Drug Catalog - Product Detail
MINOXIDIL TB 10MG 500
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00591-5643-05 | ACTAVIS PHARMA | 500 | 10MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES






Generic Name
MINOXIDIL
Substance Name
MINOXIDIL
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA071344
Description
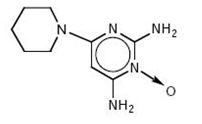
DESCRIPTION Minoxidil tablets, USP contain minoxidil, USP an antihypertensive peripheral vasodilator. Minoxidil occurs as a white to off-white, crystalline powder, soluble in alcohol and propylene glycol; sparingly soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in water; practically insoluble in chloroform, acetone and ethyl acetate. The chemical name for minoxidil, USP is 2,4-pyrimidinediamine,6-(1-piperidinyl)-, 3-oxide. The structural formula is represented below: C 9 H 15 N 5 O M.W. 209.25 Minoxidil tablets, USP for oral administration contain either 2.5 mg or 10 mg of minoxidil, USP. Minoxidil Tablets, USP 2.5 mg and 10 mg contain the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, docusate sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium benzoate and sodium starch glycolate. Structural formula of minoxidil
How Supplied
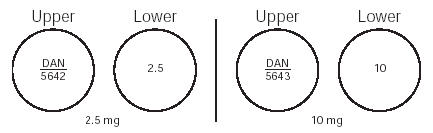
HOW SUPPLIED Minoxidil Tablets, USP 2.5 mg are 9/32 ", scored, round, white tablets imprinted “ DAN 5642 ” and “ 2.5 ” supplied in bottles of 100 NDC 0591-5642-01 and 500 NDC 0591-5642-05. Minoxidil Tablets, USP 10 mg are 9/32 ", scored, round, white tablets imprinted “ DAN 5643 ” and “ 10 ” supplied in bottles of 100 NDC 0591-5643-01 and 500 NDC 0591-5643-05. Dispense in a tight container with child-resistant closure. Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense with Patient Package Insert available at: www.tevausa.com/PatientPI Manufactured In India By: Watson Pharma Private Limited Verna, Salcette Goa 403 722, India Manufactured For: Teva Pharmaceuticals Parsippany, NJ 07054 Rev. B 2/2024
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Because of the potential for serious adverse effects, minoxidil tablets are indicated only in the treatment of hypertension that is symptomatic or associated with target organ damage and is not manageable with maximum therapeutic doses of a diuretic plus two other antihypertensive drugs. At the present time use in milder degrees of hypertension is not recommended because the benefit-risk relationship in such patients has not been defined. Minoxidil reduced supine diastolic blood pressure by 20 mm Hg or to 90 mm Hg or less in approximately 75% of patients, most of who had hypertension that could not be controlled by other drugs.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Patients over 12 years of age: The recommended initial dosage of minoxidil tablets is 5 mg of minoxidil given as a single daily dose. Daily dosage can be increased to 10, 20 and then to 40 mg in single or divided doses if required for optimum blood pressure control. The effective dosage range is usually 10 to 40 mg per day. The maximum recommended dosage is 100 mg per day. Patients under 12 years of age: The initial dosage is 0.2 mg/kg minoxidil as a single daily dose. The dosage may be increased in 50 to 100% increments until optimum blood pressure control is achieved. The effective dosage range is usually 0.25 to 1.0 mg/kg/day. The maximum recommended dosage is 50 mg daily (see 9. Pediatric Use under PRECAUTIONS ). Dose frequency: The magnitude of within-day fluctuation of arterial pressure during therapy with minoxidil is directly proportional to the extent of pressure reduction. If supine diastolic pressure has been reduced less than 30 mm Hg, the drug need be administered only once a day; if supine diastolic pressure has been reduced more than 30 mm Hg, the daily dosage should be divided into two equal parts. Frequency of dosage adjustment: Dosage must be titrated carefully according to individual response. Intervals between dosage adjustments normally should be at least 3 days since the full response to a given dose is not obtained for at least that amount of time. Where a more rapid management of hypertension is required, dose adjustments can be made every 6 hours if the patient is carefully monitored. Concomitant therapy: Diuretic and beta-blocker or other sympathetic nervous system suppressant. Diuretics: Minoxidil must be used in conjunction with a diuretic in patients relying on renal function for maintaining salt and water balance. Diuretics have been used at the following dosages when starting therapy with minoxidil: hydrochlorothiazide (50 mg, b.i.d.) or other thiazides at equieffective dosage; chlorthalidone (50 to 100 mg, once daily); furosemide (40 mg, b.i.d.). If excessive salt and water retention results in a weight gain of more than 5 pounds, diuretic therapy should be changed to furosemide; if the patient is already taking furosemide, dosage should be increased in accordance with the patient’s requirements. Beta-blocker or other sympathetic nervous system suppressants: When therapy with minoxidil is begun, the dosage of a beta-adrenergic receptor blocking drug should be the equivalent of 80 to 160 mg of propranolol per day in divided doses. If beta-blockers are contraindicated, methyldopa (250 to 750 mg, b.i.d.) may be used instead. Methyldopa must be given for at least 24 hours before starting therapy with minoxidil because of the delay in the onset of methyldopa’s action. Limited clinical experience indicates that clonidine may also be used to prevent tachycardia induced by minoxidil; the usual dosage is 0.1 to 0.2 mg twice daily. Sympathetic nervous system suppressants may not completely prevent an increase in heart rate due to minoxidil but usually do prevent tachycardia. Typically, patients receiving a beta-blocker prior to initiation of therapy with minoxidil have a bradycardia and can be expected to have an increase in heart rate toward normal when minoxidil is added. When treatment with minoxidil and beta-blocker or other sympathetic nervous system suppressant are begun simultaneously, their opposing cardiac effects usually nullify each other, leading to little change in heart rate.
