Drug Catalog - Product Detail
INDOMETHACIN ER CAPS 75MG 90CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59746-0379-90 | JUBILANT CADISTA | 90 | 75MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES

Generic Name
Substance Name
Product Type
Route
Application Number
Description
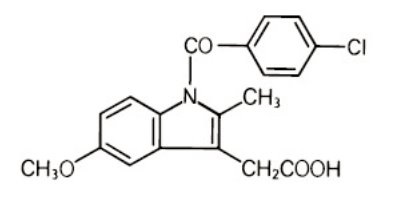
Description domethacin extended-release capsules, USP are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The chemical name is 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid. The molecular weight is 357.8. Its molecular formula is C19H16ClNO4, and it has the following chemical structure. Indomethacin, USP is a white to yellow crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in alcohol. It has a pKa of 4.5 and is stable in neutral or slightly acidic media and decomposes in strong alkali. Each extended-release capsule, for oral administration contains 75 mg of indomethacin, USP. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, ethyl cellulose, ferric oxide black, gelatin, potassium hydroxide, povidone, propylene glycol, shellac, sucrose, and talc. This product meets USP Dissolution Test 2. Indome.jpg
How Supplied
How supplied Indomethacin Extended-Release Capsules, USP for oral administration, are available as 75 mg Indomethacin extended-release capsules, USP 75 mg are supplied as clear transparent cap and body, size '2' hard gelatin capsules, printed in black ink with 'C' on cap and '379' on body containing off-white to light yellow colored pellets and are available as follows: Bottles of 60 capsules NDC 59746-379-60 Bottles of 90 capsules NDC 59746-379-90 Bottles of 100 capsules NDC 59746-379-01 Bottles of 500 capsules NDC 59746-379-05 Storage Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. KEEP TIGHTLY CLOSED.
Indications & Usage
Indications & Usage Indomethacin extended-release capsules are indicated for: Moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis including acute flares of chronic disease Moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis Moderate to severe osteoarthritis Acute painful shoulder (bursitis and/or tendinitis)
Dosage and Administration
Dosage and Administration 2.1 General Dosing Instructions Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of indomethacin extended-release and other treatment options before deciding to use indomethacin extended-release. Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. After observing the response to initial therapy with indomethacin, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient’s needs. Adverse reactions generally appear to correlate with the dose of indomethacin. Therefore, every effort should be made to determine the lowest effective dosage for the individual patient. THIS SECTION PREDOMINANTLY REFERENCES THE INDOMETHACIN IMMEDIATE-RELEASE CAPSULE ORAL DOSAGE AND IS INTENDED TO PROVIDE GUIDANCE IN USING INDOMETHACIN EXTENDED-RELEASE CAPSULES, 75 MG. Indomethacin extended-release, 75 mg once a day can be substituted for indomethacin immediate-release capsules, 25 mg three times a day. However, there will be significant differences between the two dosage regimens in indomethacin blood levels, especially after 12 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. In addition, indomethacin extended-release, 75 mg twice a day can be substituted for indomethacin immediate-release capsules 50 mg three times a day. Indomethacin extended-release may be substituted for all the indications for indomethacin immediate-release capsules except acute gouty arthritis. Dosage Recommendations for Active Stages of the Following: 2.2 Moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis including acute flares of chronic disease; moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis; and moderate to severe osteoarthritis Indomethacin immediate-release capsules, 25 mg twice a day or three times a day. If this is well tolerated, increase the daily dosage by 25 mg or by 50 mg, if required by continuing symptoms, at weekly intervals until a satisfactory response is obtained or until a total daily dose of 150 mg to 200 mg is reached. Doses above this amount generally do not increase the effectiveness of the drug. In patients who have persistent night pain and/or morning stiffness, the giving of a large portion, up to a maximum of 100 mg, of the total daily dose at bedtime may be helpful in affording relief. The total daily dose should not exceed 200 mg. In acute flares of chronic rheumatoid arthritis, it may be necessary to increase the dosage by 25 mg or, if required, by 50 mg daily. If minor adverse effects develop as the dosage is increased, reduce the dosage rapidly to a tolerated dose and observe the patient closely. If severe adverse reactions occur, stop the drug. After the acute phase of the disease is under control, an attempt to reduce the daily dose should be made repeatedly until the patient is receiving the smallest effective dose or the drug is discontinued. Careful instructions to, and observations of, the individual patient are essential to the prevention of serious, irreversible, including fatal, adverse reactions. As advancing years appear to increase the possibility of adverse reactions, indomethacin extended-release should be used with greater care in the elderly [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. 2.3 Acute painful shoulder (bursitis and/or tendinitis) Indomethacin immediate-release capsules 75 mg to 150 mg daily in 3 or 4 divided doses. Discontinue indomethacin extended-release treatment after the signs and symptoms of inflammation have been controlled for several days. The usual course of therapy is 7 to 14 days.
