Drug Catalog - Product Detail
CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL 4MG TB 30
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00378-3224-93 | MYLAN | 30 | 4MG | NA |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL
Substance Name
CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA078702
Description
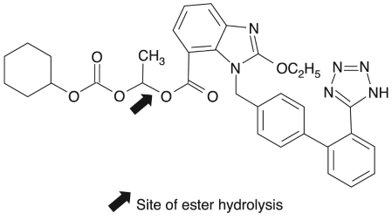
11 DESCRIPTION Candesartan cilexetil tablets USP, a prodrug, are hydrolyzed to candesartan during absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Candesartan is a selective AT 1 subtype angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Candesartan cilexetil, a nonpeptide, is chemically described as (±)2-Ethoxy-1-[[2’-(1 H -tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1’-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1 H -benzimidazole-7-carboxylic acid-1-[[(cyclohexyloxy)carbonyl]oxy]ethyl ester. Its molecular formula is C 33 H 34 N 6 O 6 , and its structural formula is: Candesartan cilexetil, USP is a white or off-white powder with a molecular weight of 610.66. It is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in methanol. Candesartan cilexetil is a racemic mixture containing one chiral center at the cyclohexyloxycarbonyloxy ethyl ester group. Following oral administration, candesartan cilexetil undergoes hydrolysis at the ester link to form the active drug, candesartan, which is achiral. Candesartan cilexetil is available for oral use as tablets containing either 4 mg, 8 mg, 16 mg, or 32 mg of candesartan cilexetil and the following inactive ingredients: carboxymethylcellulose calcium, corn starch, glyceryl stearate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate and magnesium stearate. The 8 mg, 16 mg and 32 mg tablets also contain red iron oxide. Candesartan Cilexetil Structural Formula
How Supplied
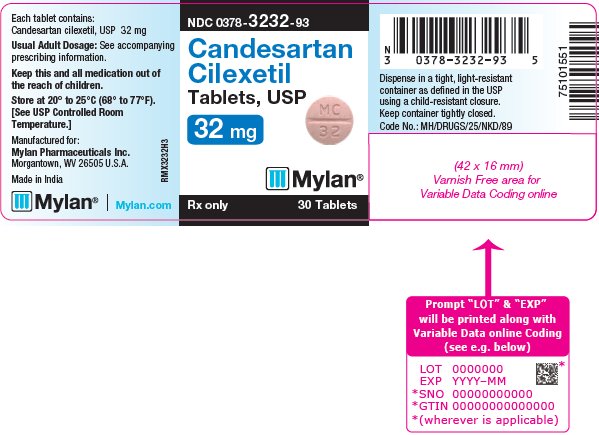
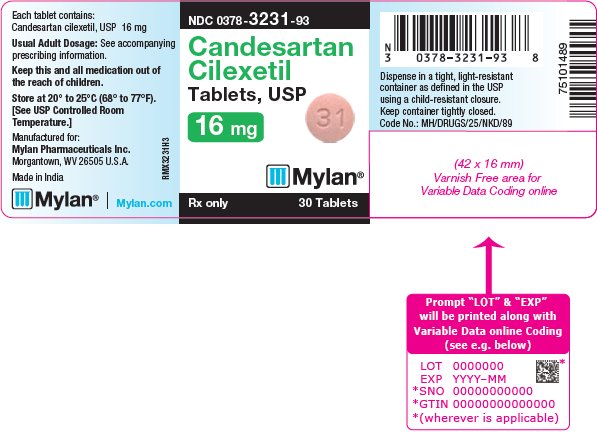
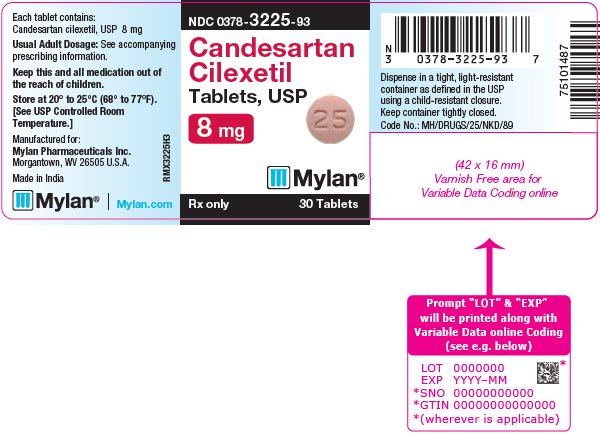
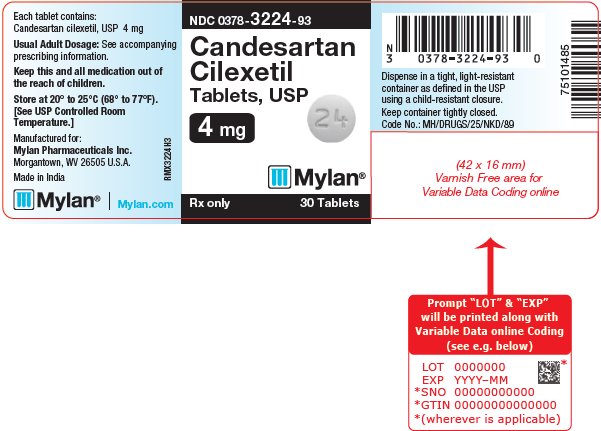
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Candesartan Cilexetil Tablets, USP are available containing 4 mg, 8 mg, 16 mg or 32 mg of candesartan cilexetil, USP. The 4 mg tablets are white to off-white, round, scored tablets debossed with M on the left side of the score and C on the right side of the score on one side of the tablet and 24 on the other side of the tablet. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-3224-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-3224-77 bottles of 90 tablets The 8 mg tablets are pink mottled, round, scored tablets debossed with M on the left side of the score and C on the right side of the score on one side of the tablet and 25 on the other side of the tablet. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-3225-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-3225-77 bottles of 90 tablets The 16 mg tablets are pink mottled, round, scored tablets debossed with M on the left side of the score and C on the right side of the score on one side of the tablet and 31 on the other side of the tablet. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-3231-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-3231-77 bottles of 90 tablets The 32 mg tablets are pink mottled, round, scored tablets debossed with MC above the score and 32 below the score on one side of the tablet and blank on the other side of the tablet. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-3232-93 bottles of 30 tablets NDC 0378-3232-77 bottles of 90 tablets Storage: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Keep container tightly closed. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Indications & Usage
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Candesartan cilexetil tablets are an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) indicated for: • Treatment of hypertension in adults and children 1 to < 17 years of age, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions ( 1.1 ). • Treatment of heart failure (NYHA class II-IV); candesartan cilexetil tablets reduce cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization ( 1.2 ). 1.1 Hypertension Candesartan cilexetil tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension in adults and in children 1 to < 17 years of age, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including the class to which this drug principally belongs. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. Candesartan cilexetil tablets may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. 1.2 Heart Failure Candesartan cilexetil tablets are indicated for the treatment of heart failure (NYHA class II-IV) in adults with left ventricular systolic dysfunction (ejection fraction ≤ 40%) to reduce cardiovascular death and to reduce heart failure hospitalizations [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Candesartan cilexetil tablets also have an added effect on these outcomes when used with an ACE inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.4) ] .
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Starting Dose Target Dose Adult Hypertension ( 2.1 ) 16 mg tablet once daily 8 – 32 mg tablet total daily dose Pediatric Hypertension (1 to < 6 years) ( 2.2 ) 0.20 mg/kg oral suspension once daily 0.05 – 0.4 mg/kg oral suspension once daily or consider divided dose Pediatric Hypertension (6 to < 17 years) ( 2.2 ) < 50 kg 4 – 8 mg tablet once daily < 50 kg 4 – 16 mg tablet once daily or consider divided dose > 50 kg 8 – 16 mg tablet once daily > 50 kg 4 – 32 mg tablet once daily or consider divided dose Adult Heart Failure ( 2.3 ) 4 mg tablet once daily 32 mg tablet once daily The target dose is 32 mg once daily, which is achieved by doubling the dose at approximately 2-week intervals, as tolerated by patient. 2.1 Adult Hypertension Dosage must be individualized. Blood pressure response is dose related over the range of 2 to 32 mg. The usual recommended starting dose of candesartan cilexetil tablets is 16 mg once daily when they are used as monotherapy in patients who are not volume depleted. Candesartan cilexetil tablets can be administered once or twice daily with total daily doses ranging from 8 mg to 32 mg. Larger doses do not appear to have a greater effect, and there is relatively little experience with such doses. Most of the antihypertensive effect is present within 2 weeks, and maximal blood pressure reduction is generally obtained within 4 to 6 weeks of treatment with candesartan cilexetil tablets. Use in Hepatic Impairment Initiate with 8 mg candesartan cilexetil tablets in patients with moderate hepatic insufficiency. Dosing recommendations cannot be provided for patients with severe hepatic insufficiency [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Candesartan cilexetil tablets may be administered with or without food. If blood pressure is not controlled by candesartan cilexetil tablets alone, a diuretic may be added. Candesartan cilexetil tablets may be administered with other antihypertensive agents. 2.2 Pediatric Hypertension 1 to < 17 Years of Age Candesartan cilexetil tablets may be administered once daily or divided into two equal doses. Adjust the dosage according to blood pressure response. For patients with possible depletion of intravascular volume (e.g., patients treated with diuretics, particularly those with impaired renal function), initiate candesartan cilexetil tablets under close medical supervision and consider administration of a lower dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . Children 1 to < 6 Years of Age The dose range is 0.05 to 0.4 mg/kg per day. The recommended starting dose is 0.20 mg/kg (oral suspension). Children 6 to < 17 Years of Age For those less than 50 kg, the dose range is 2 to 16 mg per day. The recommended starting dose is 4 to 8 mg. For those greater than 50 kg, the dose range is 4 to 32 mg per day. The recommended starting dose is 8 to 16 mg. Doses above 0.4 mg/kg (1 to < 6 year olds) or 32 mg (6 to < 17 year olds) have not been studied in pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. An antihypertensive effect is usually present within 2 weeks, with full effect generally obtained within 4 weeks of treatment with candesartan cilexetil tablets. Children < 1 year of age must not receive candesartan cilexetil tablets for hypertension. All pediatric patients with a glomerular filtration rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73m 2 should not receive candesartan cilexetil tablets since candesartan cilexetil tablets have not been studied in this population [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] . For children who cannot swallow tablets, an oral suspension may be substituted as described below: Preparation of Oral Suspension Candesartan cilexetil oral suspension can be prepared in concentrations within the range of 0.1 to 2.0 mg/mL. Typically, a concentration of 1 mg/mL will be suitable for the prescribed dose. Any strength of candesartan cilexetil tablets can be used in the preparation of the suspension. Follow the steps below for preparation of the suspension. The number of tablets and volume of vehicle specified below will yield 160 mL of a 1 mg/mL suspension. • Prepare the vehicle by adding equal volumes of Ora-Plus ® (80 mL) and Ora-Sweet SF ® (80 mL) or, alternatively, use Ora-Blend SF ® (160 mL). • Add a small amount of vehicle to the required number of candesartan cilexetil tablets (five 32 mg tablets) and grind into a smooth paste using a mortar and pestle. • Add the paste to a preparation vessel of suitable size. • Rinse the mortar and pestle clean using the vehicle and add this to the vessel. Repeat, if necessary. • Prepare the final volume by adding the remaining vehicle. • Mix thoroughly. • Dispense into suitably sized amber PET bottles. • Label with an expiry date of 100 days and include the following instructions: Store at room temperature (below 30°C/86°F). Use within 30 days after first opening. Do not use after the expiry date stated on the bottle. Do not freeze. Shake well before each use. 2.3 Adult Heart Failure The recommended initial dose for treating heart failure is 4 mg once daily. The target dose is 32 mg once daily, which is achieved by doubling the dose at approximately 2-week intervals, as tolerated by the patient.
