Drug Catalog - Product Detail
FENOFIBRATE 200MG CAP 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69097-0896-07 | CIPLA USA | 100 | 200MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
FENOFIBRATE
Substance Name
FENOFIBRATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA207378
Description
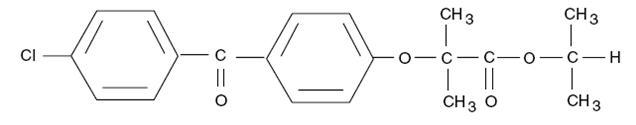
DESCRIPTION Fenofibrate capsules, USP (micronized) are a lipid regulating agent available as capsules for oral administration. The chemical name for fenofibrate is 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl) phenoxy]-2- methylpropanoic acid, 1-methylethyl ester with the following structural formula: The molecular formula is C 20 H 21 O 4 Cl and the molecular weight is 360.83; fenofibrate is insoluble in water. The melting point is 79° to 82°C. Fenofibrate, USP is a white solid which is stable under ordinary conditions. Each 67 mg fenofibrate capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, crospovidone, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, FD&C Blue No.1, FD&C Red No.3, D&C Yellow No.10, titanium dioxide and gelatin. Each 134 mg fenofibrate capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, crospovidone, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, FD&C Blue No.1, D&C Red No.28, titanium dioxide and gelatin. Each 200 mg fenofibrate capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, crospovidone, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, FD&C Blue No.1, FD&C Red No.40, FD&C Yellow No.6, titanium dioxide and gelatin. The imprinting ink contains shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, strong ammonia solution, black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide and purified water. USP dissolution test is pending. Fenofibrate Structural Formula
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Fenofibrate capsules, USP (micronized), 67 mg are hard gelatin capsule shells with pink opaque cap and pink opaque body imprinted IG and 470 with black ink. They are supplied as follows: NDC 69097-894-02 Bottles of 30 capsules NDC 69097-894-07 Bottles of 100 capsules NDC 69097-894-15 Bottles of 1,000 capsules Fenofibrate capsules, USP (micronized), 134 mg are hard gelatin capsule shells with blue opaque cap and blue opaque body imprinted IG and 471 with black ink. They are supplied as follows: NDC 69097-895-02 Bottles of 30 capsules NDC 69097-895-07 Bottles of 100 capsules NDC 69097-895-12 Bottles of 500 capsules Fenofibrate capsules, USP (micronized), 200 mg are hard gelatin capsule shells with orange opaque cap and orange opaque body imprinted IG and 472 with black ink. They are supplied as follows: NDC 69097-896-02 Bottles of 30 capsules NDC 69097-896-07 Bottles of 100 capsules NDC 69097-896-12 Bottles of 500 capsules STORAGE Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep out of the reach of children. Protect from moisture.
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia Fenofibrate capsules, USP are indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet for the reduction of LDLC, total-C, Triglycerides and apo B in adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Types IIa and IIb). Lipid altering agents should be used in addition to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol when response to diet and non-pharmacological interventions alone has been inadequate (see National Cholesterol Education Program [NCEP] Treatment Guidelines , below). Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia Fenofibrate capsules, USP are also indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet for treatment of adult patients with hypertriglyceridemia (Fredrickson Types IV and V hyperlipidemia). Improving glycemic control in diabetic patients showing fasting chylomicronemia will usually reduce fasting triglycerides and eliminate chylomicronemia thereby obviating the need for pharmacologic intervention. Markedly elevated levels of serum triglycerides (e.g. > 2,000 mg/dL) may increase the risk of developing pancreatitis. The effect of fenofibrate therapy on reducing this risk has not been adequately studied. Drug therapy is not indicated for patients with Type I hyperlipoproteinemia, who have elevations of chylomicrons and plasma triglycerides, but who have normal levels of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL). Inspection of plasma refrigerated for 14 hours is helpful in distinguishing Types I, IV and V hyperlipoproteinemia 2 . The initial treatment for dyslipidemia is dietary therapy specific for the type of lipoprotein abnormality. Excess body weight and excess alcoholic intake may be important factors in hypertriglyceridemia and should be addressed prior to any drug therapy. Physical exercise can be an important ancillary measure. Diseases contributory to hyperlipidemia, such as hypothyroidism or diabetes mellitus should be looked for and adequately treated. Estrogen therapy, like thiazide diuretics and beta-blockers, is sometimes associated with massive rises in plasma triglycerides, especially in subjects with familial hypertriglyceridemia. In such cases, discontinuation of the specific etiologic agent may obviate the need for specific drug therapy of hypertriglyceridemia. The use of drugs should be considered only when reasonable attempts have been made to obtain satisfactory results with non-drug methods. If the decision is made to use drugs, the patient should be instructed that this does not reduce the importance of adhering to diet (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS ). Fredrickson Classification of Hyperlipoproteinemias C = cholesterol TG = triglycerides LDL = low density lipoprotein VLDL = very lot density lipoprotein IDL = intermediate density lipoprotein Lipid Elevation Type Lipoprotein Elevated Major Minor I (rare) IIa IIb III (rare) IV V (rare) Chylomicrons LDL LDL, VLDL IDL VLDL Chylomicrons, VLDL TG C C C, TG TG TG ↑ ↔ C - TG - ↑ ↔ C ↑ ↔ The NCEP Treatment Guidelines Definite Atherosclerotic Two or More Other LDL-Cholesterol mg/dL (mmol/L) Disease Coronary heart disease or peripheral vascular disease (including symptomatic carotid artery disease). Risk Factors Other risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) include: age (males: ≥ 45 years; females: ≥ 55 years or premature menopause without estrogen replacement therapy); family history of premature CHD; current cigarette smoking; hypertension; confirmed HDL-C < 35 mg/dL (< 0.91 mmol/L); and diabetes mellitus. Subtract I risk favor if HDL-C is ≥ 60 mg/dL (≥ 1.6 mmol/L) Initiation Level Goal No No Yes No Yes Yes or No ≥ 190 (≥ 4.9) ≥ 160 (≥ 4.1) ≥ 130 In CHD patients with LDL-C levels 100 to 129 mg/dL, the physician should exercise clinical judgment in deciding whether to initiate drug treatment. (≥ 3.4) < 160 (< 4.1) < 130 (< 3.4) < 100 (< 2.6)
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Patients should be placed on an appropriate lipid-lowering diet before receiving fenofibrate capsules, and should continue this diet during treatment with fenofibrate capsules. Fenofibrate capsules should be given with meals, thereby optimizing the bioavailability of the medication. For the treatment of adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed hyperlipidemia, the initial dose of fenofibrate capsules is 200 mg per day. For adult patients with hypertriglyceridemia, the initial dose is 67 to 200 mg per day. Dosage should be individualized according to patient response, and should be adjusted if necessary following repeat lipid determinations at 4 to 8 week intervals. The maximum dose is 200 mg per day. Treatment with fenofibrate capsules should be initiated at a dose of 67 mg/day in patients having impaired renal function, and increased only after evaluation of the effects on renal function and lipid levels at this dose. In the elderly, the initial dose should likewise be limited to 67 mg/day. Lipid levels should be monitored periodically and consideration should be given to reducing the dosage of fenofibrate capsules if lipid levels fall significantly below the targeted range.
