Drug Catalog - Product Detail
AMPICILLIN SODIUM FOR INJECTION INJECT. 2GM/ML 10X20ML
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55150-0114-20 | EUGIA US LLC | 1 | 2GM | SOLUTION |
PACKAGE FILES



Generic Name
AMPICILLIN SODIUM
Substance Name
AMPICILLIN SODIUM
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
INTRAVENOUS
Application Number
ANDA065499
Description
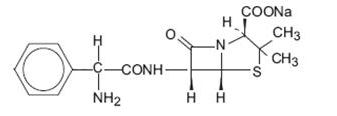
DESCRIPTION Ampicillin for injection, USP the monosodium salt of [2S-[2α, 5α, 6β(S*)]]-6-[(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, is a synthetic penicillin. It is an antibacterial agent with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against both penicillin-susceptible Gram-positive organisms and many common Gram-negative pathogens. Ampicillin for injection, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder. The reconstituted solution is clear, colorless and free from visible particulates. Each vial of ampicillin for injection, USP contains ampicillin sodium equivalent to 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 gram or 2 grams ampicillin. Ampicillin for injection, USP contains sodium content as 16.46 mg (0.72 mEq) per 250 mg, 32.91 mg (1.43 mEq) per 500 mg, 65.83 mg (2.86 mEq) per 1 g or 131.66 mg (5.72 mEq) per 2 g of ampicillin. It has the following molecular structure: The molecular formula is C 16 H 18 N 3 NaO 4 S, and the molecular weight is 371.39. The pH range of the reconstituted solution is 8 to 10. Formula1.jpg
How Supplied
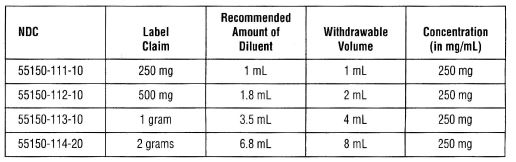
HOW SUPPLIED Ampicillin for injection, USP for intramuscular or intravenous injection. It is a white to off-white crystalline powder supplied in vials containing ampicillin sodium equivalent to 250 mg, 500 mg, 1 gram or 2 grams ampicillin per vial. The following packages are available: Product repackaged by: Henry Schein, Inc., Bastian, VA 24314 From Original Manufacturer/Distributor's NDC and Unit of Sale To Henry Schein Repackaged Product NDC and Unit of Sale Total Strength/Total Volume (Concentration) per unit NDC 55150-113-10 Box of 10 vials NDC 0404-9816-99 1 15 mL vial in a bag (Vial bears NDC 55150-113-10) 1 g in 15 mL vial NDC 55150-114-20 Box of 10 vials NDC 0404-9818-99 1 24 mL vial in a bag (Vial bears NDC 55150-114-20) 2 g in 24 mL vial Storage Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect the constituted solution from freezing. The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex. Clinitest is a registered trademark of Miles, Inc. Clinistix is a registered trademark of Bayer Corporation. Tes-Tape is a registered trademark of Eli Lilly Company. Distributed by: Eugia US LLC 279 Princeton-Hightstown Rd. E. Windsor, NJ 08520 Manufactured by: Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited Hyderabad – 500032 India Revised: January 2024 Image4.jpg
Indications & Usage
INDICATIONS AND USAGE Ampicillin for injection is indicated in the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated organisms in the following conditions: Respiratory Tract Infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus (penicillinase and nonpenicillinase-producing), H. influenzae, and Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. Bacterial Meningitis caused by E. coli, Group B Streptococci, and other Gram-negative bacteria ( Listeria monocytogenes, N. meningitidis ). The addition of an aminoglycoside with ampicillin may increase its effectiveness against Gram-negative bacteria. Septicemia and Endocarditis caused by susceptible Gram-positive organisms including Streptococcus spp., penicillin G-susceptible staphylococci, and enterococci. Gram-negative sepsis caused by E. coli, Proteus mirabilis and Salmonella spp. responds to ampicillin. Endocarditis due to enterococcal strains usually respond to intravenous therapy. The addition of an aminoglycoside may enhance the effectiveness of ampicillin when treating streptococcal endocarditis. Urinary Tract Infections caused by sensitive strains of E. coli and Proteus mirabilis. Gastrointestinal Infections caused by Salmonella typhi (typhoid fever), other Salmonella spp., and Shigella spp. (dysentery) usually respond to oral or intravenous therapy. Bacteriology studies to determine the causative organisms and their susceptibility to ampicillin should be performed. Therapy may be instituted prior to obtaining results of susceptibility testing. It is advisable to reserve the parenteral form of this drug for moderately severe and severe infections and for patients who are unable to take the oral forms. A change to oral ampicillin may be made as soon as appropriate. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of ampicillin for injection and other antibacterial drugs, ampicillin for injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. Indicated surgical procedures should be performed.
Dosage and Administration
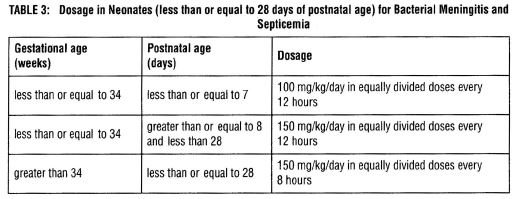
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Infections of the respiratory tract and soft tissues. Patients weighing 40 kg (88 lbs) or more: 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours. Patients weighing less than 40 kg (88 lbs): 25 to 50 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses at 6- to 8-hour intervals. Infections of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts (including those caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae in females). Patients weighing 40 kg (88 lbs) or more: 500 mg every 6 hours. Patients weighing less than 40 kg (88 lbs): 50 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses at 6- to 8-hour intervals. In the treatment of chronic urinary tract and intestinal infections, frequent bacteriological and clinical appraisal is necessary. Smaller doses than those recommended above should not be used. Higher doses should be used for stubborn or severe infections. In stubborn infections, therapy may be required for several weeks. It may be necessary to continue clinical and/or bacteriological follow-up for several months after cessation of therapy. Urethritis in males due to N. gonorrhoeae. Adults - Two doses of 500 mg each at an interval of 8 to 12 hours. Treatment may be repeated if necessary or extended if required. In the treatment of complications of gonorrheal urethritis, such as prostatitis and epididymitis, prolonged and intensive therapy is recommended. Cases of gonorrhea with a suspected primary lesion of syphilis should have darkfield examinations before receiving treatment. In all other cases where concomitant syphilis is suspected, monthly serological tests should be made for a minimum of four months. The doses for the preceding infections may be given by either the intramuscular or intravenous route. A change to oral ampicillin may be made when appropriate. Bacterial Meningitis Adults and children – 150 to 200 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses every 3 to 4 hours. (Treatment may be initiated with intravenous drip therapy and continued with intramuscular injections.) The doses for other infections may be given by either the intravenous or intramuscular route. Neonates (less than or equal to 28 days of postnatal age) – Dosage should be based on Gestational age and Postnatal age according to Table 1. Table 1: Dosage in Neonates (less than or equal to 28 days of postnatal age) for Bacterial Meningitis and Septicemia Septicemia Adults and children - 150 to 200 mg/kg/day. Start with intravenous administration for at least three days and continue with the intramuscular route every 3 to 4 hours. Neonates (less than or equal to 28 days of postnatal age) – Dosage should be based on Gestational age and Postnatal age according to Table 1 (above). Treatment of all infections should be continued for a minimum of 48 to 72 hours beyond the time that the patient becomes asymptomatic or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained. A minimum of 10 days treatment is recommended for any infection caused by Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci to help prevent the occurrence of acute rheumatic fever or acute glomerulonephritis. DIRECTIONS FOR USE Use only freshly prepared solutions. Intramuscular and intravenous injections should be administered within one hour after preparation since the potency may decrease significantly after this period. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. For Intramuscular Use – Dissolve contents of a vial with the amount of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, listed in the table below: While ampicillin for injection, USP, 1 g and 2 g, are primarily for intravenous use, they may be administered intramuscularly when the 250 mg or 500 mg vials are unavailable. In such instances, dissolve in 3.5 or 6.8 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, respectively. The resulting solution will provide a concentration of 250 mg per mL. Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP is not to be used as a diluent when the product will be used in newborns. For Direct Intravenous Use – Add 5 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP to the 250 mg, and 500 mg vials and administer slowly over a 3- to 5-minute period. Ampicillin for injection, USP, 1 g or 2 g may also be given by direct intravenous administration. Dissolve in 7.4 or 14.8 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP, respectively, and administer slowly over at least 10 to 15 minutes. CAUTION: More rapid administration may result in convulsive seizures. For Administration by Intravenous Drip – Reconstitute as directed above (For Direct Intravenous Use) prior to diluting with Intravenous Solution. Stability studies on ampicillin sodium at several concentrations in various intravenous solutions indicate the drug will lose less than 10% activity at the temperatures noted for the time periods stated. Only those solutions listed above should be used for the intravenous infusion of ampicillin for injection, USP. The concentrations should fall within the range specified. The drug concentration and the rate and volume of the infusion should be adjusted so that the total dose of ampicillin is administered before the drug loses its stability in the solution in use. Image1.jpg Image2.jpg Image3.jpg
