Drug Catalog - Product Detail
DEFERASIROX TABLETS FOR ORAL SUSP 125MG
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45963-0454-30 | ACTAVIS | 30 | 125MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES


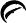

Generic Name
DEFERASIROX
Substance Name
DEFERASIROX
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA203560
Description
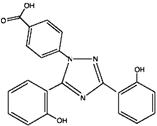
11 DESCRIPTION Deferasirox is an iron chelating agent. Deferasirox Tablets For Oral Suspension contain 125 mg, 250 mg, or 500 mg of deferasirox. Deferasirox is designated chemically as 4-[3,5-Bis (2-hydroxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-benzoic acid and its structural formula is: C 21 H 15 N 3 O 4 M.W. 373.4 Deferasirox is an off-white to pale yellow powder. Inactive Ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone and sodium lauryl sulfate. 9c6b4e1d-figure-04
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Deferasirox is provided as 125 mg, 250 mg, and 500 mg tablets for oral suspension. 125 mg – White to off-white, round, unscored tablets, debossed with and 454 on one side and plain on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 45963-454-30) with a child-resistant closure. 250 mg – White to off-white, round, unscored tablets, debossed with and 455 on one side and plain on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 45963-455-30) with a child-resistant closure. 500 mg – White to off-white, round, unscored tablets, debossed with and 456 on one side and plain on the other side. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 45963-456-30) with a child-resistant closure. Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted to 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP. Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children. 9c6b4e1d-figure-06 9c6b4e1d-figure-07 9c6b4e1d-figure-08
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Deferasirox tablets for oral suspension are an iron chelator indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions in patients 2 years of age and older. ( 1.1 ) Deferasirox tablets for oral suspension are indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload in patients 10 years of age and older with non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia (NTDT) syndromes, and with a liver iron (Fe) concentration (LIC) of at least 5 mg Fe per gram of dry weight and a serum ferritin greater than 300 mcg/L. ( 1.2 ) L imitations of Use: The safety and efficacy of deferasirox when administered with other iron chelation therapy have not been established. ( 1.3 ) 1.1 Treatment of Chronic Iron Overload Due to Blood Transfusions (Transfusional Iron Overload) Deferasirox tablets for oral suspension are indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions (transfusional hemosiderosis) in patients 2 years of age and older. 1.2 Treatment of Chronic Iron Overload in Non-Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Syndromes Deferasirox tablets for oral suspension are indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload in patients 10 years of age and older with non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia (NTDT) syndromes and with a liver iron concentration (LIC) of at least 5 milligrams of iron per gram of liver dry weight (mg Fe/g dw) and a serum ferritin greater than 300 mcg/L. 1.3 Limitations of Use The safety and efficacy of deferasirox when administered with other iron chelation therapy have not been established.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Transfusional Iron Overload: Initial dose for patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) greater than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 is 20 mg per kg body weight once daily, as oral suspension. Calculate dose to the nearest whole tablet. ( 2.1 ) NTDT Syndromes: Initial dose for patients with eGFR greater than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 is 10 mg per kg body weight once daily, as oral suspension. Calculate dose to the nearest whole tablet. ( 2.2 ) 2.1 Transfusional Iron Overload Deferasirox therapy should only be considered when a patient has evidence of chronic transfusional iron overload. The evidence should include the transfusion of at least 100 mL/kg of packed red blood cells (e.g., at least 20 units of packed red blood cells for a 40 kg person or more in individuals weighing more than 40 kg), and a serum ferritin consistently greater than 1,000 mcg/L. Prior to starting therapy or increasing dose, evaluate: Serum ferritin level Baseline renal function: Obtain serum creatinine in duplicate (due to variations in measurements) to establish accurate baseline Calculate the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Use a prediction equation appropriate for adult patients (e.g., CKD-EPI, MDRD method) and in pediatric patients (e.g., Schwartz equations). Obtain urinalyses and serum electrolytes to evaluate renal tubular function [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )]. Serum transaminases and bilirubin [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2 )] Baseline auditory and ophthalmic examinations [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10 )] Initiating Therapy: The recommended initial dose of deferasirox for patients 2 years of age and older with eGFR greater than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 is 20 mg per kg body weight orally, once daily. Calculate doses (mg per kg per day) to the nearest whole tablet. During Therapy: Monitor serum ferritin monthly and adjust the dose of deferasirox, if necessary, every 3 to 6 months based on serum ferritin trends. Use the minimum effective dose to achieve a trend of decreasing ferritin. Make dose adjustments in steps of 5 or 10 mg per kg and tailor adjustments to the individual patient’s response and therapeutic goals. In patients not adequately controlled with doses of 30 mg per kg (e.g., serum ferritin levels persistently above 2,500 mcg/L and not showing a decreasing trend over time), doses of up to 40 mg per kg may be considered. Doses above 40 mg per kg are not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] . Adjust dose based on serum ferritin levels If the serum ferritin falls below 1,000 mcg/L at 2 consecutive visits, consider dose reduction, especially if the dose is greater than 25 mg/kg/day [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 )] . If the serum ferritin falls below 500 mcg/L, interrupt deferasirox to minimize the risk of overchelation, and continue monthly monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] . Evaluate the need for ongoing chelation therapy for patients whose conditions no longer require regular blood transfusions. Use the minimum effective dose to maintain iron burden in the target range [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] . Monitor blood counts, liver function, renal function and ferritin monthly [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.2 , 5.4 )] . Interrupt deferasirox for pediatric patients who have acute illnesses, which can cause volume depletion, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or prolonged decreased oral intake, and monitor more frequently. Resume therapy as appropriate, based on assessments of renal function, when oral intake and volume status are normal [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4, 2.5 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] . 2.2 Iron Overload in Non-Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Syndromes Deferasirox therapy should only be considered when a patient with NTDT syndrome has an LIC of at least 5 mg Fe/g dw and a serum ferritin greater than 300 mcg/L. Prior to starting therapy, obtain: LIC by liver biopsy or by an FDA-cleared or approved method for identifying patients for treatment with deferasirox therapy Serum ferritin level on at least 2 measurements 1-month apart [see Clinical Studies ( 14 )] Baseline renal function: Obtain serum creatinine in duplicate (due to variations in measurements) to establish accurate baseline Calculate eGFR. Use a prediction equation appropriate for adult patients (e.g., CKD-EPI, MDRD method) and in pediatric patients (e.g., Schwartz equations). Obtain urinalyses and serum electrolytes to evaluate renal tubular function [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )]. Serum transaminases and bilirubin [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2 )] Baseline auditory and ophthalmic examinations [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10 )] Initiating Therapy: The recommended initial dose of deferasirox for patients with eGFR greater than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 is 10 mg per kg body weight orally once daily. Calculate doses (mg per kg per day) to the nearest whole tablet. If the baseline LIC is greater than 15 mg Fe/g dw, consider increasing the dose to 20 mg/kg/day after 4 weeks. During Therapy: Monitor serum ferritin monthly to assess the patient’s response to therapy and to minimize the risk of overchelation [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6 )] . Interrupt treatment when serum ferritin is less than 300 mcg/L and obtain an LIC to determine whether the LIC has fallen to less than 3 mg Fe/g dw. Use the minimum effective dose to achieve a trend of decreasing ferritin. Monitor LIC every 6 months. After 6 months of therapy, if the LIC remains greater than 7 mg Fe/g dw, increase the dose of deferasirox to a maximum of 20 mg/kg/day. Do not exceed a maximum of 20 mg/kg/day. If after 6 months of therapy, the LIC is 3 to 7 mg Fe/g dw, continue treatment with deferasirox at no more than 10 mg/kg/day. When the LIC is less than 3 mg Fe/g dw, interrupt treatment with deferasirox and continue to monitor the LIC. Monitor blood counts, liver function, renal function and ferritin monthly [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 , 5.2 , 5.4 )] . Increase monitoring frequency for pediatric patients who have acute illness, which can cause volume depletion, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or prolonged decreased oral intake. Consider dose interruption until oral intake and volume status are normal [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.4 , 2.5 ), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )] . Restart treatment when the LIC rises again to more than 5 mg Fe/g dw. 2.3 Administration Do not chew tablets or swallow them whole. Take deferasirox once daily on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before food, preferably at the same time each day. Completely disperse tablets by stirring in water, orange juice, or apple juice until a fine suspension is obtained. Disperse doses of less than 1 g in 3.5 ounces of liquid and doses of 1 g or greater in 7 ounces of liquid. After swallowing the suspension, resuspend any residue in a small volume of liquid and swallow. Do not take deferasirox with aluminum-containing antacid products [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . 2.4 Use in Patients with Baseline Hepatic or Renal Impairment Patients with Baseline Hepatic Impairment Mild (Child-Pugh A) Hepatic Impairment: No dose adjustment is necessary. Moderate (Child-Pugh B) Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the starting dose by 50%. Severe (Child-Pugh C) Hepatic Impairment: Avoid deferasirox [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) , Use in Specific Populations ( 8.7 )] . Patients with Baseline Renal Impairment Do not use deferasirox in adult or pediatric patients with eGFR less than 40 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.5 ), Contraindications ( 4 )] . For patients with renal impairment (eGFR 40 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), reduce the starting dose by 50% [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6 )] . Exercise caution in pediatric patients with eGFR between 40 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . If treatment is needed, use the minimum effective dose and monitor renal function frequently. Individualize dose titration based on improvement in renal injury [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.6 )] . 2.5 Dose Modifications for Decreases in Renal Function While on Deferasirox Deferasirox is contraindicated in patients with eGFR less than 40 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Contraindications ( 4 )]. For decreases in renal function while receiving deferasirox [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )], modify the dose as follows: Transfusional Iron Overload Adults: If the serum creatinine increases by 33% or more above the average baseline measurement, repeat the serum creatinine within 1 week, and if still elevated by 33% or more, reduce the dose by 10 mg per kg. Pediatric Patients (ages 2 years to 17 years): Reduce the dose by 10 mg/kg/day if eGFR decreases by greater than 33% below the average baseline measurement and repeat the eGFR within 1 week. Interrupt deferasirox for acute illnesses, which can cause volume depletion, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or prolonged decreased oral intake, and monitor more frequently. Resume therapy as appropriate, based on assessments of renal function, when oral intake and volume status are normal. Avoid use of other nephrotoxic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . In the setting of decreased renal function, evaluate the risk benefit profile of continued deferasirox use. Use the minimum effective deferasirox dose and monitor renal function more frequently, by evaluating tubular and glomerular function. Titrate dosing based on renal injury. Consider dose reduction or interruption and less nephrotoxic therapies until improvement of renal function. If signs of renal tubular or glomerular injury occur in the presence of other risk factors such as volume depletion, reduce or interrupt deferasirox to prevent severe and irreversible renal injury [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . All Patients (regardless of age): Discontinue therapy for eGFR less than 40 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Contraindications ( 4 )]. Non-Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Syndromes Adults: If the serum creatinine increases by 33% or more above the average baseline measurement, repeat the serum creatinine within 1 week, and if still elevated by 33% or more, interrupt therapy if the dose is 5 mg per kg, or reduce by 50% if the dose is 10 or 20 mg per kg. Pediatric Patients (ages 10 years to 17 years): Reduce the dose by 5 mg/kg/day if eGFR decreases by greater than 33% below the average baseline measurement and repeat the eGFR within 1 week. Increase monitoring frequency for pediatric patients who have acute illnesses, which can cause volume depletion, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or prolonged decreased oral intake. Consider dose interruption until oral intake and volume status are normal. Avoid use of other nephrotoxic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )]. In the setting of decreased renal function, evaluate the risk benefit profile of continued deferasirox use. Use the minimum effective deferasirox dose and monitor renal function more frequently, by evaluating tubular and glomerular function. Titrate dosing based on renal injury. Consider dose reduction or interruption and less nephrotoxic therapies until improvement of renal function. If signs of renal tubular or glomerular injury occur in the presence of other risk factors such as volume depletion, reduce or interrupt deferasirox to prevent severe and irreversible renal injury [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 )] . All Patients (regardless of age): Discontinue therapy for eGFR less than 40 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Contraindications ( 4 )] . 2.6 Dose Modifications Based on Concomitant Medications UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) Inducers Concomitant use of UGT inducers decreases deferasirox systemic exposure. Avoid the concomitant use of potent UGT inducers (e.g., rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ritonavir) with deferasirox. If you must administer deferasirox with 1 of these agents, consider increasing the initial dose of deferasirox by 50%, and monitor serum ferritin levels and clinical responses for further dose modification [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1 , 2.2 ), Drug Interactions ( 7.5 )] . Bile Acid Sequestrants Concomitant use of bile acid sequestrants decreases deferasirox systemic exposure. Avoid the concomitant use of bile acid sequestrants (e.g., cholestyramine, colesevelam, colestipol) with deferasirox. If you must administer deferasirox with 1 of these agents, consider increasing the initial dose of deferasirox by 50%, and monitor serum ferritin levels and clinical responses for further dose modification [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1 , 2.2) , Drug Interactions ( 7.6 )] .
