Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CLOMIPRAMINE HCL CAPS 50MG 100CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00406-8807-01 | MALLINCKRODT PHARM | 100 | 50MG | CAPSULE |
PACKAGE FILES


Generic Name
CLOMIPRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Substance Name
CLOMIPRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
NDA019906
Description
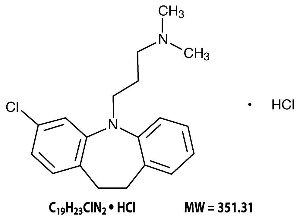
DESCRIPTION Clomipramine Hydrochloride Capsules USP are an antiobsessional drug that belongs to the class (dibenzazepine) of pharmacologic agents known as tricyclic antidepressants. Clomipramine hydrochloride capsules are available as capsules of 25, 50, and 75 mg for oral administration. Clomipramine hydrochloride USP is 3-chloro-5-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-10,11-dihydro-5 H -dibenz[ b , f ]azepine monohydrochloride, and its structural formula is: Clomipramine hydrochloride USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water, in methanol, and in methylene chloride, and insoluble in ethyl ether and in hexane. Inactive Ingredients . D&C Red No. 33 (25 mg capsules only), D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Blue No. 1 (50 mg capsules only), FD&C Yellow No. 6, gelatin, magnesium stearate, methylparaben, propylparaben, starch (corn), and titanium dioxide. Chemical Structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Clomipramine Hydrochloride Capsules USP Capsules 25 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with “ ” and melon-yellow cap imprinted in black with “25 mg” Bottles of 100................................... NDC 0406-8806-01 Capsules 50 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with “ ” and aqua blue cap imprinted in black with “50 mg” Bottles of 100................................... NDC 0406-8807-01 Capsules 75 mg – ivory body imprinted in black with “ ” and yellow cap imprinted in black with “75 mg” Bottles of 100................................... NDC 0406-8808-01 Storage – Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in well-closed containers with a child-resistant closure. Protect from moisture. Boxed M Boxed M Boxed M
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Clomipramine Hydrochloride Capsules USP are indicated for the treatment of obsessions and compulsions in patients with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). The obsessions or compulsions must cause marked distress, be time-consuming, or significantly interfere with social or occupational functioning, in order to meet the DSM-III-R (circa 1989) diagnosis of OCD. Obsessions are recurrent, persistent ideas, thoughts, images, or impulses that are ego-dystonic. Compulsions are repetitive, purposeful, and intentional behaviors performed in response to an obsession or in a stereotyped fashion, and are recognized by the person as excessive or unreasonable. The effectiveness of clomipramine hydrochloride capsules for the treatment of OCD was demonstrated in multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group studies, including two 10-week studies in adults and one 8-week study in children and adolescents 10 to 17 years of age. Patients in all studies had moderate-to-severe OCD (DSM-III), with mean baseline ratings on the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (YBOCS) ranging from 26 to 28 and a mean baseline rating of 10 on the NIMH Clinical Global Obsessive Compulsive Scale (NIMH-OC). Patients taking CMI experienced a mean reduction of approximately 10 on the YBOCS, representing an average improvement on this scale of 35% to 42% among adults and 37% among children and adolescents. CMI-treated patients experienced a 3.5 unit decrement on the NIMH-OC. Patients on placebo showed no important clinical response on either scale. The maximum dose was 250 mg/day for most adults and 3 mg/kg/day (up to 200 mg) for all children and adolescents. The effectiveness of clomipramine hydrochloride capsules for long-term use (i.e., for more than 10 weeks) has not been systematically evaluated in placebo-controlled trials. The physician who elects to use clomipramine hydrochloride capsules for extended periods should periodically reevaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient ( see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ).
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The treatment regimens described below are based on those used in controlled clinical trials of clomipramine hydrochloride capsules in 520 adults, and 91 children and adolescents with OCD. During initial titration, clomipramine hydrochloride capsules should be given in divided doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. The goal of this initial titration phase is to minimize side effects by permitting tolerance to side effects to develop or allowing the patient time to adapt if tolerance does not develop. Because both CMI and its active metabolite, DMI, have long elimination half-lives, the prescriber should take into consideration the fact that steady-state plasma levels may not be achieved until 2 to 3 weeks after dosage change ( see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ). Therefore, after initial titration, it may be appropriate to wait 2 to 3 weeks between further dosage adjustments. Initial Treatment/Dose Adjustment (Adults) Treatment with clomipramine hydrochloride capsules should be initiated at a dosage of 25 mg daily and gradually increased, as tolerated, to approximately 100 mg during the first 2 weeks. During initial titration, clomipramine hydrochloride capsules should be given in divided doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Thereafter, the dosage may be increased gradually over the next several weeks, up to a maximum of 250 mg daily. After titration, the total daily dose may be given once daily at bedtime to minimize daytime sedation. Initial Treatment/Dose Adjustment (Children and Adolescents) As with adults, the starting dose is 25 mg daily and should be gradually increased (also given in divided doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects) during the first 2 weeks, as tolerated, up to a daily maximum of 3 mg/kg or 100 mg, whichever is smaller. Thereafter, the dosage may be increased gradually over the next several weeks up to a daily maximum of 3 mg/kg or 200 mg, whichever is smaller ( see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use ). As with adults, after titration, the total daily dose may be given once daily at bedtime to minimize daytime sedation. Maintenance/Continuation Treatment (Adults, Children, and Adolescents) While there are no systematic studies that answer the question of how long to continue clomipramine hydrochloride capsules, OCD is a chronic condition and it is reasonable to consider continuation for a responding patient. Although the efficacy of clomipramine hydrochloride capsules after 10 weeks has not been documented in controlled trials, patients have been continued in therapy under double-blind conditions for up to 1 year without loss of benefit. However, dosage adjustments should be made to maintain the patient on the lowest effective dosage, and patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for treatment. During maintenance, the total daily dose may be given once daily at bedtime. Switching a Patient To or From a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of therapy with clomipramine hydrochloride capsules. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping clomipramine hydrochloride capsules before starting an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders ( see CONTRAINDICATIONS ). Use of Clomipramine Hydrochloride Capsules With Other MAOIs, Such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue Do not start clomipramine hydrochloride capsules in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, other interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered ( see CONTRAINDICATIONS ). In some cases, a patient already receiving clomipramine hydrochloride capsules therapy may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, clomipramine hydrochloride capsules should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for two weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with clomipramine hydrochloride capsules may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue ( see WARNINGS ). The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg/kg with clomipramine hydrochloride capsules is unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use ( see WARNINGS ).
