 1500 2100 2.7 Dosage Modification for Patients with Renal Impairment In patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) initiate oxcarbazepine tablets at one-half the usual starting dose (300 mg/day, given twice-a-day) and increase slowly to achieve the desired clinical response [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. 2.8 Administration Information Oxcarbazepine tablets can be taken with or without food [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Oxcarbazepine oral suspension and oxcarbazepine film-coated tablets may be interchanged at equal doses.
