Drug Catalog - Product Detail
NIFEDIPINE CAP 20MG 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69315-0212-01 | LEADING PHARMA | 100 | 20MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
NIFEDIPINE
Substance Name
NIFEDIPINE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA074045
Description
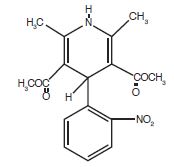
DESCRIPTION Nifedipine capsules, USP (nifedipine) is an antianginal drug belonging to a class of pharmacological agents, the calcium channel blockers. Nifedipine is 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-, dimethyl ester, C 17 H 18 N 2 O 6 , and has the structural formula: Nifedipine is a yellow crystalline substance, practically insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 346.3. Nifedipine capsules, USP are formulated as soft gelatin capsules for oral administration each containing 20 mg nifedipine. Inert ingredients in the formulations are: glycerin, peppermint oil, polyethylene glycol, saccharin sodium, gelatin, FD&C Yellow #6, FD&C Red #40, titanium dioxide, ink white opacode (WB) NSP- 78-18022 (comprises of: polyethylene glycol/macrogol, polyvinyl acetate phthalate, titanium dioxide, propylene glycol) and water. Chem Structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Nifedipine capsules USP, 20 mg: Each opaque red soft gelatin capsule, imprinted N20, contains nifedipine USP, packaged in bottles of 100: 20 mg (NDC 69315-212-01). Store at 59° to 77°F (15° to 25°C) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. DO NOT PERMIT TO FREEZE. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP. PROTECT FROM MOISTURE AND HUMIDITY. Manufactured by: Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC 2725 Scherer Drive North, St Petersburg, Florida (FL) 33716-1016, United States (USA). Distributed by: Leading Pharma, LLC Fairfield, NJ 07004. Rev. 01 12/19 Logo
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Vasospastic Angina Nifedipine capsules, USP (nifedipine) is indicated for the management of vasospastic angina confirmed by any of the following criteria: 1) classical pattern of angina at rest accompanied by ST segment elevation, 2) angina or coronary artery spasm provoked by ergonovine, or 3) angiographically demonstrated coronary artery spasm. In those patients who have had angiography, the presence of significant fixed obstructive disease is not incompatible with the diagnosis of vasospastic angina, provided that the above criteria are satisfied. Nifedipine capsules, USP may also be used where the clinical presentation suggests a possible vasospastic component but where vasospasm has not been confirmed, e.g., where pain has a variable threshold on exertion or when angina is refractory to nitrates and/or adequate doses of beta-blockers. Chronic Stable Angina (Classical Effort-Associated Angina) Nifedipine capsules, USP is indicated for the management of chronic stable angina (effort-associated angina) without evidence of vasospasm in patients who remain symptomatic despite adequate doses of beta-blockers and/or organic nitrates or who cannot tolerate those agents. In chronic stable angina (effort-associated angina), nifedipine capsules, USP has been effective in controlled trials of up to eight weeks duration in reducing angina frequency and increasing exercise tolerance, but confirmation of sustained effectiveness and evaluation of long-term safety in these patients are incomplete. Controlled studies in small numbers of patients suggest concomitant use of nifedipine capsules, USP and beta-blocking agents may be beneficial in patients with chronic stable angina, but available information is not sufficient to predict with confidence the effects of concurrent treatment, especially in patients with compromised left ventricular function or cardiac conduction abnormalities. When introducing such concomitant therapy, care must be taken to monitor blood pressure closely since severe hypotension can occur from the combined effects of the drugs. ( See WARNINGS ).
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The dosage of nifedipine needed to suppress angina and that can be tolerated by the patient must be established by titration. Excessive doses can result in hypotension. Therapy should be initiated with the 10 mg capsule. The starting dose is one 10 mg capsule, swallowed whole, 3 times/day. The usual effective dose range is 10 to 20 mg three times daily. Some patients, especially those with evidence of coronary artery spasm, respond only to higher doses, more frequent administration, or both. In such patients, doses of 20 to 30 mg three or four times daily may be effective. Doses above 120 mg daily are rarely necessary. More than 180 mg per day is not recommended. In most cases, nifedipine titration should proceed over a 7 to 14 day period so that the physician can assess the response to each dose level and monitor the blood pressure before proceeding to higher doses. If symptoms so warrant, titration may proceed more rapidly provided that the patient is assessed frequently. Based on the patient’s physical activity level, attack frequency, and sublingual nitroglycerin consumption, the dose of nifedipine may be increased from 10 mg t.i.d. to 20 mg t.i.d. and then to 30 mg t.i.d. over a three-day period. In hospitalized patients under close observation, the dose may be increased in 10 mg increments over four- to six-hour periods as required to control pain and arrhythmias due to ischemia. A single dose should rarely exceed 30 mg. Avoid co-administration of nifedipine with grapefruit juice (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS: Other Interactions ). No “rebound effect” has been observed upon discontinuation of nifedipine. However, if discontinuation of nifedipine is necessary, sound clinical practice suggests that the dosage should be decreased gradually with close physician supervision. Co-Administration with other Antianginal Drugs Sublingual nitroglycerin may be taken as required for the control of acute manifestations of angina, particularly during nifedipine titration. See PRECAUTIONS , Drug Interactions , for information on co-administration of nifedipine with beta-blockers or long-acting nitrates.
