Drug Catalog - Product Detail
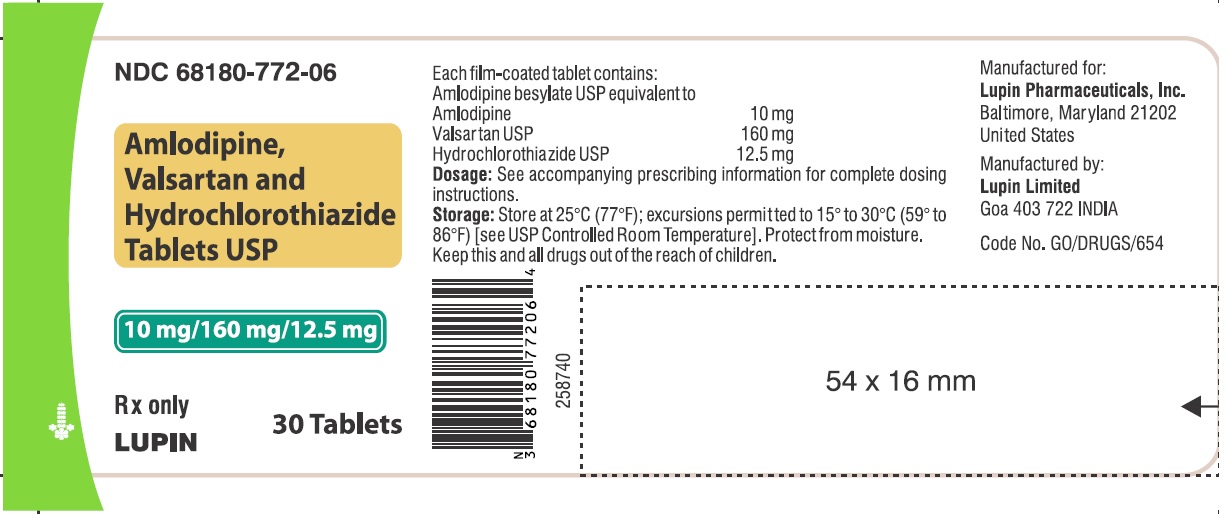
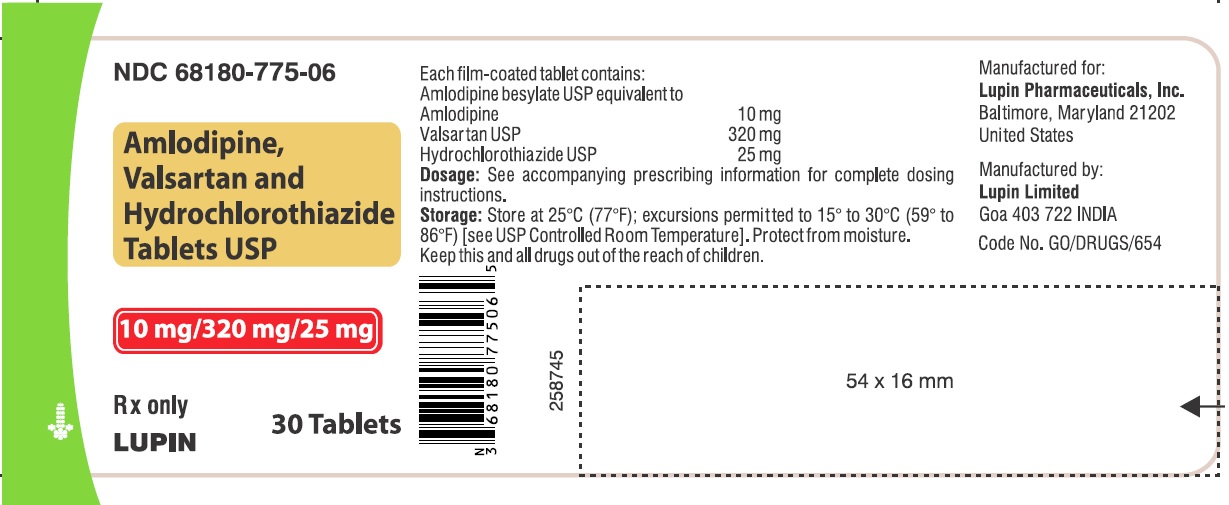
AMLODIPINE-VALSARTAN-HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE TAB 10-160-12.5 MG 30 CT
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68180-0772-06 | LUPIN PHARMACEUTICALS | 30 | 10-160-12.5MG | TABLET |
PACKAGE FILES
Generic Name
AMLODIPINE, VALSARTAN AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
Substance Name
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA200797
Description
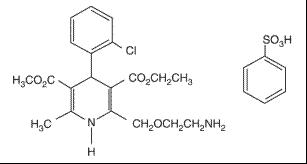
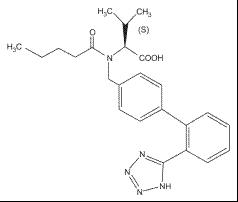
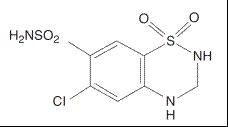
11 DESCRIPTION Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP are a fixed combination of amlodipine, valsartan, and hydrochlorothiazide. Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP contain the besylate salt of amlodipine, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (CCB). Amlodipine besylate USP is a white to almost white powder, freely soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in water and 2-propanol; and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Amlodipine besylate's chemical name is 3-ethyl 5-methyl (±)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-( o -chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, monobenzenesulfonate ; its structural formula is: Its empirical formula is C 20 H 25 ClN 2 O 5 •C 6 H 6 O 3 S and its molecular weight is 567.1. Valsartan USP is a nonpeptide, orally active, and specific angiotensin II antagonist acting on the AT 1 receptor subtype. Valsartan is a white to off white fine hygroscopic powder, soluble in ethanol and methanol; and slightly soluble in water. Valsartan's chemical name is N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2′-(1 H -tetrazol-5-yl) [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-L-valine; its structural formula is: Its empirical formula is C 24 H 29 N 5 O 3 and its molecular weight is 435.5. Hydrochlorothiazide USP is a white, or practically white, practically odorless, crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in n -butylamine, and in dimethylformamide; sparingly soluble in methanol; and insoluble in ether, in chloroform, and in dilute mineral acids. Hydrochlorothiazide is chemically described as 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2 H -1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide. Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic. Its empirical formula is C 7 H 8 ClN 3 O 4 S 2 , its molecular weight is 297.73, and its structural formula is: Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide film-coated tablets USP are formulated in five strengths for oral administration with a combination of amlodipine besylate, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide, providing for the following available combinations: 5/160/12.5 mg, 10/160/12.5 mg, 5/160/25 mg, 10/160/25 mg and 10/320/25 mg amlodipine besylate/valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide. The inactive ingredients for all strengths of the tablets include colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide. Additionally, the 10/160/12.5 mg strength contains yellow iron oxide; the 5/160/25 mg strength contains red iron oxide and yellow iron oxide, the 10/160/25 mg strength contains black iron oxide, red iron oxide and yellow iron oxide and the 10/320/25 mg strength contains iron oxide red. Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP meets USP Dissolution Test 2. 01 02 03
How Supplied
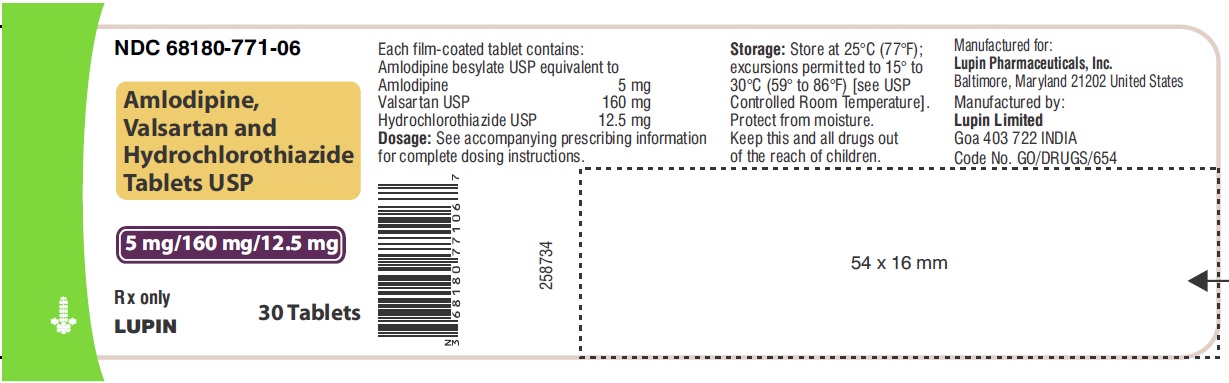
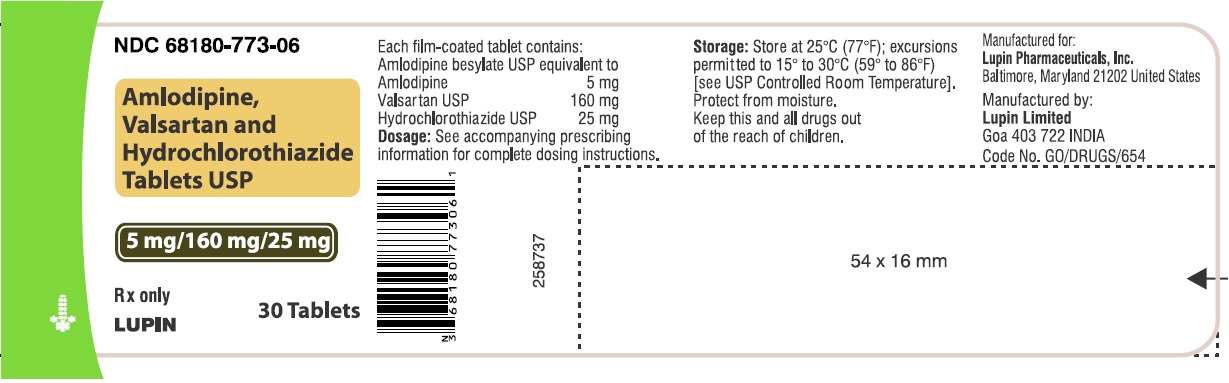
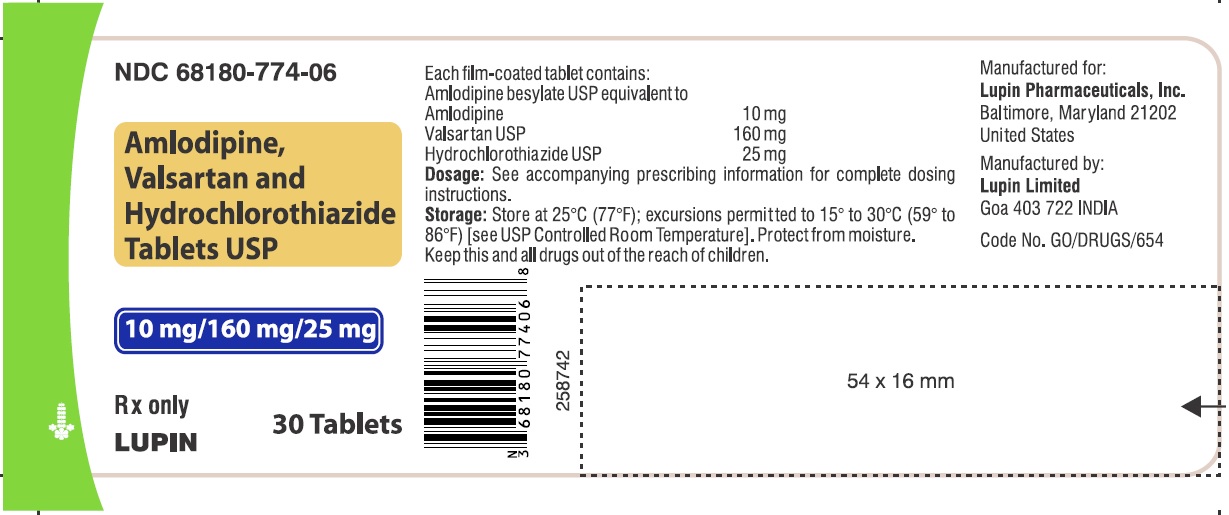
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP, are available as film-coated tablets containing amlodipine besylate equivalent to 5 mg or 10 mg of amlodipine free-base with valsartan 160 mg or 320 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg or 25 mg, providing for the following available combination: 5/160/12.5 mg, 10/160/12.5 mg, 5/160/25 mg, 10/160/25 mg and 10/320/25 mg. All strengths are packaged in bottles of 30, 90 and 500 tablets. Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP, 5 mg/160 mg/12.5 mg – White to off-white, capsule shaped, film coated, biconvex tablets, debossed with 'LU' on one side and 'W41' on the other side. Bottles of 30 NDC 68180-771-06 Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-771-09 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-771-02 Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP, 10 mg/160 mg/12.5 mg – Mustard colored, capsule shaped, film coated, biconvex tablets, debossed with 'LU' on one side and 'W43' on the other side. Bottles of 30 NDC 68180-772-06 Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-772-09 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-772-02 Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP, 5 mg/160 mg/25 mg – Yellow colored, capsule shaped, film coated, biconvex tablets, debossed with 'LU' on one side and 'W42' on the other side. Bottles of 30 NDC 68180-773-06 Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-773-09 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-773-02 Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP, 10 mg/160 mg/25 mg – Beige colored, capsule shaped, film coated, biconvex tablets, debossed with 'LU' on one side and 'W44' on the other side. Bottles of 30 NDC 68180-774-06 Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-774-09 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-774-02 Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets USP, 10 mg/320 mg/25 mg – Light brick red colored, capsule shaped, film coated, biconvex tablets, debossed with 'LU' on one side and 'W45' on the other side. Bottles of 30 NDC 68180-775-06 Bottles of 90 NDC 68180-775-09 Bottles of 500 NDC 68180-775-02 Store at 20°C-25°C (68°F-77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. Dispense in tight container (USP).
Indications & Usage
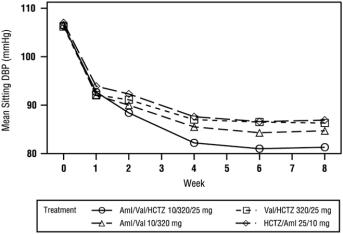
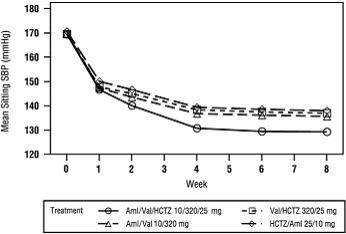
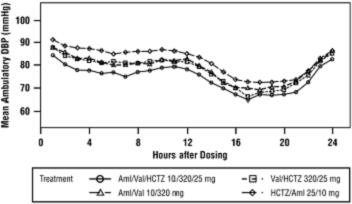
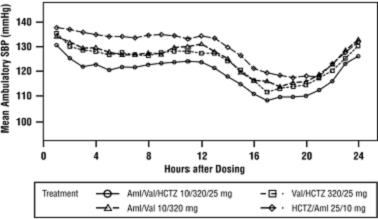
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes, including amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide, and the ARB class to which valsartan principally belongs. There are no controlled trials demonstrating risk reduction with amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than 1 drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program's Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (e.g., patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. Limitation of Use Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are not indicated for the initial therapy of hypertension [ see Dosage and Administration ( 2 ) ]. Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are combination tablet of amlodipine, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (DHP CCB), valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), and hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic. Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes, and myocardial infarctions. ( 1 ) Limitation of Use Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets are not indicated for initial treatment of hypertension.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Dose once-daily. Titrate up to a maximum dose of 10/320/25 mg Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be used as add-on/switch therapy for patients not adequately controlled on any two of the following antihypertensive classes: calcium channel blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, and diuretics. Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be substituted for its individually titrated components ( 2 ) 2.1 General Considerations Dose once-daily. The dosage may be increased after 2 weeks of therapy. The full blood pressure lowering effect was achieved 2 weeks after being on the maximal dose of amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets. The maximum recommended dose of amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets is 10/320/25 mg. 2.2 Add-on / Switch Therapy Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be used for patients not adequately controlled on any 2 of the following antihypertensive classes: calcium channel blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, and diuretics. A patient who experiences dose-limiting adverse reactions to an individual component while on any dual combination of the components of amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be switched to amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets containing a lower dose of that component to achieve similar blood pressure reductions. 2.3 Replacement Therapy Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be substituted for the individually titrated components. 2.4 Use with Other Antihypertensive Drugs Amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablets may be administered with other antihypertensive agents.
