Drug Catalog - Product Detail
GUANFACINE ER TB 1MG 100
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00228-2850-11 | ACTAVIS PHARMA | 100 | 1MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES




Generic Name
GUANFACINE
Substance Name
GUANFACINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA200881
Description
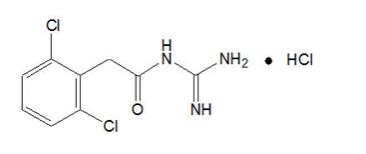
11 DESCRIPTION Guanfacine Extended-Release is a once-daily, extended-release formulation of guanfacine hydrochloride (HCl) in a matrix tablet formulation for oral administration only. The chemical designation is N-amidino-2-(2, 6-dichlorophenyl) acetamide monohydrochloride. The chemical structure is: C 9 H 9 Cl 2 N 3 O•HCl M.W. 282.55 Guanfacine hydrochloride, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water (approximately 1 mg/mL) and alcohol and slightly soluble in acetone. The only organic solvent in which it has relatively high solubility is methanol (>30 mg/mL). Each tablet contains guanfacine hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, or 4 mg of guanfacine base. The tablets also contain colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, fumaric acid, glyceryl behenate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, and povidone. In addition, the 1 mg and 2 mg tablets contain FD&C Yellow #6 Aluminum Lake and the 3 mg and 4 mg tablets contain D&C Yellow #10 Aluminum Lake. The following chemical structure of Guanfacine hydrochloride, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water (approximately 1 mg/mL) and alcohol and slightly soluble in acetone. The only organic solvent in which it has relatively high solubility is methanol (greater than 30 mg/mL). Each tablet contains guanfacine hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, or 4 mg of guanfacine base.
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Guanfacine Extended-Release Tablets are available as follows: 1 mg - Each orange, round, unscored tablet debossed with on one side and 850 on the other side contains guanfacine hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 1 mg of guanfacine base. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2850-11). 2 mg - Each orange, oval, unscored tablet debossed with on one side and 851 on the other side contains guanfacine hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 2 mg of guanfacine base. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2851-11). 3 mg - Each yellow, round, unscored tablet debossed with on one side and 853 on the other side contains guanfacine hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 3 mg of guanfacine base. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2853-11). 4 mg - Each yellow, oval, unscored tablet debossed with on one side and 855 on the other side contains guanfacine hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 4 mg of guanfacine base. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2855-11). Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP. round tablet debossed round tablet debossed round tablet debossed round tablet debossed
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Guanfacine extended-release tablets are indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications [see Clinical Studies ( 14 )] . Guanfacine extended-release is a central alpha 2A -adrenergic receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications ( 1 , 14 ).
Dosage and Administration
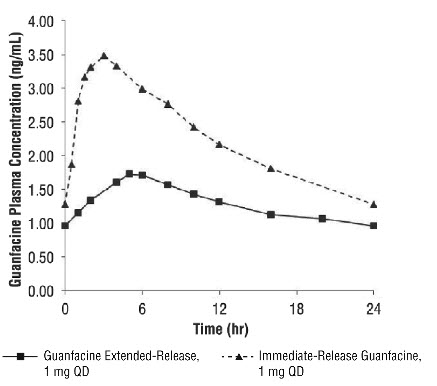
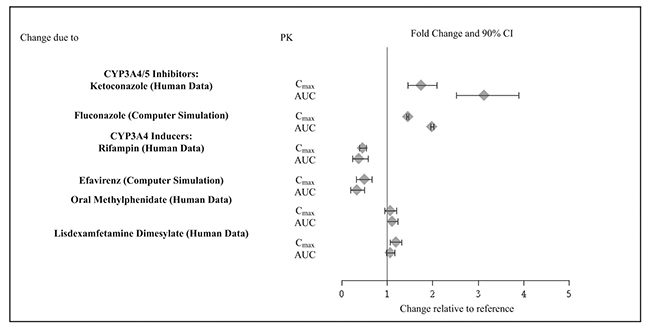
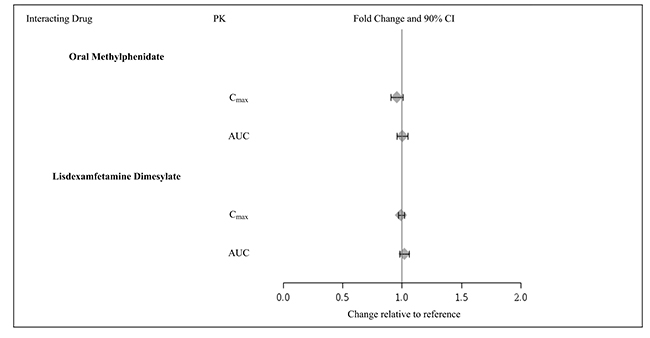
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Recommended dose: 1 mg to 7 mg (0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg target weight based dose range) once daily in the morning or evening based on clinical response and tolerability ( 2.2 ). Begin at a dose of 1 mg once daily and adjust in increments of no more than 1 mg/week ( 2.2 ). Do not crush, chew or break tablets before swallowing ( 2.1 ). Do not administer with high-fat meals, because of increased exposure ( 2.1 ). Do not substitute for immediate-release guanfacine tablets on a mg-per-mg basis, because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles ( 2.3 ). If switching from immediate-release guanfacine, discontinue that treatment and titrate with guanfacine extended-release as directed ( 2.3 ). When discontinuing, taper the dose in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days to avoid rebound hypertension ( 2.5 ). 2.1 General Instruction for Use Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, or break tablets because this will increase the rate of guanfacine release. Do not administer with high fat meals, due to increased exposure. 2.2 Dose Selection Take guanfacine extended-release tablets orally once daily, either in the morning or evening, at approximately the same time each day. Begin at a dose of 1 mg/day, and adjust in increments of no more than 1 mg/week. In monotherapy-clinical trials, there was dose- and exposure-related clinical improvement as well as risks for several clinically significant adverse reactions (hypotension, bradycardia, sedative events). To balance the exposure-related potential benefits and risks, the recommended target dose range depending on clinical response and tolerability for guanfacine extended-release is 0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg/day (total daily dose between 1 to 7 mg) (See Table 1). Table 1: Recommended Target Dose Range for Therapy with Guanfacine Extended-Release Weight Target dose range (0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg/day) 25 to 33.9 kg 2 to 3 mg/day 34 to 41.4 kg 2 to 4 mg/day 41.5 to 49.4 kg 3 to 5 mg/day 49.5 to 58.4 kg 3 to 6 mg/day 58.5 to 91 kg 4 to 7 mg/day >91 kg 5 to 7 mg/day Doses above 4 mg/day have not been evaluated in children (ages 6 to 12 years) and doses above 7 mg/day have not been evaluated in adolescents (ages 13 to 17 years) In the adjunctive trial which evaluated guanfacine extended-release treatment with psychostimulants, the majority of patients reached optimal doses in the 0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg/day range. Doses above 4 mg/day have not been studied in adjunctive trials. 2.3 Switching from Immediate-Release Guanfacine to Guanfacine E xtended- R elease If switching from immediate-release guanfacine, discontinue that treatment, and titrate with guanfacine extended-release following above recommended schedule. Do not substitute for immediate-release guanfacine tablets on a milligram-per-milligram basis, because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles. Guanfacine extended-release has significantly reduced C max (60% lower), bioavailability (43% lower), and a delayed T max (3 hours later) compared to those of the same dose of immediate-release guanfacine [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )]. 2.4 Maintenance Treatment Pharmacological treatment of ADHD may be needed for extended periods. Healthcare providers should periodically re-evaluate the long-term use of guanfacine extended-release, and adjust weight-based dosage as needed. The majority of children and adolescents reach optimal doses in the 0.05 to 0.12 mg/kg/day range. Doses above 4 mg/day have not been evaluated in children (ages 6 to 12 years) and above 7 mg/day have not been evaluated in adolescents (ages 13 to 17 years) [see Clinical Studies (14)] . 2.5 Discontinuation of Treatment Following discontinuation of guanfacine extended-release, patients may experience increases in blood pressure and heart rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reaction s (6) ] . Patients/caregivers should be instructed not to discontinue guanfacine extended-release without consulting their health care provider. Monitor blood pressure and pulse when reducing the dose or discontinuing the drug. Taper the daily dose in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days to minimize the risk of rebound hypertension. 2.6 Missed Doses When reinitiating patients to the previous maintenance dose after two or more missed consecutive doses, consider titration based on patient tolerability. 2.7 Dosage Adjustment with Concomitant Use of Strong and Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Inducers Dosage adjustments for guanfacine extended-release are recommended with concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole), or CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., carbamazepine) (Table 2) [see Drug Interactions ( 7 )]. Table 2: Guanfacine Extended-Release Dosage Adjustments for Patients Taking Concomitant CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Inducers Clinical Scenarios Starting guanfacine extended-release while currently on a CYP3A4 modulator Continuing guanfacine extended- release while adding a CYP3A4 modulator Continuing guanfacine extended-release while stopping a CYP3A4 modulator CYP3A4 Strong and M oderate Inhibitors Decrease guanfacine extended-release dosage to half the recommended level. (see Table 1) Decrease guanfacine extended-release dosage to half the recommended level. (see Table 1) Increase guanfacine extended-release dosage to recommended level. (see Table 1) CYP3A4 Strong and M oderate Inducers Consider increasing guanfacine extended- release dosage up to double the recommended level. (see Table 1) Consider increasing guanfacine extended-release dosage up to double the recommended level over 1 to 2 weeks. (see Table 1) Decrease guanfacine extended-release dosage to recommended level over 1 to 2 weeks. (see Table 1)
