Drug Catalog - Product Detail
LISINOPRIL TB 40MG 1000
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68180-0517-03 | LUPIN PHARMACEUTICALS | 1000 | 40MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
Substance Name
Product Type
Route
Application Number
Description
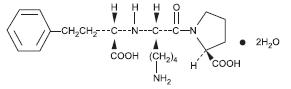
DESCRIPTION Lisinopril is an oral long-acting angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. Lisinopril, a synthetic peptide derivative, is chemically described as (S)-1-[N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline dihydrate. Its empirical formula is C 21 H 31 N 3 O 5 (2H 2 O and its structural formula is: Lisinopril is a white to off-white, crystalline powder, with a molecular weight of 441.53. It is soluble in water and sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in ethanol. Lisinopril tablets are supplied as 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg and 40 mg tablets for oral administration. Inactive Ingredients: 2.5 mg tablets - colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, pre-gelatinized starch, starch. 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg and 30 mg tablets – colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, pre-gelatinized starch, red iron oxide, starch. 40 mg tablets - colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, pre-gelatinized starch, starch, yellow iron oxide. Lisinopril USP
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Lisinopril Tablets, USP are available as: 2.5 mg tablet is a white to off-white, round, biconvex uncoated tablet with ‘LUPIN" debossed on one side and "2.5" on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-512-09 Bottles of 100 NDC 68180-512-01 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-512-02 Bottles of 1000 NDC 68180-512-03 5 mg tablet is a pink coloured, round, biconvex uncoated tablet with "5" debossed on one side and breakline on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-513-09 Bottles of 100 NDC 68180-513-01 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-513-02 Bottles of 1000 NDC 68180-513-03 Bottles of 5000 NDC 68180-513-05 10 mg tablet is a pink coloured, round, biconvex uncoated tablet with "LUPIN" debossed on one side and "10" on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-514-09 Bottles of 100 NDC 68180-514-01 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-514-02 Bottles of 1000 NDC 68180-514-03 Bottles of 5000 NDC 68180-514-05 20 mg tablet is a pink coloured, round, biconvex uncoated tablet with "LUPIN" debossed on one side and "20" on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-515-09 Bottles of 100 NDC 68180-515-01 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-515-02 Bottles of 1000 NDC 68180-515-03 Bottles of 5000 NDC 68180-515-05 30 mg tablet is a red coloured, round, biconvex uncoated tablet with "LUPIN" debossed on one side and "30" on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-516-09 Bottles of 100 NDC 68180-516-01 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-516-02 Bottles of 1000 NDC 68180-516-03 40 mg tablet is a yellow coloured, round, biconvex uncoated tablet with "LUPIN" debossed on one side and "40" on other side. They are available as follows: Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-517-09 Bottles of 100 NDC 68180-517-01 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-517-02 Bottles of 1000 NDC 68180-517-03 Bottles of 2000 NDC 68180-517-04 Storage: Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF)[see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture, freezing and excessive heat. Dispense in a tight container.
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Hypertension Lisinopril tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. They may be used alone as initial therapy or concomitantly with other classes of antihypertensive agents. Heart Failure Lisinopril tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy in the management of heart failure in patients who are not responding adequately to diuretics and digitalis. Acute Myocardial Infarction Lisinopril tablets are indicated for the treatment of hemodynamically stable patients within 24 hours of acute myocardial infarction, to improve survival. Patients should receive, as appropriate, the standard recommended treatments such as thrombolytics, aspirin and beta-blockers. In using lisinopril tablets, consideration should be given to the fact that another angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril, has caused agranulocytosis, particularly in patients with renal impairment or collagen vascular disease, and that available data are insufficient to show that lisinopril tablets does not have a similar risk. (See WARNINGS ). In considering the use of lisinopril tablets, it should be noted that in controlled clinical trials ACE inhibitors have an effect on blood pressure that is less in Black patients than in non-Blacks. In addition, ACE inhibitors have been associated with a higher rate of angioedema in Black than in non-Black patients (see WARNINGS, Anaphylactoid and Possibly Related Reactions ).
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Hypertension Initial Therapy: In patients with uncomplicated essential hypertension not on diuretic therapy, the recommended initial dose is 10 mg once a day. Dosage should be adjusted according to blood pressure response. The usual dosage range is 20 to 40 mg per day administered in a single daily dose. The antihypertensive effect may diminish toward the end of the dosing interval regardless of the administered dose, but most commonly with a dose of 10 mg daily. This can be evaluated by measuring blood pressure just prior to dosing to determine whether satisfactory control is being maintained for 24 hours. If it is not, an increase in dose should be considered. Doses up to 80 mg have been used but do not appear to give greater effect. If blood pressure is not controlled with lisinopril tablet alone, a low dose of a diuretic may be added. Hydrochlorothiazide, 12.5 mg has been shown to provide an additive effect. After the addition of a diuretic, it may be possible to reduce the dose of lisinopril tablet. Diuretic Treated Patients: In hypertensive patients who are currently being treated with a diuretic, symptomatic hypotension may occur occasionally following the initial dose of lisinopril tablet. The diuretic should be discontinued, if possible, for two to three days before beginning therapy with lisinopril tablet to reduce the likelihood of hypotension (See WARNINGS ). The dosage of lisinopril tablet should be adjusted according to blood pressure response. If the patient's blood pressure is not controlled with lisinopril tablet alone, diuretic therapy may be resumed as described above. If the diuretic cannot be discontinued, an initial dose of 5 mg should be used under medical supervision for at least two hours and until blood pressure has stabilized for at least an additional hour (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions ). Concomitant administration of lisinopril with potassium supplements, potassium salt substitutes, or potassium-sparing diuretics may lead to increases of serum potassium (See PRECAUTIONS ). Dosage Adjustment in Renal Impairment: The usual dose of lisinopril tablet (10 mg) is recommended for patients with creatinine clearance > 30 mL/min (serum creatinine of up to approximately 3 mg/dL). For patients with creatinine clearance ≥ 10 mL/min ≤ 30 mL/min (serum creatinine ≥ 3 mg/dL), the first dose is 5 mg once daily. For patients with creatinine clearance < 10 mL/min (usually on hemodialysis) the recommended initial dose is 2.5 mg. The dosage may be titrated upward until blood pressure is controlled or to a maximum of 40 mg daily. Renal Status Creatinine Clearance mL / min Initial Dose mg / day Normal Renal Function to Mild Impairment >30 10 Moderate to Severe Impairment ≥10 ≤30 5 Dialysis Patients <10 2.5 Heart Failure: Lisinopril tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy with diuretics and (usually) digitalis. The recommended starting dose is 5 mg once a day. When initiating treatment with lisinopril in patients with heart failure, the initial dose should be administered under medical observation, especially in those patients with low blood pressure (systolic blood pressure below 100 mmHg). The mean peak blood pressure lowering occurs six to eight hours after dosing. Observation should continue until blood pressure is stable. The concomitant diuretic dose should be reduced, if possible, to help minimize hypovolemia which may contribute to hypotension. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions ). The appearance of hypotension after the initial dose of lisinopril tablet does not preclude subsequent careful dose titration with the drug, following effective management of the hypotension. The usual effective dosage range is 5 to 40 mg per day administered as a single daily dose. The dose of lisinopril tablets can be increased by increments of no greater than 10 mg, at intervals of no less than 2 weeks to the highest tolerated dose, up to a maximum of 40 mg daily. Dose adjustment should be based on the clinical response of individual patients. Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Heart Failure and Renal Impairment or Hyponatremia: In patients with heart failure who have hyponatremia (serum sodium < 130 mEq/L) or moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 30 mL/min or serum creatinine > 3 mg/dL), therapy with lisinopril tablet should be initiated at a dose of 2.5 mg once a day under close medical supervision. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions ). Acute Myocardial Infarction: In hemodynamically stable patients within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms of acute myocardial infarction, the first dose of lisinopril tablet is 5 mg given orally, followed by 5 mg after 24 hours, 10 mg after 48 hours and then 10 mg of lisinopril once daily. Dosing should continue for six weeks. Patients should receive, as appropriate, the standard recommended treatments such as thrombolytics, aspirin, and beta-blockers. Patients with a low systolic blood pressure (≤ 120 mmHg) when treatment is started or during the first 3 days after the infarct should be given a lower 2.5 mg oral dose of lisinopril tablet (see WARNINGS ). If hypotension occurs (systolic blood pressure ≤ 100 mmHg) a daily maintenance( dose of 5 mg may be given with temporary reductions to 2.5 mg if needed. If prolonged hypotension occurs (systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg for more than 1 hour) lisinopril tablet should be withdrawn. For patients who develop symptoms of heart failure, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Heart Failure . Dosage Adjustment in Patients With Myocardial Infarction with Renal Impairment: In acute myocardial infarction, treatment with lisinopril tablet should be initiated with caution in patients with evidence of renal dysfunction, defined as serum creatinine concentration exceeding 2 mg/dL. No evaluation of dosing adjustments in myocardial infarction patients with severe renal impairment has been performed. Use in Elderly: In general, the clinical response was similar in younger and older patients given similar doses of lisinopril. Pharmacokinetic studies, however, indicate that maximum blood levels and area under the plasma concentration time curve (AUC) are doubled in older patients, so that dosage adjustments should be made with particular caution. Pediatric Hypertensive Patients ≥ 6 years of age: The usual recommended starting dose is 0.07 mg/kg once daily (up to 5 mg total). Dosage should be adjusted according to blood pressure response. Doses above 0.61 mg/kg (or in excess of 40 mg) have not been studied in pediatric patients. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism and Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects ). Lisinopril is not recommend in pediatric patients < 6 years or in pediatric patients with glomerular filtration rate < 30 mL/min/1.73 min 2 (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism and Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects and PRECAUTIONS ).
