Drug Catalog - Product Detail
FENOFIBRATE TABS. TB 120MG 90
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00378-4391-77 | MYLAN | 90 | 120MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
FENOFIBRATE
Substance Name
FENOFIBRATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA204475
Description
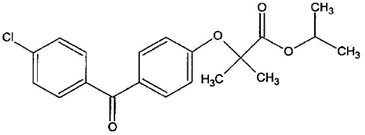
11 DESCRIPTION Fenofibrate tablets, USP are a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha agonist available as tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 40 mg or 120 mg of fenofibrate. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-4-chlorobenzoylphenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid 1-methylethyl ester with the following structural formula: The empirical formula is C 20 H 21 ClO 4 and the molecular weight is 360.83; fenofibrate is insoluble in water. The melting point is 79° to 82°C. Fenofibrate, USP is a white or almost white crystalline powder which is stable under ordinary conditions. Inactive Ingredients: Each tablet contains colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, povidone, pregelatinized starch (corn), silicified microcrystalline cellulose and vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate. Meets USP Dissolution Test 3. fenofibrate structural formula
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Fenofibrate Tablets, USP are available containing 40 mg or 120 mg of fenofibrate, USP. The 40 mg tablets are white, capsule shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and FT1 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4390-77 bottles of 90 tablets The 120 mg tablets are white, capsule shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and FT2 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4391-77 bottles of 90 tablets Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Fenofibrate tablets are indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet: • to reduce triglyceride (TG) levels in adults with severe hypertriglyceridemia (TG greater than or equal to 500 mg/dL). • to reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia when use of recommended LDL-C lowering therapy is not possible. Limitations of Use • Markedly elevated levels of serum TG (e.g., > 2,000 mg/dL) may increase the risk of developing pancreatitis. The effect of fenofibrate therapy on reducing this risk has not been determined [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] . • Fenofibrate did not reduce coronary heart disease morbidity and mortality in two large, randomized controlled trials of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . Fenofibrate tablets are a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha agonist indicated as an adjunct to diet: • to reduce triglyceride (TG) levels in adults with severe hypertriglyceridemia (TG greater than or equal to 500 mg/dL). ( 1 ) • to reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia when use of recommended LDL-C lowering therapy is not possible. ( 1 ) Limitations of Use: • Markedly elevated levels of serum TG (e.g., > 2,000 mg/dL) may increase the risk of developing pancreatitis. The effect of fenofibrate therapy on reducing this risk has not been determined. ( 1 ) • Fenofibrate did not reduce coronary heart disease morbidity and mortality in two large, randomized controlled trials of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. ( 1 )
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION • Severe hypertriglyceridemia: 40 mg to 120 mg orally once daily; the dosage should be adjusted according to patient response. ( 2.2 ) • Primary hyperlipidemia: 120 mg orally once daily ( 2.2 ) • Administer as a single dose, at any time of day, with food. ( 2.2 ) • Assess TG when clinically appropriate, as early as 4 to 8 weeks after initiating FIBRICOR ® . Discontinue fenofibrate tablets in patients who do not have an adequate response after 2 months of treatment. ( 2.2 ) • Renal impairment: Initial dosage of 40 mg orally once daily ( 2.3 ) • Geriatric patients: Select the dosage on the basis of renal function. ( 2.4 ) 2.1 Prior to Initiation of Fenofibrate Tablets • Assess lipid levels before initiating therapy. Identify other causes (e.g., diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, or medications) of high TG levels and manage as appropriate. • Patients should be placed on an appropriate lipid-lowering diet before receiving fenofibrate tablets and should continue this diet during treatment with fenofibrate tablets. • In patients with diabetes and fasting chylomicronemia, improve glycemic control prior to considering starting fenofibrate tablets. 2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration Severe hypertriglyceridemia: o The recommended dosage of fenofibrate tablets is 40 mg or 120 mg orally once daily. o Dosage should be individualized according to patient response and should be adjusted if necessary following repeat lipid determinations at 4 to 8 week intervals. • Primary hyperlipidemia: o The recommended dosage of fenofibrate tablets is 120 mg orally once daily. • Administer fenofibrate tablets as a single dose at any time of day, with food. • Advise patients to swallow fenofibrate tablets whole. Do not crush, break, dissolve, or chew tablets. • Assess TG when clinically appropriate, as early as 4 to 8 weeks after initiating fenofibrate tablets. Discontinue fenofibrate tablets in patients who do not have an adequate response after 2 months of treatment. • If a dose is missed, advise patients not to take an extra dose. Resume treatment with the next dose. • Advise patients to take fenofibrate tablets at least 1 hour before or 4 hours to 6 hours after a bile acid binding resin to avoid impeding its absorption. 2.3 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment Assess renal function prior to initiation of fenofibrate tablets and periodically thereafter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] . • Treatment with fenofibrate tablets should be initiated at a dosage of 40 mg orally once daily in patients with mild to moderately impaired renal function (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) and increased only after evaluation of the effects on renal function and TG levels at this dosage. • Fenofibrate tablets are contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m 2 ), including those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and those receiving dialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . 2.4 Recommended Dosage in Geriatric Patients Dosage selection for geriatric patients should be made on the basis of renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
