Drug Catalog - Product Detail
DICLOFENAC DR 50MG TABLETS 1000
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00228-2550-96 | ACTAVIS PHARMA | 1000 | 50MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
Substance Name
Product Type
Route
Application Number
Description
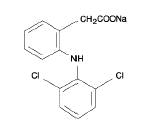
DESCRIPTION Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are a benzeneacetic acid derivative. The chemical name is 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt. The molecular weight is 318.13. Its molecular formula is C 14 H 10 C l2 NNaO 2 , and it has the following structural formula Each enteric-coated tablet for oral administration contains 50 mg or 75 mg of diclofenac sodium. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: aluminum hydrate, colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, polyvinyl acetate phthalate, propylene glycol, silica, sodium alginate, sodium starch glycolate (Type A), stearic acid, synthetic black iron oxide, talc, and titanium dioxide.
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Repackaged by Aphena Pharma Solutions - TN. See Repackaging Information for available configurations. Diclofenac Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets, USP are available as follows: 50 mg — Each white, round, enteric-coated tablet printed with on one side and 550 on the other side with black ink contains 50 mg of Diclofenac Sodium, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 60 (NDC 0228-2550-06), 100 (NDC 0228-2550-11) and 1000 (NDC 0228-2550-96). 75 mg — Each white, round, enteric-coated tablet printed with on one side and 551 on the other side with black ink contains 75 mg of Diclofenac Sodium, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 60 (NDC 0228-2551-06), 100 (NDC 0228-2551-11), and 1000 (NDC 0228-2551-96). Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Protect from moisture. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP. Manufactured by: Actavis Elizabeth LLC 200 Elmora Avenue, Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USA 40-8780 Revised — March 2011 Medication Guide for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) (See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.) What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Non- Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? NSAID medicines may increase the chance of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This chance increases: with longer use of NSAID medicines in people who have heart disease NSAID medicines should never be used right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).” NSAID medicines can cause ulcers and bleeding in the stomach and intestines at any time during treatment. Ulcers and bleeding: can happen without warning symptoms may cause death The chance of a person getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with: taking medicines called “corticosteroids” and “anticoagulants” longer use smoking drinking alcohol older age having poor health NSAID medicines should only be used: exactly as prescribed at the lowest dose possible for your treatment for the shortest time needed What are Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? NSAID medicines are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as: different types of arthritis menstrual cramps and other types of short-term pain Who should not take a Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)? Do not take an NSAID medicine: if you had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAID medicine for pain right before or after heart bypass surgery Tell your healthcare provider: about all your medical conditions. about all of the medicines you take. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Keep a list of your medicines to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist. if you are pregnant. NSAID medicines should not be used by pregnant women late in their pregnancy. if you are breastfeeding. Talk to your doctor. What are the possible side effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? Serious side effects include: Other side effects include: • heart attack • stomach pain • stroke • constipation • high blood pressure • diarrhea • heart failure from body swelling (fluid retention) • gas • kidney problems including kidney failure • heartburn • bleeding and ulcers in the stomach and intestine • nausea • low red blood cells (anemia) • vomiting • life-threatening skin reactions • life-threatening allergic reactions Continued on reverse side Continued Serious side effects include: Other side effects include: • liver problems including liver failure • dizziness • asthma attacks in people who have asthma Get emergency help right away if you have any of the following symptoms: • shortness of breath or trouble breathing • slurred speech • chest pain • swelling of the face • weakness in one part or side of your body • or throat Stop your NSAID medicine and call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms: • nausea •there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar • more tired or weaker than usual • itching •unusual weight gain • your skin or eyes look yellow • skin rash or blisters with fever • stomach pain • swelling of the arms and legs, hands and feet • flu-like symptoms • vomit blood These are not all the side effects with NSAID medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about NSAID medicines. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. Other information about Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Aspirin is an NSAID medicine but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines. Some of these NSAID medicines are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days. NSAID medicines that need a prescription Generic Name Tradename * Vicoprofen contains the same dose of ibuprofen as over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs, and is usually used for less than 10 days to treat pain. The OTC NSAID label warns that long term continuous use may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Celecoxib Celebrex Diclofenac Cataflam, Voltaren, Arthrotec (combined with misoprostol) Diflunisal Dolobid Etodolac Lodine, Lodine XL Fenoprofen Nalfon, Nalfon 200 Flurbirofen Ansaid Ibuprofen Motrin, Tab-Profen, Vicoprofen (combined with hydrocodone), Combunox (combined with oxycodone) Indomethacin Indocin, Indocin SR, Indo-Lemmon, Indomethagan Ketoprofen Oruvail Ketorolac Toradol Mefenamic Acid Ponstel Meloxicam Mobic Nabumetone Relafen Naproxen Naprosyn, Anaprox, Anaprox DS, EC-Naproxyn, Naprelan, Naprapac (copackaged with lansoprazole) Oxaprozin Daypro Piroxicam Feldene Sulindac Clinoril Tolmetin Tolectin, Tolectin DS, Tolectin 600
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac sodium delayed-release. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ). Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are indicated: • For relief of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis • For relief of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis • For acute or long-term use in the relief of signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac sodium delayed-release. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS ). After observing the response to initial therapy with diclofenac sodium delayed-release, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient’s needs. For the relief of osteoarthritis, the recommended dosage is 100-150 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg b.i.d. or t.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.). For the relief of rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended dosage is 150-200 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.). For the relief of ankylosing spondylitis, the recommended dosage is 100-125 mg/day, administered as 25 mg q.i.d., with an extra 25-mg dose at bedtime if necessary. Different formulations of diclofenac (diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets; diclofenac sodium extended-release tablets; diclofenac potassium immediate-release tablets) are not necessarily bioequivalent even if the milligram strength is the same.
