Drug Catalog - Product Detail
IRBESARTAN TB 75MG 90
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43547-0374-09 | SOLCO HEALTHCARE | 90 | 75MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
IRBESARTAN
Substance Name
IRBESARTAN
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA203071
Description
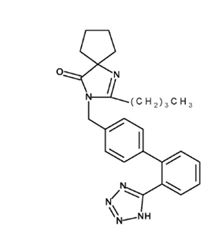
11 DESCRIPTION Irbesartan is an angiotensin II receptor (AT 1 subtype) antagonist. Irbesartan is a non-peptide compound, chemically described as a 2-butyl-3-[ p -( o -1 H -tetrazol-5‑ylphenyl)benzyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.4]non-1-en-4-one. Its empirical formula is C 25 H 28 N 6 O, and the structural formula: Irbesartan, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 428.5. It is a nonpolar compound with a partition coefficient (octanol/water) of 10.1 at pH of 7.4. Irbesartan is slightly soluble in alcohol and methylene chloride and practically insoluble in water. Irbesartan tablets, USP are available for oral administration in unscored tablets containing 75 mg, 150 mg, or 300 mg of irbesartan. Inactive ingredients include: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Irbesartan tablets, USP are available as white to off-white biconvex oval tablets, debossed with “HH” on one side and a code on the other (see Table below). Unit-of-use bottles contain 30 tablets, 90 tablets or 500 tablets as follows: 75 mg 150 mg 300 mg Debossing 329 330 331 Bottle of 30 43547-374-03 43547-375-03 43547-376-03 Bottle of 90 43547-374-09 43547-375-09 43547-376-09 Bottle of 500 43547-374-50 43547-375-50 43547-376-50 Store at 20 o C-25 o C (68 o F-77 o F); excursions permitted to 15 o C-30 o C (59 o F-86 o F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
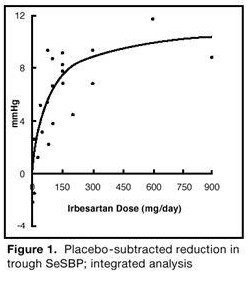
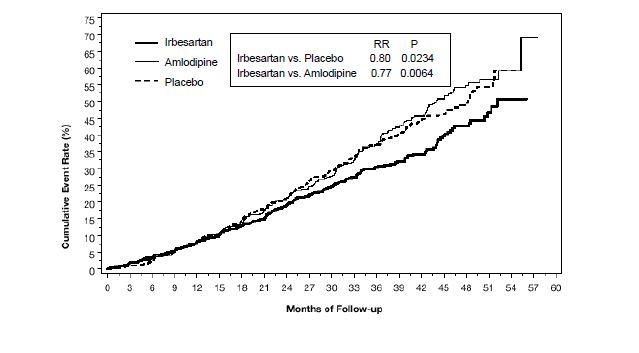
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Irbesartan tablets are an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) indicated for: • Treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. ( 1.1 ) Treatment of diabetic nephropathy in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes, an elevated serum creatinine, and proteinuria. ( 1.2 ) 1.1 Hypertension Irbesartan tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure lowers the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular (CV) events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarction. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including this drug. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than 1 drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. Irbesartan tablets may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. 1.2 Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Irbesartan tablets are indicated for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension, an elevated serum creatinine, and proteinuria (>300 mg/day). In this population, irbesartan tablets reduce the rate of progression of nephropathy as measured by the occurrence of doubling of serum creatinine or end-stage renal disease (need for dialysis or renal transplantation) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Indication Dose Hypertension ( 2.2 ) 150 to 300 mg once daily Diabetic Nephropathy ( 2.3 ) 300 mg once daily 2.1 General Considerations Irbesartan tablets may be administered with other antihypertensive agents and with or without food. 2.2 Hypertension The recommended initial dose of irbesartan tablets is 150 mg once daily. The dosage can be increased to a maximum dose of 300 mg once daily as needed to control blood pressure [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. 2.3 Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients The recommended dose is 300 mg once daily [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]. 2.4 Dose Adjustment in Volume and Salt-Depleted Patients The recommended initial dose is 75 mg once daily in patients with depletion of intravascular volume or salt (e.g., patients treated vigorously with diuretics or on hemodialysis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
