Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CIPROFLOXACIN TAB 500MG 500CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61442-0223-05 | CARLSBAD TECHNOLOGIES | 500 | 500MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE
Substance Name
CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA076126
Description
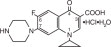
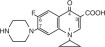
11 DESCRIPTION Ciprofloxacin (Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) Tablets are synthetic antimicrobial agents for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1, 4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. It is a faintly yellowish to light yellow crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 385.8. Its empirical formula is C 17 H 18 FN 3 O 3 •HCl•H 2 O and its chemical structure is as follows: Ciprofloxacin is 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. Its empirical formula is C 17 H 18 FN 3 O 3 and its molecular weight is 331.4. It is a faintly yellowish to light yellow crystalline substance and its chemical structure is as follows: Ciprofloxacin film-coated tablets are available in 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg (ciprofloxacin equivalent) strengths. Ciprofloxacin tablets are white to slightly yellowish. The inactive ingredients are Lactose Monohydrate, Magnesium Stearate, Sodium Starch Gylcolate, and Starch 1500 (Modified Corn Starch). Chemical Structure Chemical Structure
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP (white to off-white round tablets) containing 250 mg of Ciprofloxacin and engraved with “CTI 222” Bottle of 100.............................................................................(NDC 61442-222-01) Bottle of 1,000..........................................................................(NDC 61442-222-10) Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP (white to off-white capsule-shaped tablets) containing 500 mg of ciprofloxacin and engraved with “CTI 223” Bottle of 100.............................................................................(NDC 61442-223-01) Bottle of 500.............................................................................(NDC 61442-223-05) Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP (white to off-white capsule-shaped tablets) containing 750 mg of ciprofloxacin and engraved with “CTI 224” Bottle of 50...............................................................................(NDC 61442-224-50) Bottle of 100.............................................................................(NDC 61442-224-01) Bottle of 400.............................................................................(NDC 61442-224-04) Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Ciprofloxacin Tablets 250 mg, 500 mg, and 750 mg are a fluoroquinolone antibacterial indicated in adults (≥18 years of age) with the following infections caused by designated, susceptible bacteria and in pediatric patients where indicated: Skin and Skin Structure Infections ( 1.1 ) Bone and Joint Infections ( 1.2 ) Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections ( 1.3 ) Infectious Diarrhea ( 1.4 ) Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) ( 1.5 ) Uncomplicated Cervical and Urethral Gonorrhea ( 1.6 ) Inhalational Anthrax post-exposure in adult and pediatric patients ( 1.7 ) Plague in adult and pediatric patients ( 1.8 ) Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis ( 1.9 ) Lower Respiratory Tract Infections ( 1.10 ) Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis Urinary Tract Infections ( 1.11 ) Urinary Tract Infections (UTI) Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis Complicated UTI and Pyelonephritis in Pediatric Patients Acute Sinusitis ( 1.12 ) Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin and other antibacterial drugs, Ciprofloxacin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. ( 1.13 ) 1.1 Skin and Skin Structure Infections Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of skin and skin structure infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia stuartii, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Streptococcus pyogenes. 1.2 Bone and Joint Infections Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of bone and joint infections caused by Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 1.3 Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (used in combination with metronidazole) caused by Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Bacteroides fragilis. 1.4 Infectious Diarrhea Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of infectious diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic isolates), Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella boydii † , Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella flexneri or Shigella sonnei † when antibacterial therapy is indicated. † Although treatment of infections due to this organism in this organ system demonstrated a clinically significant outcome, efficacy was studied in fewer than 10 patients. 1.5 Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of typhoid fever (enteric fever ) caused by Salmonella typhi. The efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the eradication of the chronic typhoid carrier state has not been demonstrated. 1.6 Uncomplicated Cervical and Urethral Gonorrhea Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of uncomplicated cervical and urethral gonorrhea due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.16 )]. 1.7 Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure) Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adults and pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) to reduce the incidence or progression of disease following exposure to aerosolized Bacillus anthracis. Ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans served as a surrogate endpoint reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit and provided the initial basis for approval of this indication. 1 Supportive clinical information for ciprofloxacin for anthrax post-exposure prophylaxis was obtained during the anthrax bioterror attacks of October 2001 [see Clinical Studies ( 14.2 )]. 1.8 Plague Ciprofloxacin is indicated for treatment of plague, including pneumonic and septicemic plague, due to Yersinia pestis (Y. pestis) and prophylaxis for plague in adults and pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age. Efficacy studies of Ciprofloxacin could not be conducted in humans with plague for feasibility reasons. Therefore this indication is based on an efficacy study conducted in animals only [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3 )] . 1.9 Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis caused by Escherichia coli or Proteus mirabilis. 1.10 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of lower respiratory tract infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, or Streptococcus pneumoniae. Ciprofloxacin is not a drug of first choice in the treatment of presumed or confirmed pneumonia secondary to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Ciprofloxacin is indicated for the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (AECB) caused by Moraxella catarrhalis. Because fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin, have been associated with serious adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 – 5.15 )] and for some patients AECB is self-limiting, reserve Ciprofloxacin for treatment of AECB in patients who have no alternative treatment options. 1.11 Urinary Tract Infections Urinary Tract Infections in Adults Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli , Klebsiella pneumoniae , Enterobacter cloacae , Serratia marcescens , Proteus mirabilis , Providencia rettgeri , Morganella morganii , Citrobacter koseri , Citrobacter freundii , Pseudomonas aeruginosa , methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis , Staphylococcus saprophyticus , or Enterococcus faecalis . Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult female patients for treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis caused by Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Because fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin, have been associated with serious adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 - 5.15 )] and for some patients acute uncomplicated cystitis is self-limiting, reserve Ciprofloxacin for treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis in patients who have no alternative treatment options. Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis in Pediatric Patients Ciprofloxacin is indicated in pediatric patients aged one to 17 years of age for treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) and pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 )] . Although effective in clinical trials, Ciprofloxacin is not a drug of first choice in the pediatric population due to an increased incidence of adverse reactions compared to controls, including reactions related to joints and/or surrounding tissues. Ciprofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, is associated with arthropathy and histopathological changes in weight-bearing joints of juvenile animals [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.12 ), Adverse Reactions ( 6.1 ), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4 ) and Nonclinical Toxicology ( 13.2 )]. 1.12 Acute Sinusitis Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of acute sinusitis caused by or Ciprofloxacin is indicated in adult patients for treatment of acute sinusitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Moraxella catarrhalis. Because fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin, have been associated with serious adverse reactions and for some patients acute sinusitis is self-limiting, reserve Ciprofloxacin for treatment of acute sinusitis in patients who have no alternative treatment options. Because fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin, have been associated with serious adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 - 5.15 )] and for some patients acute sinusitis is self-limiting, reserve Ciprofloxacin for treatment of acute sinusitis in patients who have no alternative treatment options. 1.13 Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin and other antibacterial drugs, Ciprofloxacin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. If anaerobic organisms are suspected of contributing to the infection, appropriate therapy should be administered. Appropriate culture and susceptibility tests should be performed before treatment in order to isolate and identify organisms causing infection and to determine their susceptibility to Ciprofloxacin. Therapy with Ciprofloxacin may be initiated before results of these tests are known; once results become available appropriate therapy should be continued. As with other drugs, some isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa may develop resistance fairly rapidly during treatment with ciprofloxacin. Culture and susceptibility testing performed periodically during therapy will provide information not only on the therapeutic effect of the antimicrobial agent but also on the possible emergence of bacterial resistance.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Ciprofloxacin Tablets should be administered orally as described in the appropriate Dosage Guidelines tables. Adult Dosage Guidelines Infection Dose Frequency Duration Skin and Skin Structure 500 -750 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Bone and Joint 500-750 mg every 12 hours 4 to 8 weeks Complicated Intra-Abdominal 500 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Infectious Diarrhea 500 mg every 12 hours 5 to 7 days Typhoid Fever 500 mg every 12 hours 10 days Uncomplicated Gonorrhea 250 mg single dose single dose Inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) 500 mg every 12 hours 60 days Plague 500–750 mg every 12 hours 14 days Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis 500 mg every 12 hours 28 days Lower Respiratory Tract 500 -750 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Urinary Tract 250-500 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis 250 mg every 12 hours 3 days Acute Sinusitis 500 mg every 12 hours 10 days Adults with creatinine clearance 30–50 mL/min 250–500 mg q 12 h ( 2.3 ) Adults with creatinine clearance 5–29 mL/min 250–500 mg q 18 h ( 2.3 ) Patients on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis 250–500 mg q 24 h (after dialysis) ( 2.3 ) Pediatric Oral Dosage Guidelines Infection Dose Frequency Duration Complicated UTI and Pyelonephritis (1 to 17 years of age) 10–20 mg/kg (maximum 750 mg per dose) Every 12 hours 10–21 days Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure) 15 mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) Every 12 hours 60 days Plague 15mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) Every 8 to 12 hours 10–21 days 2.1 Dosage in Adults The determination of dosage and duration for any particular patient must take into consideration the severity and nature of the infection, the susceptibility of the causative microorganism, the integrity of the patient's host-defense mechanisms, and the status of renal and hepatic function. The determination of dosage and duration for any particular patient must take into consideration the severity and nature of the infection, the susceptibility of the causative microorganism, the integrity of the patient's host-defense mechanisms, and the status of renal and hepatic function. Table 1: Adult Dosage Guidelines 1. Generally ciprofloxacin should be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared, except for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure). 1. Generally ciprofloxacin should be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection have disappeared, except for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure). 2. Used in conjunction with metronidazole. 2. Used in conjunction with metronidazole. 3. Begin drug administration as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure. 3. Begin drug administration as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure. Infection Dose Frequency Usual Durations 1 Skin and Skin Structure 500–750 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Bone and Joint 500–750 mg every 12 hours 4 to 8 weeks Complicated Intra–Abdominal 2 500 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Infectious Diarrhea 500 mg every 12 hours 5 to 7 days Typhoid Fever 500 mg every 12 hours 10 days Uncomplicated Urethral and Cervical Gonococcal Infections 250 mg single dose single dose Inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) 3 500 mg every 12 hours 60 days Plague 3 500–750 mg every 12 hours 14 days Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis 500 mg every 12 hours 28 days Lower Respiratory Tract Infections 500–750 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Urinary Tract Infections 250–500 mg every 12 hours 7 to 14 days Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis 250 mg every 12 hours 3 days Acute Sinusitis 500 mg every 12 hours 10 days Conversion of IV to Oral Dosing in Adults Patients whose therapy is started with Ciprofloxacin IV may be switched to Ciprofloxacin Tablets or Oral Suspension when clinically indicated at the discretion of the physician ( Table 2 ) [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )]. Table 2: Equivalent AUC Dosing Regimens Ciprofloxacin Oral Dosage Equivalent Ciprofloxacin IV Dosage 250 mg Tablet every 12 hours 200 mg intravenous every 12 hours 500 mg Tablet every 12 hours 400 mg intravenous every 12 hours 750 mg Tablet every 12 hours 400 mg intravenous every 8 hours 2.2 Dosage in Pediatric Patients Dosing and initial route of therapy (that is, IV or oral) for cUTI or pyelonephritis should be determined by the severity of the infection. Ciprofloxacin should be administered as described in Table 3 . Table 3: Pediatric Dosage Guidelines 1. The total duration of therapy for cUTI and pyelonephritis in the clinical trial was determined by the physician. The mean duration of treatment was 11 days (range 10 to 21 days). 2. Begin drug administration as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure. 3. Begin drug administration as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure to Y. pestis . Infection Dose Frequency Total Duration Complicated Urinary Tract or Pyelonephritis (patients from 1 to 17 years of age) 10 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg (maximum 750 mg per dose; not to be exceeded even in patients weighing more than 51 kg) Every 12 hours 10–21 days 1 Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure) 2 15 mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) Every 12 hours 60 days Plague 2,3 15 mg/kg (maximum 500 mg per dose) Every 8 to 12 hours 10–21 days 2.3 Dosage Modifications in Patients with Renal Impairment Ciprofloxacin is eliminated primarily by renal excretion; however, the drug is also metabolized and partially cleared through the biliary system of the liver and through the intestine. These alternative pathways of drug elimination appear to compensate for the reduced renal excretion in patients with renal impairment. Nonetheless, some modification of dosage is recommended, particularly for patients with severe renal dysfunction. Dosage guidelines for use in patients with renal impairment are shown in Table 4 . Table 4: Recommended Starting and Maintenance Doses for Adult Patients with Impaired Renal Function Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Dose > 50 See Usual Dosage. 30–50 250–500 mg every12 hours 5–29 250–500 mg every 18 hours Patients on hemodialysis or Peritoneal dialysis 250–500 mg every 24 hours (after dialysis) When only the serum creatinine concentration is known, the following formulas may be used to estimate creatinine clearance: Men - Creatinine clearance (mL/min) = Weight (kg) x (140–age) 72 x serum creatinine (mg/dL) Women - 0.85 x the value calculated for men. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function. In patients with severe infections and severe renal impairment, a unit dose of 750 mg may be administered at the intervals noted above. Patients should be carefully monitored. Pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency were excluded from the clinical trial of cUTI and pyelonephritis. No information is available on dosing adjustments necessary for pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency (that is, creatinine clearance of < 50 mL/min/1.73m 2 ). 2.4 Important Administration Instructions With Multivalent Cations Administer Ciprofloxacin at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after magnesium/aluminum antacids; polymeric phosphate binders (for example, sevelamer, lanthanum carbonate) or sucralfate; Videx ® (didanosine) chewable/buffered tablets or pediatric powder for oral solution; other highly buffered drugs; or other products containing calcium, iron or zinc. With Dairy Products Concomitant administration of Ciprofloxacin with dairy products (like milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone should be avoided since decreased absorption is possible; however, Ciprofloxacin may be taken with a meal that contains these products. Hydration of Patients Receiving Ciprofloxacin Assure adequate hydration of patients receiving Ciprofloxacin to prevent the formation of highly concentrated urine. Crystalluria has been reported with quinolones. Instruct the patient of the appropriate Ciprofloxacin administration [see Patient Counseling Information ( 17 )].
