Drug Catalog - Product Detail
GABAPENTIN 300MG CP 500CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69097-0943-12 | CIPLA USA | 500 | 300MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES






Generic Name
GABAPENTIN
Substance Name
GABAPENTIN
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA090705
Description
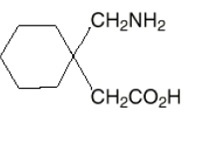
11 DESCRIPTION The active ingredient in gabapentin capsules is gabapentin, USP which has the chemical name 1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexane acetic acid. The molecular formula of gabapentin is C 9 H 17 NO 2 and the molecular weight is 171.24. The structural formula of gabapentin is: Gabapentin, USP is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a pK a1 of 3.7 and a pK a2 of 10.7. It is freely soluble in water and both basic and acidic aqueous solutions. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is –1.25. Gabapentin Capsules, USP are supplied as imprinted hard gelatin capsules containing 300 mg of gabapentin, USP. The inactive ingredients are mannitol, pre-gelatinized starch and talc. The 300 mg capsule contains FD&C Red 40, D&C Yellow 10 and titanium dioxide. image
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Gabapentin Capsules, USP are supplied as follows: 300 mg capsules: Hard Gelatin Capsules size “0” with Yellow Opaque Cap and Yellow Opaque Body imprinted with 300 mg and IG322, filled with White to Off-white powder; supplied in bottles of 30’s count (NDC 76420-020-30 repackaged from NDC 69097-943-12), 60’s count (NDC 76420-020-60 repackaged from NDC 69097-943-12), 90’s count (NDC 76420-020-90 repackaged from NDC 69097-943-12) and 240’s count (NDC 76420-020-24 repackaged from NDC 69097-943-12). Store at 20°C to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Gabapentin capsules are indicated for: Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy Gabapentin is indicated for: Postherpetic neuralgia in adults ( 1 ) Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in adults and pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Postherpetic Neuralgia ( 2.1 ) Dose can be titrated up as needed to a dose of 1,800 mg/day Day 1: Single 300 mg dose Day 2: 600 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg two times a day) Day 3: 900 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg three times a day) Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures ( 2.2 ) Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily Patients 3 to 11 years of age: starting dose range is 10 to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses; recommended dose in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses; the recommended dose in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended dose is reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days Dose should be adjusted in patients with reduced renal function ( 2.3 , 2.4 ) 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1,800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range of doses from 1,800 mg/day to 3,600 mg/day with comparable effects across the dose range; however, in these clinical studies, the additional benefit of using doses greater than 1,800 mg/day was not demonstrated. 2.2 Dosage for Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures Patients 12 years of age and above The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin Capsules is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2,400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3,600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. Administer gabapentin capsules three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. Pediatric Patients Age 3 to 11 years The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. The maximum time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): The use of gabapentin in patients less than 12 years of age with compromised renal function has not been studied. image 2.4 Dosage in Elderly Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and dose should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance values in these patients. 2.5 Administration Information Administer gabapentin orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with water. If the gabapentin dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week (a longer period may be needed at the discretion of the prescriber).
