Drug Catalog - Product Detail
AMPICILLIN/SULBACTAM SOD. FOR INJECTION INJECT. 1.5GM/1ML 10X1ML
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55150-0116-20 | AUROMEDICS PHARMA | 1 | 1.5 (1-0.5)GM | SOLUTION |
PACKAGE FILES





Generic Name
AMPICILLIN SODIUM AND SULBACTAM SODIUM
Substance Name
AMPICILLIN SODIUM
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
INTRAMUSCULAR
Application Number
ANDA090349
Description
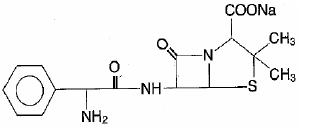
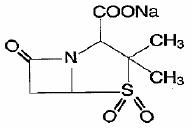
DESCRIPTION Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, USP is an injectable antibacterial combination consisting of the semisynthetic antibacterial ampicillin sodium and the beta-lactamase inhibitor sulbactam sodium for intravenous and intramuscular administration. Ampicillin sodium is derived from the penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Chemically, it is monosodium (2S, 5R, 6R)-6-[(R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3, 3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylate and has a molecular weight of 371.39. Its chemical formula is C 16 H 18 N 3 NaO 4 S. The structural formula is: Sulbactam sodium is a derivative of the basic penicillin nucleus. Chemically, sulbactam sodium is sodium penicillinate sulfone; sodium (2S, 5R)-3, 3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylate 4, 4-dioxide. Its chemical formula is C 8 H 10 NNaO 5 S with a molecular weight of 255.22. The structural formula is: Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, USP parenteral combination, is available as a white to off-white, crystalline powder for reconstitution. Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, USP crystalline powder is freely soluble in aqueous diluents to yield pale yellow to yellow solutions containing ampicillin sodium and sulbactam sodium equivalent to 250 mg ampicillin per mL and 125 mg sulbactam per mL. The pH of the solutions is between 8 and 10. Dilute solutions (up to 30 mg ampicillin and 15 mg sulbactam per mL) are essentially colorless to pale yellow. The pH of dilute solutions remains the same. 1.5 g of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, USP (equivalent to 1 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 g sulbactam as the sodium salt). The sodium content per vial is 115 mg (5 mEq). 3 g of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, USP (equivalent to 2 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 1 g sulbactam as the sodium salt). The sodium content per vial is 230 mg (10 mEq). Ampicillin Chemical Structure Sulbactam Sodium Chemical Structure
How Supplied
HOW SUPPLIED Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP is supplied as a sterile white to off-white, powder as follows: NDC Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP Package Factor 55150-116-20 1.5 g of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection (equivalent to 1 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) in a Single-Dose vial 10 vials per carton 55150-117-20 3 g of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection (equivalent to 2 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 1 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) in a Single- Dose vial 10 vials per carton 55150-178-99 1.5 g of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection (equivalent to 1 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) in an infusion bottle 10 bottles per carton 55150-179-99 3 g of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection (equivalent to 2 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 1 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) in an infusion bottle 10 bottles per carton Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Sterile, Nonpyrogenic, Preservative-free. The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE EVENTS, contact Eugia US LLC at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or http://www.fda.gov/ for voluntary reporting of adverse reactions. All brands listed are the trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited. This product’s labeling may have been updated. For the most recent prescribing information, please visit eugiaus.com. Distributed by: Eugia US LLC 279 Princeton-Hightstown Rd. E. Windsor, NJ 08520 Manufactured by: Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited Hyderabad - 500032 India Revised: December 2022
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection is indicated for the treatment of infections due to susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below. Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by beta-lactamase producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus , Escherichia coli , * Klebsiella spp. * (including K. pneumoniae * ), Proteus mirabilis , * Bacteroides fragilis , * Enterobacter spp., * and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus . * NOTE: For information on use in pediatric patients (see PRECAUTIONS–Pediatric Use and CLINICAL STUDIES sections). Intra-Abdominal Infections caused by beta-lactamase producing strains of Escherichia coli , Klebsiella spp. (including K. pneumoniae * ), Bacteroides spp. (including B. fragilis ), and Enterobacter spp. * Gynecological Infections caused by beta-lactamase producing strains of Escherichia coli , * and Bacteroides spp. * (including B. fragilis * ). * Efficacy for this organism in this organ system was studied in fewer than 10 infections. While ampicillin and sulbactam for injection is indicated only for the conditions listed above, infections caused by ampicillin-susceptible organisms are also amenable to treatment with ampicillin and sulbactam for injection due to its ampicillin content. Therefore, mixed infections caused by ampicillin-susceptible organisms and beta-lactamase producing organisms susceptible to ampicillin and sulbactam for injection should not require the addition of another antibacterial. Appropriate culture and susceptibility tests should be performed before treatment in order to isolate and identify the organisms causing infection and to determine their susceptibility to ampicillin and sulbactam for injection. Therapy may be instituted prior to obtaining the results from bacteriological and susceptibility studies when there is reason to believe the infection may involve any of the beta-lactamase producing organisms listed above in the indicated organ systems. Once the results are known, therapy should be adjusted if appropriate. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain effectiveness of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection and other antibacterial drugs, ampicillin and sulbactam for injection should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Dosage and Administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection may be administered by either the IV or the IM routes. For IV administration, the dose can be given by slow intravenous injection over at least 10 to 15 minutes or can also be delivered in greater dilutions with 50 to 100 mL of a compatible diluent as an intravenous infusion over 15 to 30 minutes. Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection may be administered by deep intramuscular injection. (see DIRECTIONS FOR USE-Preparation for Intramuscular Injection section). The recommended adult dosage of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection is 1.5 g (1 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) to 3 g (2 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 1 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) every six hours. This 1.5 to 3 g range represents the total of ampicillin content plus the sulbactam content of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, and corresponds to a range of 1 g ampicillin/0.5 g sulbactam to 2 g ampicillin/1 g sulbactam. The total dose of sulbactam should not exceed 4 grams per day. Pediatric Patients 1 Year of Age or Older The recommended daily dose of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection in pediatric patients is 300 mg per kg of body weight administered via intravenous infusion in equally divided doses every 6 hours. This 300 mg/kg/day dosage represents the total ampicillin content plus the sulbactam content of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, and corresponds to 200 mg ampicillin/100 mg sulbactam per kg per day. The safety and efficacy of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection administered via intramuscular injection in pediatric patients have not been established. Pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or more should be dosed according to adult recommendations, and the total dose of sulbactam should not exceed 4 grams per day. The course of intravenous therapy should not routinely exceed 14 days. In clinical trials, most children received a course of oral antimicrobials following initial treatment with intravenous ampicillin and sulbactam for injection. (see CLINICAL STUDIES section). Impaired Renal Function In patients with impairment of renal function the elimination kinetics of ampicillin and sulbactam are similarly affected, hence the ratio of one to the other will remain constant whatever the renal function. The dose of ampicillin and sulbactam in such patients should be administered less frequently in accordance with the usual practice for ampicillin and according to the following recommendations: TABLE 3 Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection Dosage Guide for Patients with Renal Impairment Creatinine Clearance (mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) Ampicillin/Sulbactam Half-Life (Hours) Recommended Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection Dosage ≥30 1 1.5 to 3 g q 6 h to q 8 h 15 to 29 5 1.5 to 3 g q 12 h 5 to 14 9 1.5 to 3 g q 24 h When only serum creatinine is available, the following formula (based on sex, weight, and age of the patient) may be used to convert this value into creatinine clearance. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function. Males weight (kg) × (140 – age) 72 × serum creatinine Females 0.85 × above value COMPATIBILITY, RECONSTITUTION AND STABILITY Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection sterile powder is to be stored at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] prior to reconstitution. When concomitant therapy with aminoglycosides is indicated, ampicillin and sulbactam and aminoglycosides should be reconstituted and administered separately, due to the in vitro inactivation of aminoglycosides by any of the aminopenicillins. DIRECTIONS FOR USE General Dissolution Procedures Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection sterile powder for intravenous and intramuscular use may be reconstituted with any of the compatible diluents described in this insert. Solutions should be allowed to stand after dissolution to allow any foaming to dissipate in order to permit visual inspection for complete solubilization. Preparation for Intravenous Use 1.5 g and 3 g infusion bottles: Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection sterile powder in infusion bottles may be reconstituted directly to the desired concentrations using any of the following parenteral diluents. Reconstitution of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection, at the specified concentrations, with these diluents provide stable solutions for the time periods indicated in the following table: (After the indicated time periods, any unused portions of solutions should be discarded). TABLE 4 Diluent Maximum Concentration (mg/mL)Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection Use Periods Sterile Water for Injection 45 (30/15) 8 hrs at 25°C 45 (30/15) 48 hrs at 4°C 30 (20/10) 72 hrs at 4°C 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection 45 (30/15) 8 hrs at 25°C 45 (30/15) 48 hrs at 4°C 30 (20/10) 72 hrs at 4°C 5% Dextrose Injection 30 (20/10) 2 hrs at 25°C 30 (20/10) 4 hrs at 4°C 3 (2/1) 4 hrs at 25°C Lactated Ringer's Injection 45 (30/15) 8 hrs at 25°C 45 (30/15) 24 hrs at 4°C M/6 Sodium Lactate Injection 45 (30/15) 8 hrs at 25°C 45 (30/15) 8 hrs at 4°C 5% Dextrose in 0.45% Saline 3 (2/1) 4 hrs at 25°C 15 (10/5) 4 hrs at 4°C 10% Invert Sugar 3 (2/1) 4 hrs at 25°C 30 (20/10) 3 hrs at 4°C Initially, the vials may be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection to yield solutions containing 375 mg ampicillin and sulbactam per mL (250 mg ampicillin/125 mg sulbactam per mL). An appropriate volume should then be immediately diluted with a suitable parenteral diluent to yield solutions containing 3 to 45 mg ampicillin and sulbactam per mL (2 to 30 mg ampicillin/1 to 15 mg sulbactam/per mL). Preparation for Intramuscular Injection 1.5 g and 3 g Standard Vials: Vials for intramuscular use may be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection USP, 0.5% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection USP or 2% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection USP. Consult the following table for recommended volumes to be added to obtain solutions containing 375 mg ampicillin and sulbactam per mL (250 mg ampicillin/125 mg sulbactam per mL). Note: Use only freshly prepared solutions and administer within one hour after preparation. TABLE 6 Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection Vial Size Volume of Diluent to be Added Withdrawal Volume* * There is sufficient excess present to allow withdrawal and administration of the stated volumes. 1.5 g 3.2 mL 4 mL 3 g 6.4 mL 8 mL
