Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CARBIDOPA W/LEVODOPA TB 25/250MG 500
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62756-0519-13 | SUN PHARMACEUTICALS | 500 | 25-250MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
CARBIDOPA AND LEVODOPA
Substance Name
CARBIDOPA
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA078536
Description
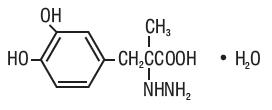
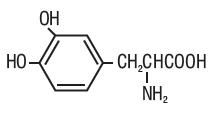
DESCRIPTION Carbidopa and levodopa tablet, USP is a combination of carbidopa and levodopa for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and syndrome. Carbidopa USP, an inhibitor of aromatic amino acid decarboxylation, is a white, crystalline compound, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 244.24. It is designated chemically as (-)-L-α-hydrazino-α-methyl-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid monohydrate. Its molecular formula is C 10 H 14 N 2 O 4 •H 2 O and its structural formula is: Tablet content is expressed in terms of anhydrous carbidopa which has a molecular weight of 226.23. Levodopa USP, an aromatic amino acid, is a white, crystalline compound, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 197.2. It is designated chemically as (-)-L-α-amino-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid. Its molecular formula is C 9 H 11 NO 4 and its structural formula is: Carbidopa and levodopa is supplied as tablets in three strengths: Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP, 25 mg/100 mg, containing 25 mg of carbidopa and 100 mg of levodopa. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP, 10 mg/100 mg, containing 10 mg of carbidopa and 100 mg of levodopa. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP, 25 mg/250 mg, containing 25 mg of carbidopa and 250 mg of levodopa. Inactive ingredients are microcrystalline cellulose, corn starch, pregelatinized maize starch, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 10 mg/100 mg and 25 mg/250 mg also contain FD&C Blue 2. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 25 mg/100 mg also contain D&C Yellow 10 and FD&C Yellow 6. FDA approved dissolution method differs from that of the USP. cdld-structure-carbidopa cdld-structure-levodopa
How Supplied
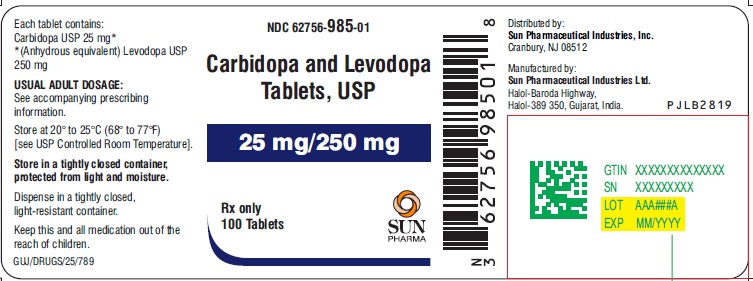
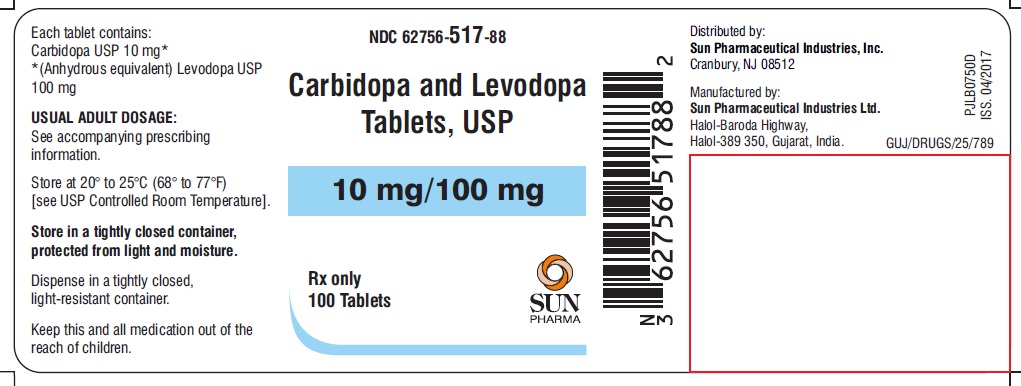
HOW SUPPLIED Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 25 mg/100 mg are mottled (orange colored speckles) yellow to light yellow colored oval shaped, biconvex, uncoated tablets debossed with "518" on one side and plain on the other side. They are supplied as follows: Bottle of 30 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-518-83 Bottle of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-518-88 Bottle of 100, NDC 62756-518-08 Bottle of 500, NDC 62756-518-13 Bottle of 1000, NDC 62756-518-18 Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 10 mg/100 mg are mottled blue to light blue colored oval shaped, biconvex, uncoated tablets debossed with "517" on one side and plain on the other side. They are supplied as follows: Bottle of 30 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-517-83 Bottle of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-517-88 Bottle of 100, NDC 62756-517-08 Bottle of 500, NDC 62756-517-13 Bottle of 1000, NDC 62756-517-18 Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 25 mg/250 mg are mottled blue to light blue colored oval shaped, biconvex, uncoated tablets debossed with "519" on one side and plain on the other side. They are supplied as follows: Bottle of 30 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-519-83 Bottle of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-519-88 Bottle of 100, NDC 62756-519-08 Bottle of 500, NDC 62756-519-13 Bottle of 1000, NDC 62756-519-18 Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP 25 mg/250 mg are mottled blue to light blue colored round shaped, biconvex, uncoated tablets debossed with "519" on one side and plain on the other side. They are supplied as follows: Bottle of 100 with child-resistant closure, NDC 62756-985-01 Bottle of 500, NDC 62756-985-02 Storage Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store in a tightly closed container, protected from light and moisture. Dispense in a tightly closed, light-resistant container.
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP are indicated in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, post-encephalitic parkinsonism, and symptomatic parkinsonism that may follow carbon monoxide intoxication or manganese intoxication. Carbidopa allows patients treated for Parkinson's disease to use much lower doses of levodopa. Some patients who responded poorly to levodopa have improved on carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP. This is most likely due to decreased peripheral decarboxylation of levodopa caused by administration of carbidopa rather than by a primary effect of carbidopa on the nervous system. Carbidopa has not been shown to enhance the intrinsic efficacy of levodopa. Carbidopa may also reduce nausea and vomiting and permit more rapid titration of levodopa.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION The optimum daily dosage of carbidopa and levodopa must be determined by careful titration in each patient. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are available in a 1:4 ratio of carbidopa to levodopa (carbidopa and levodopa tablets 25 mg/100 mg) as well as 1:10 ratio (carbidopa and levodopa tablets 25 mg/250 mg and carbidopa and levodopa tablets 10 mg/100 mg). Tablets of the two ratios may be given separately or combined as needed to provide the optimum dosage. Studies show that peripheral dopa decarboxylase is saturated by carbidopa at approximately 70 to 100 mg a day. Patients receiving less than this amount of carbidopa are more likely to experience nausea and vomiting. Usual Initial Dosage Dosage is best initiated with one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg three times a day. This dosage schedule provides 75 mg of carbidopa per day. Dosage may be increased by one tablet every day or every other day, as necessary, until a dosage of eight tablets of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg a day is reached. If carbidopa and levodopa tablets 10 mg/100 mg are used, dosage may be initiated with one tablet three or four times a day. However, this will not provide an adequate amount of carbidopa for many patients. Dosage may be increased by one tablet every day or every other day until a total of eight tablets (2 tablets q.i.d.) is reached. How to Transfer Patients from Levodopa Levodopa must be discontinued at least twelve hours before starting carbidopa and levodopa tablets. A daily dosage of carbidopa and levodopa should be chosen that will provide approximately 25% of the previous levodopa dosage. Patients who are taking less than 1,500 mg of levodopa a day should be started on one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg three or four times a day. The suggested starting dosage for most patients taking more than 1,500 mg of levodopa is one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/250 mg three or four times a day. Maintenance Therapy should be individualized and adjusted according to the desired therapeutic response. At least 70 to 100 mg of carbidopa per day should be provided. When a greater proportion of carbidopa is required, one tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 25 mg/100 mg may be substituted for each tablet of carbidopa and levodopa 10 mg/100 mg. When more levodopa is required, carbidopa and levodopa tablets 25 mg/250 mg should be substituted for carbidopa and levodopa tablets 25 mg/100 mg or carbidopa and levodopa tablets 10 mg/100 mg. If necessary, the dosage of carbidopa and levodopa tablets 25 mg/250 mg may be increased by one-half or one tablet every day or every other day to a maximum of eight tablets a day. Experience with total daily dosages of carbidopa greater than 200 mg is limited. Because both therapeutic and adverse responses occur more rapidly with carbidopa and levodopa than with levodopa alone, patients should be monitored closely during the dose adjustment period. Specifically, involuntary movements will occur more rapidly with carbidopa and levodopa than with levodopa. The occurrence of involuntary movements may require dosage reduction. Blepharospasm may be a useful early sign of excess dosage in some patients. Addition of Other Antiparkinsonian Medications Standard drugs for Parkinson's disease, other than levodopa without a decarboxylase inhibitor, may be used concomitantly while carbidopa and levodopa tablets are being administered, although dosage adjustments may be required. Interruption of Therapy Sporadic cases of hyperpyrexia and confusion have been associated with dose reductions and withdrawal of carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Patients should be observed carefully if abrupt reduction or discontinuation of carbidopa and levodopa tablets is required, especially if the patient is receiving neuroleptics. (See WARNINGS . ) If general anesthesia is required, carbidopa and levodopa may be continued as long as the patient is permitted to take fluids and medication by mouth. If therapy is interrupted temporarily, the patient should be observed for symptoms resembling NMS, and the usual daily dosage may be administered as soon as the patient is able to take oral medication.
