Drug Catalog - Product Detail
LEVONORGESTREL/ETHINYL ESTRADIOL (LESSINA) TB 0.1/0.02MG 3X28
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00555-9014-67 | TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA | 28 | 0.1-20MG-MCG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
LEVONORGESTREL AND ETHINYL ESTRADIOL
Substance Name
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
Application Number
ANDA075803
Description
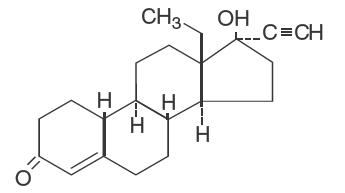
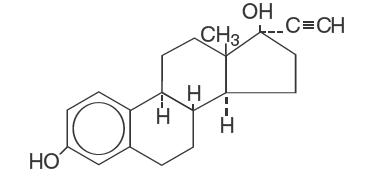
DESCRIPTION Each cycle of Lessina ® 28 (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP) consists of 21 pink active tablets each containing 0.1 mg levonorgestrel, USP and 0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP; and seven white inert tablets. The inactive ingredients include anhydrous lactose, FD&C red no. 40 aluminum lake, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, corn starch, and titanium dioxide. Each white tablet contains only inert ingredients as follows: anhydrous lactose, hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, and magnesium stearate. The structural formulas are as follows: Levonorgestrel, USP C 21 H 28 O 2 Molecular Weight: 312.4 Ethinyl Estradiol, USP C 20 H 24 O 2 Molecular Weight: 296.4 levonorgestrel structural formula ethinyl estradiol
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Lessina ® (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP 0.1 mg/ 0.02 mg) are packaged in blister cards. Each card contains 21 pink, round, film-coated, biconvex, unscored tablets, debossed stylized b on one side and 965 on the other side, and 7 white, round, biconvex, unscored tablets, debossed stylized b on one side and 208 on the other side. Available in cartons of 3 blister cards (NDC: 0555-9014-67). Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Oral contraceptives are indicated for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use this product as a method of contraception. Oral contraceptives are highly effective. Table III lists the typical accidental pregnancy rates for users of combination oral contraceptives and other methods of contraception. The efficacy of these contraceptive methods, except sterilization, depends upon the reliability with which they are used. Correct and consistent use of methods can result in lower failure rates. TABLE III. Percentage of women experiencing an unintended pregnancy during the first year of typical use and first year of perfect use of contraception and the percentage continuing use at the end of the first year. United States. % of Women Experiencing an Accidental Pregnancy within the First Year of Use % of Women Continuing Use at One Year 3 Method (1) Typical Use 1 (2) Perfect Use 2 (3) (4) Chance 4 85 85 Spermicides 5 26 6 40 Periodic abstinence 25 63 Calendar 9 Ovulation method 3 Sympto-thermal 6 2 Post ovulation 1 Withdrawal 19 4 Cap 7 Parous women 40 26 42 Nulliparous women 20 9 56 Sponge Parous women 40 20 42 Nulliparous women 20 9 56 Diaphragm 7 20 6 56 Condom 8 Female (Reality) 21 5 56 Male 14 3 61 Pill 5 71 Progestin only 0.5 Combined 0.1 IUD Progesterone T 2 1.5 81 Copper T 380A 0.8 0.6 78 Lng 20 0.1 0.1 81 Depo Provera 0.3 0.3 70 Norplant and Norplant-2 0.05 0.05 88 Female sterilization 0.5 0.5 100 Male sterilization 0.15 0.1 100 Source: Trussell J, Contraceptive efficacy. In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Stewart F, Cates W, Stewart GK, Kowal D, Guest F, Contraceptive Technology: Seventeenth Revised Edition. New York NY: Irvington Publishers, 1998, in press. 1. Among typical couples who initiate use of a method (not necessarily for the first time), the percentage who experience an accidental pregnancy during the first year if they do not stop use for any other reason. 2. Among couples who initiate use of a method (not necessarily for the first time) and who use it perfectly (both consistently and correctly), the percentage who experience an accidental pregnancy during the first year if they do not stop use for any other reason. 3. Among couples attempting to avoid pregnancy, the percentage who continue to use a method for one year. 4. The percentages becoming pregnant in columns (2) and (3) are based on data from populations where contraception is not used and from women who cease using contraception in order to become pregnant. Among such populations, about 89% become pregnant within one year. This estimate was lowered slightly (to 85%) to represent the percentage who would become pregnant within one year among women now relying on reversible methods of contraception if they abandoned contraception altogether. 5. Foams, creams, gels, vaginal suppositories, vaginal film. 6. Cervical mucus (ovulation) method supplemented by calendar in the pre-ovulatory and basal body temperature in the postovulatory phases. 7. With spermicidal cream or jelly. 8. Without spermicides.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness , Lessina ® (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP) must be taken exactly as directed at intervals not exceeding 24-hours. Lessina Tablets are a monophasic preparation plus 7 inert tablets. The dosage of Lessina Tablets is one tablet daily for 21 consecutive days per menstrual cycle plus 7 white inert tablets according to the prescribed schedule. It is recommended that Lessina Tablets be taken at the same time each day, preferably after the evening meal or at bedtime. During the first cycle of medication, the patient should be instructed to take one pink Lessina Tablet daily and then 7 white inert tablets for twenty-eight (28) consecutive days, beginning on day one (1) of her menstrual cycle. (The first day of menstruation is day one.) Withdrawal bleeding usually occurs within 3 days following the last pink tablet. (If Lessina Tablets are first taken later than the first day of the first menstrual cycle of medication or postpartum, contraceptive reliance should not be placed on Lessina Tablets until after the first 7 consecutive days of administration. The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of medication should be considered.) When switching from another oral contraceptive, Lessina Tablets should be started on the first day of bleeding following the last active tablet taken of the previous oral contraceptive. The patient begins her next and all subsequent 28-day courses of Lessina Tablets on the same day of the week that she began her first course, following the same schedule. She begins taking her pink tablets on the next day after ingestion of the last white tablet, regardless of whether or not a menstrual period has occurred or is still in progress. Anytime a subsequent cycle of Lessina Tablets is started later than the next day, the patient should be protected by another means of contraception until she has taken a tablet daily for seven consecutive days. If spotting or breakthrough bleeding occurs, the patient is instructed to continue on the same regimen. This type of bleeding is usually transient and without significance, however, if the bleeding is persistent or prolonged, the patient is advised to consult her physician. Although the occurrence of pregnancy is highly unlikely if Lessina Tablets are taken according to directions, if withdrawal bleeding does not occur, the possibility of pregnancy must be considered. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule (missed one or more active tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), the probability of pregnancy should be considered at the time of the first missed period and appropriate diagnostic measures taken before the medication is resumed. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out before continuing the contraceptive regimen. The risk of pregnancy increases with each active (pink) tablet missed. For additional patient instructions regarding missed pills, see the “WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS” section in the DETAILED PATIENT LABELING below. If breakthrough bleeding occurs following missed tablets, it will usually be transient and of no consequence. If the patient misses one or more white tablets, she is still protected against pregnancy provided she begins taking pink tablets again on the proper day. In the nonlactating mother, Lessina Tablets may be initiated postpartum, for contraception. When the tablets are administered in the postpartum period, the increased risk of thromboembolic disease associated with the postpartum period must be considered. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS , WARNINGS , and PRECAUTIONS concerning thromboembolic disease.) It is to be noted that early resumption of ovulation may occur if bromocriptine mesylate has been used for the prevention of lactation.
