Drug Catalog - Product Detail
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE/ATORVASTATIN CALCIUM TB 5/40MG 30
| NDC | Mfr | Size | Str | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00378-4515-93 | MYLAN | 30 | 5-40MG | NA |
PACKAGE FILES








Generic Name
AMLODIPINE AND ATORVASTATIN
Substance Name
AMLODIPINE BESYLATE
Product Type
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG
Route
ORAL
Application Number
ANDA200465
Description
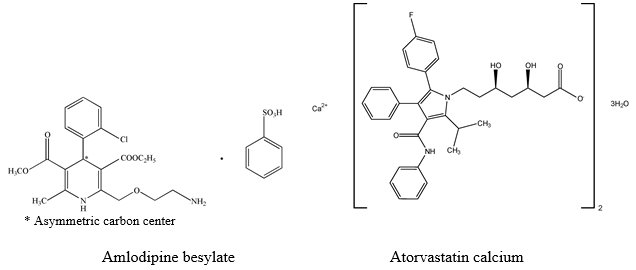
11 DESCRIPTION Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets, USP combine the calcium channel blocker amlodipine besylate with the HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitor atorvastatin calcium. Amlodipine besylate is chemically described as 3-ethyl 5-methyl (4 RS )-2-[(2-aminoethoxy) methyl]-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate benzenesulfonate. Its emperical formula is C 20 H 25 ClN 2 O 5 •C 6 H 6 O 3 S. Atorvastatin calcium is chemically described as Calcium ( βR , δR )-2-( p -fluorophenyl)- β , δ -dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoate (1:2), trihydrate. Its emperical formula is C 66 H 68 CaF 2 N 4 O 10 •3H 2 O. The structural formulae for amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin calcium are shown below. Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets contain amlodipine besylate USP, a white or almost white powder, and atorvastatin calcium USP, a white to off-white crystalline powder. Amlodipine besylate has a molecular weight of 567.1 and atorvastatin calcium has a molecular weight of 1209.42. Amlodipine besylate is slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol. Atorvastatin calcium is insoluble in aqueous solutions of pH 4 and below. Atorvastatin calcium is very slightly soluble in distilled water, pH 7.4 phosphate buffer, and acetonitrile; slightly soluble in ethanol; and freely soluble in methanol. Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets are available as film-coated tablets containing: • 5 mg amlodipine equivalent to 6.94 mg amlodipine besylate and 10 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 10.844 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 5 mg amlodipine equivalent to 6.94 mg amlodipine besylate and 20 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 21.688 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 5 mg amlodipine equivalent to 6.94 mg amlodipine besylate and 40 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 43.376 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 5 mg amlodipine equivalent to 6.94 mg amlodipine besylate and 80 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 86.751 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 10 mg amlodipine equivalent to 13.88 mg amlodipine besylate and 10 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 10.844 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 10 mg amlodipine equivalent to 13.88 mg amlodipine besylate and 20 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 21.688 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 10 mg amlodipine equivalent to 13.88 mg amlodipine besylate and 40 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 43.376 mg atorvastatin calcium. • 10 mg amlodipine equivalent to 13.88 mg amlodipine besylate and 80 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 86.751 mg atorvastatin calcium. Each film-coated tablet also contains colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, L-arginine, lecithin, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, pregelatinized starch (corn), sodium carbonate anhydrous, talc, titanium dioxide and xanthan gum. The 10 mg/10 mg, 10 mg/20 mg, 10 mg/40 mg and 10 mg/80 mg tablets also contain FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake. Atorvastatin Calcium Meets USP Organic Impurities Procedure 2. Amlodipine Besylate and Atorvastatin Calcium Structural Formulae
How Supplied
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Amlodipine and Atorvastatin Tablets, USP are available containing 5 mg or 10 mg amlodipine equivalent to 6.94 mg or 13.88 mg amlodipine besylate USP, respectively, and 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg or 80 mg atorvastatin equivalent to 10.844 mg, 21.688 mg, 43.376 mg or 86.751 mg atorvastatin calcium USP, respectively, providing for the following combinations: 5 mg/10 mg, 5 mg/20 mg, 5 mg/40 mg, 5 mg/80 mg, 10 mg/10 mg, 10 mg/20 mg, 10 mg/40 mg and 10 mg/80 mg. The 5 mg/10 mg tablets are white to off-white, film-coated, oval, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA4 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4513-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 5 mg/20 mg tablets are white to off-white, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA5 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4514-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 5 mg/40 mg tablets are white to off-white, film-coated, capsule shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA6 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4515-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 5 mg/80 mg tablets are white to off-white, film-coated, oval, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA7 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4516-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 10 mg/10 mg tablets are blue, film-coated, barrel shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA8 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4517-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 10 mg/20 mg tablets are blue, film-coated, oval, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA9 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4518-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 10 mg/40 mg tablets are blue, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA10 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4519-93 bottles of 30 tablets The 10 mg/80 mg tablets are blue, film-coated, capsule shaped, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and AA11 on the other side. They are available as follows: NDC 0378-4520-93 bottles of 30 tablets Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Indications & Usage
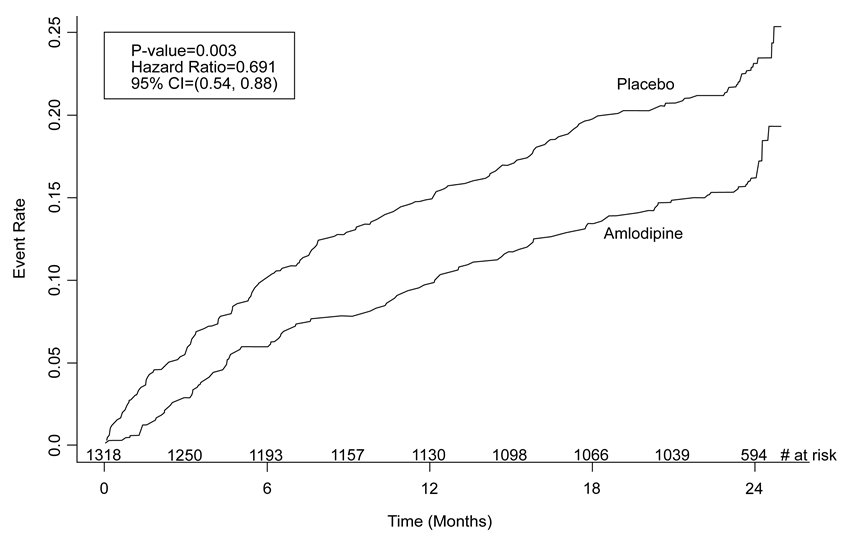
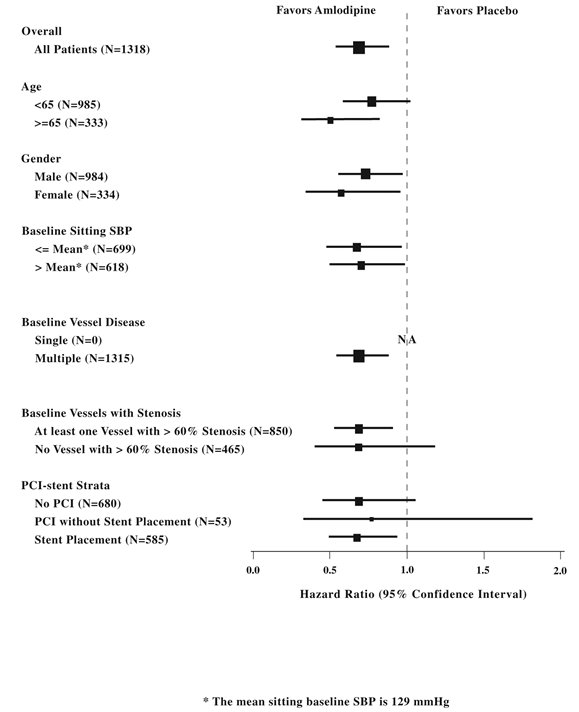
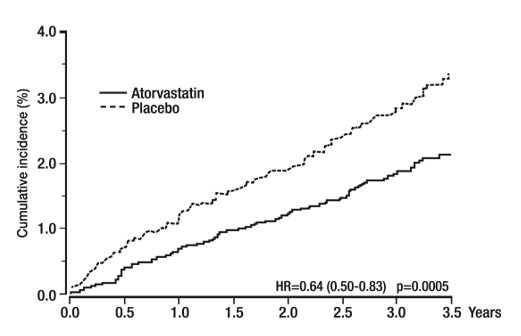
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets are indicated in patients for whom treatment with both amlodipine and atorvastatin is appropriate. Amlodipine Hypertension Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes including amlodipine. Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC). Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal. Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy. Amlodipine may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Chronic Stable Angina Amlodipine is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of chronic stable angina. Amlodipine may be used alone or in combination with other antianginal agents. Vasospastic Angina (Prinzmetal’s or Variant Angina) Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of confirmed or suspected vasospastic angina. Amlodipine may be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antianginal agents. Angiographically Documented CAD In patients with recently documented CAD by angiography and without heart failure or an ejection fraction < 40%, amlodipine is indicated to reduce the risk of hospitalization for angina and to reduce the risk of a coronary revascularization procedure. Atorvastatin Atorvastatin is indicated: • To reduce the risk of: o Myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, revascularization procedures, and angina in adults with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) but without clinically evident CHD o MI and stroke in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple risk factors for CHD but without clinically evident CHD o Non-fatal MI, fatal and non-fatal stroke, revascularization procedures, hospitalization for congestive heart failure, and angina in adults with clinically evident CHD • As an adjunct to diet to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in: o Adults with primary hyperlipidemia. o Adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). • As an adjunct to other LDL-C-lowering therapies, or alone if such treatments are unavailable, to reduce LDL-C in adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). As an adjunct to diet for the treatment of adults with: o Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia o Hypertriglyceridemia Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets are a combination of amlodipine besylate, a calcium channel blocker, and atorvastatin calcium, a HMG-CoA-reductase inhibitor (statin), indicated in patients for whom treatment with both amlodipine and atorvastatin is appropriate ( 1 ). Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. Amlodipine is indicated for the treatment of Coronary Artery Disease ( 1 ). Atorvastatin is indicated ( 1 ): • To reduce the risk of: o Myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, revascularization procedures, and angina in adults with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) but without clinically evident CHD. o MI and stroke in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple risk factors for CHD but without clinically evident CHD. o Non-fatal MI, fatal and non-fatal stroke, revascularization procedures, hospitalization for congestive heart failure, and angina in adults with clinically evident CHD. • As an adjunct to diet to reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) in: o Adults with primary hyperlipidemia. o Adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). • As an adjunct to other LDL-C-lowering therapies to reduce LDL-C in adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. • As an adjunct to diet for the treatment of adults with: o Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia. o Hypertriglyceridemia.
Dosage and Administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Amlodipine and Atorvastatin Tablets Dosage of amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets must be individualized on the basis of both effectiveness and tolerance for each individual component in the treatment of hypertension/angina and hyperlipidemia. Select doses of amlodipine and atorvastatin independently. Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets may be substituted for their individually titrated components. Patients may be given the equivalent dose of amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets or a dose of amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets with increased amounts of amlodipine, atorvastatin, or both for additional antianginal effects, blood pressure lowering, or lipid-lowering effect. Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets may be used to provide additional therapy for patients already on one of their components. Amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets may be used to initiate treatment in patients with hyperlipidemia and either hypertension or angina. Important Dosage Information Take amlodipine and atorvastatin tablets orally once daily at any time of the day, with or without food. Amlodipine The usual initial antihypertensive oral dosage of amlodipine is 5 mg once daily, and the maximum dose is 10 mg once daily. Pediatric (age > 6 years), small adult, fragile, or elderly patients, or patients with hepatic insufficiency may be started on 2.5 mg once daily and this dose may be used when adding amlodipine to other antihypertensive therapy. Adjust dosage according to blood pressure goals. In general, wait 7 to 14 days between titration steps. Titration may proceed more rapidly, however, if clinically warranted, provided the patient is assessed frequently. Angina: The recommended dosage of amlodipine for chronic stable or vasospastic angina is 5-10 mg, with the lower dose suggested in the elderly and in patients with hepatic insufficiency. Most patients will require 10 mg for adequate effect. Coronary Artery Disease: The recommended dosage range of amlodipine for patients with CAD is 5-10 mg once daily. In clinical studies, the majority of patients required 10 mg [see Clinical Studies (14.4)] . Pediatrics: The effective antihypertensive oral dose of amlodipine in pediatric patients ages 6-17 years is 2.5 mg to 5 mg once daily. Doses in excess of 5 mg daily have not been studied in pediatric patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Atorvastatin Assess LDL-C when clinically appropriate, as early as 4 weeks after initiating atorvastatin, and adjust the dosage if necessary. Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients The recommended starting dosage of atorvastatin is 10 mg to 20 mg once daily. The dosage range is 10 mg to 80 mg once daily. Patients who require reduction in LDL-C greater than 45% may be started at 40 mg once daily. Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients 10 Years of Age and Older with HeFH The recommended starting dosage of atorvastatin is 10 mg once daily. The dosage range is 10 mg to 20 mg once daily. Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients 10 Years of Age and Older with HoFH The recommended starting dosage of atorvastatin is 10 mg to 20 mg once daily. The dosage range is 10 mg to 80 mg once daily. Dosage Modifications Due to Drug Interactions Concomitant use of atorvastatin with the following drugs requires dosage modification of atorvastatin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . Anti-Viral Medications • In patients taking saquinavir plus ritonavir, darunavir plus ritonavir, fosamprenavir, fosamprenavir plus ritonavir, elbasvir plus grazoprevir or letermovir, do not exceed atorvastatin 20 mg once daily. • In patients taking nelfinavir, do not exceed atorvastatin 40 mg once daily. Select Azole Antifungals or Macrolide Antibiotics • In patients taking clarithromycin or itraconazole, do not exceed atorvastatin 20 mg once daily. For additional recommendations regarding concomitant use of atorvastatin with other anti-viral medications, azole antifungals or macrolide antibiotics, [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] . Usual Starting Dose (mg daily) Maximum Dose (mg daily) Amlodipine 5 a 10 Atorvastatin 10-20 b 80 a Start small adults or children, fragile, or elderly patients, or patients with hepatic insufficiency on 2.5 mg once daily ( 2 ). b Start patients requiring large LDL-C reduction (> 45%) at 40 mg once daily ( 2 ).
